| 5952748574 | Hernan Cortes | The Spanish conquistador who took over the Aztec Empire between 1485 and 1547. He took over the city of Tenochtituan using many advantages that the Europeans had, such as weapons, immunity to disease, and the use of allies from the Aztec Empire itself. Hernan Cortes was important because most of the Aztec population was killed off, leaving room for job opportunity and land for the Europeans. Without the takeover of the Aztecs, the Columbian Exchange along with a more global economy may not have happened. Themes: P, E | | 0 |
| 5952748575 | Little Ice Age and General Crisis | A large population drop of Native Americans in the mid 17th century. The Little Ice Age was a period of cooling in the Northern Hemisphere that was said to be a cause of low sunspot activity, volcano ashes blocking the sun, or the abandoning of American land. This led to shorter growing seasons and a decrease in food. The General Crisis was similar to the Little Ice Age, and it was in China and Europe too. Weather varied among regions, disease, and many people died because of this. This was important because it lead to a decrease in population, leaving room for jobs and opportunity that helped change the world forever. Themes: G | | 1 |
| 6069496385 | Columbian Exchange | The communication, migration, trade, disease spreading, and exchange of plants and animals in the 15th and 16th centuries that caused for all 4 major regions to be connected (Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas). This was because of the General Crisis in response to the population decrease, and it connected the world for the first time. In Europe, this was important because it led to the Scientific Revolution, Industrial Revolution, new ideas, and a population growth. | | 2 |
| 6069496386 | Mercantilism | An economic system in the 17th and 18th centuries where European nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver, bullion, and by selling more goods than they bought (increase export, decrease import). The colonies in the Americas provided closed markets for the mother country. Mercantilism was important because it started war, rivalry, and competition throughout the European states, and it is said to be similar to a form of capitalism. Also, it required a large labor force to mine the gold and silver, which Europeans looked to enslaved Africans. Themes: G, E, S | | 3 |
| 6069496387 | Encomienda | A legal system in Mesoamerica in the 16th and 17th centuries that granted Natives to the Spanish people to do work for them. This is very similar to slavery, and the Native people were allowed protection and to practice Catholicism. This was important because it led to more intense forms of slavery, such as the repartimiento and hacienda systems. These were much more restrictive, and it caused for an even larger decrease in the Native population. With this population decreasing and the need for laborers increasing, Europeans looked to Africa for slaves. Themes: R, P, E, S | | 4 |
| 6069496388 | Mulatto, mestizos, and peninsulares | These are the different social classes that were apparent starting around the 16th and 17th centuries. In Brazil, the Mulattos were usually mixed African and white parents, but there was 40 other groups as well. Similarly, the Mestizos in Mesoamerica were a mixed race between Spanish and Native people. The Peninsulares, however, were Spaniards born in Spain itself and had most control. These classes were important because it caused for a more divided society, and in Mesoamerica the concept of race was almost taken out. Themes: G, R, A, P, E, S | | 5 |
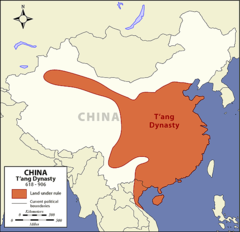
| 6069496389 | Qing /Manchu | A Chinese dynasty from 1644 to 1912 that witnessed great imperial expansion for 80 years, and incorporated non-Chinese people into their dynasty. They are of foreign origin in the region of Manchuria, and they maintained some of that distinctiveness by forbidding marriage with the Chinese, but many of the Qing elite mastered the Chinese language and used Confucianism. This dynasty was important because it brought and somewhat united huge regions under Chinese by using their technology and weapons for security reasons (Zunghars (Mongols) and the Russians). The Chinese governed Central Asia via the Court of Colonial Affairs, relying on Muslims, Mongols, and Buddhists to keep it inexpensive. This expansion allowed for the Chinese transformation of Central Asia. It went from hosting the Silk Roads and bringing in wealth to a site of poverty in the 18th and 19th centuries because of the change to maritime trade. Themes: G, P, E, S | | 6 |
| 6069496390 | Akbar | A ruler (1556-1605) in India's Mughal Empire who helped settle the diversity of India's various religions by creating an Indian-Persian-Turkic culture. He kept many Hindus in the elite, lessened restrictions on women, and imposed a policy of Islamic toleration by removing the ulama and jizya. Akbar was important because he created a period of cultural comfort in the empire by blending these three cultures, and also he created The House of Worship, a building in India that had Muslim, Christian, Hindu, Buddhist, Jewish, Jainism, and Zoroastrian works. Themes: G, R, A, P, E, S | | 7 |
| 6069496391 | Ottoman Empire | The heir empire to the Byzantines that was created around 1300 by Turkic warriors in northwest Anatolia. They replaced the Christian City of Constantinople for the Muslim City of Istanbul in 1453. They represented a large population of Arabs, and had the responsibility of protecting the holy cities of Jerusalem, Mecca, and Medina. The Ottoman leader, the sultan, was a turkic warrior prince, a Muslim caliph, and conqueror. They were important because they took the Middle East, North Africa, and southeast Europe into Islam's most significant empire. The empire transformed Turkic social life by restricting the rights of women because of Islam, but some women did receive political rights via the "sultanate of women". Also, it added another cross cultural interaction between Christianity and Islam once again. Themes: G, R, P, S | | 8 |
| 6069496392 | Devshirme | A process of collecting, gathering, and siphoning Christian boys from the Balkan region to work for the state, specifically military affairs. This began in the mid 14th century (c. 1350), and was because the Ottomans were expanding and needed soldiers to do so. These children were mainly Serbs, Greeks, and Albanians ranging from 10 to 18 years of age. The Devshirme system was important because it provided the Muslims with soldiers to help expand their Ottoman Empire, and it also continued the relationship between Islam and Christianity. In Europe, Muslims were now often seen as a threat because of this devshirme system, the takeover of Constantinople, and the takeover of Vienna. Themes: G, R, P | | 9 |
| 6116067384 | Trading Post Empire | An empire aiming to control commerce that does not have a large territory or population, and they control it by force not by competition. The Portuguese did this around the 16th century by setting up fortified bases in Mombasa (East Africa), Hormuz at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, Goa on the western coast of India, Malacca in SE Asia, and Macao on the southern coast of China. The Portuguese tried to dominate the Indian Ocean by monopolizing the spice trade, but they failed by 1600. This was important because it was one of the first European countries to start getting involved in the Indian Ocean Trade, and other European powers followed them. Themes: G, P, E | | 10 |
| 6116067385 | Philippines (Spain) | The region that Spain colonized in the 17th century shortly after realizing what Portugal could have done. This region was near China and the spice islands, and it had small and militarily weak societies with the absence of competing peoples. Because of this, the Spanish colonized the area instead of making a trading post empire. This was important because it got Europeans involved even more in the Indian Ocean Trade, and it was able to bring Spain the spices they needed and China the silver they wanted. Themes: G, P, E | | 11 |
| 6116070447 | British/Dutch East India Companies and Joint stock companies | Unlike the Spanish, these companies became highly commercialized and urban societies, organizing themselves through private trade enterprises that took part in risk of merchant investors. These private trade enterprises are called joint stock companies. They received charters from governments giving them the opportunity for trading monopolies and war. The Dutch focused on gaining trading posts in Indonesia, and the British focused on East India. The Dutch were more violent and demanding in the spice trade, but the British were not because the had to go through the Mughals. These companies were important because they continued the exchange of goods and ideas, such as spices, silver, Christianity, or Islam to be spread throughout Eurasia. Themes: G, P, E | | 12 |
| 6116073595 | Tokugawa shogun | 16th century Japanese military rulers that were more successful with their silver production. These rulers were important because they were able to use the profit made from the silver to defeat feudal lords and unify the country. They made deals with merchants too, and were able to create a market based economy. This commercialized economy was one of the factors in Japan's 19th century Industrial Revolution. Themes: G, E | | 13 |
| 6116076249 | Potosi | This is the silver mine in Bolivia in the mid 16th century that is owned by Spain, and the silver that is mined here gets sent to Manila, the capital of Spain's Philippines. This was important because it provided a critical link between the Americas and Asia, starting Pacific Ocean trade. Also, it enriched the Spanish Crown with all of the wealth being accumulated, but it did end up inflating the economy. When the value of silver dropped, Spain's dominance in western Europe did too. Themes: G, E | | 14 |
| 6116077010 | African Diaspora | The forced removal of Africans from their home and family and the bringing of them to various places in the Americas. They were spread to the colonies in North America, Brazil and the Caribbean, and Mesoamerica and the Andean region. From 1500 to 1866, around 12.5 million African slaves were shipped through the Middle Passage. Most slaves were removed from their culture, but some were able to diffuse elements of African religious ideas, music and art, and cuisine in the Americas. This was important because it led to forced labor, death, social oppression, and racial stereotypes. Themes: G, R, A, P, E, S | | 15 |
| 6116080292 | Atlantic System/Triangular System | This is the trade system used between the 16th and 19th centuries between Europe, Africa, and the Americas in the Atlantic Ocean. The Europeans used the economic system of mercantilism, which required plantations and laborers in their colonies. To get these workers, the Europeans trade with African leaders for slaves, and they were then sent to the Americas to work. In the Americas, the slaves produced goods and sent them to Europe. This was important because it helped in the European's economy, but it crushed African people via the hard labor, death, racism, and separation from home. Themes: G, E, S | | 16 |
| 6116080293 | Chattel slavery | This is a form of slavery in which one has absolute legal ownership of another person, and they have the right to buy or sell that person. This was starting around the 16th and 17th centuries, and it was way more restrictive than all previous forms of slavery. This was important because it caused for much racism, discrimination, and death of the Africans. Themes: E, S | | 17 |
| 6116082403 | Protestant Reformation | A 16th century religious movement in Europe that was sparked by Martin Luther when he posted his Ninety-Five Theses. It divided Christianity into different groups based on beliefs, including Protestants, Calvinists, and Anglicans. This was important because it shattered the unity of Christianity even to present day society. There was much conflict in Europe because of this from Catholics and Huguenots, and the Thirty Years' War. Themes: R, P | | 18 |
| 6116083217 | Catholic/Counter Reformation | The Catholic Church's response to the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century where the Church re-stated their beliefs and doctrines. In the Council of Trent, beliefs were reaffirmed about the Pope, priests, celibacy, veneration of saints, and views on good works. This was important because it sparked the Catholic Church to spread its religion via missionaries, and many religious orders such as the Jesuits and Dominicans were created. Themes: R, P | | 19 |
| 6116084426 | Sikhism | Indian religion founded by the Guru Nanak (1469-1539) in the Punjab region of northern India. This was important because the religion blended ideas of Hinduism and Islam that divided India into one religion. It did not draw on caste distinctions, and it ended the seclusion of women. They were disliked, and they became a separate community and had their own temple called the Golden Temple of Amritsar. After a period of time, they were so disliked that they had to turn into a military community. Themes: R, P, S | | 20 |