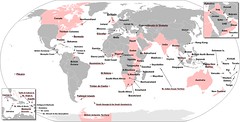
| 8682114728 | Carthage | City located in present-day Tunisia, founded by Phoenicians ca. 800 B.C.E. It became a major commercial center and naval power in the western Mediterranean until defeated by the expanding Roman Republic in the third century B.C.E. | | 0 |
| 8682114551 | Agriculture | The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain. | | 1 |
| 8682114552 | Agrarian | pertaining to land or its cultivation; Ex. agrarian reform, agrarian society | | 2 |
| 8682114553 | Bands/ Clans | extended family groups that generally lived together | | 3 |
| 8682114554 | Civilization | a society in an advanced state of social development (e.g., with complex legal and political and religious organizations) | | 4 |
| 8682114555 | City-States | different sections of land owned by the same country but ruled by different rulers (e.g. Greece) | | 5 |
| 8682114556 | Domestication | process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans | | 6 |
| 8682114557 | Economy | system by which goods and services are produced and distributed to meet people's needs | | 7 |
| 8682114558 | Egalitarian | a person who believes in the equality of all people | | 8 |
| 8682114559 | Foraging | the process of scavenging for food | | 9 |
| 8682114560 | Hierarchy | a series of ordered groupings of people or things within a system | | 10 |
| 8682114561 | Hunter-Gatherer | A hunter-gatherer society is one whose primary subsistence method involves the direct procurement of edible plants and animals from the wild, foraging and hunting without significant recourse to the domestication of either plants nor animals | | 11 |
| 8682114562 | Irrigation | supplying dry land with water by means of ditches, sprinklers, etc. | | 12 |
| 8682114563 | Monarchy | a government in which power is in the hands of a single person who usually inherits their power | | 13 |
| 8682114564 | Monotheism | belief in a single God | | 14 |
| 8682114565 | Neolithic | The New Stone Age from circa 8500 to 4500 BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution(s) | | 15 |
| 8682114566 | Nomadic | (of groups of people) tending to travel and change settlements frequently | | 16 |
| 8682114567 | Pastoral | relating to shepherds or herdsmen or devoted to raising sheep or cattle (e.g. pastoral peoples) | | 17 |
| 8682114568 | Paleolithic | The Old Stone Age from circa 750,00 to 500,000 years BCE to 8,500 years BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans and the development of minor tools | | 18 |
| 8682114569 | Philosophy | the rational investigation of questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics | | 19 |
| 8682114570 | Polytheism | belief in multiple Gods | | 20 |
| 8682114571 | River Valley | the fertile land surrounding a river- the first civilizations arose near them | | 21 |
| 8682114572 | Sedentary | remaining in one place | | 22 |
| 8682114573 | Settlement | the act of colonizing or a small group of people in a sedentary position | | 23 |
| 8682114574 | Subsistence | the necessities of life, the resources of survival | | 24 |
| 8682114575 | Surplus | a quantity much larger than is needed | | 25 |
| 8682114576 | Sustenance | the act of sustaining life by food or providing a means of subsistence | | 26 |
| 8682114577 | Theocracy | government run by religious leaders | | 27 |
| 8682114578 | Traditional | consisting of or derived from tradition; customary practices | | 28 |
| 8682114579 | Urbanization | the social process whereby cities grow and societies become more urban | | 29 |
| 8682114580 | Bronze Age | a period between the Stone and Iron ages, characterized by the manufacture and use of bronze tools and weapons |  | 30 |
| 8682114581 | Code of Hammurabi | the set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi dating to the 18th century BC, the earliest legal code known in its entirety |  | 31 |
| 8682114582 | Cuneiform | One of the first written languages known: A system of writing in which wedge-shaped symbols represented words or syllables. It originated in Mesopotamia and was used initially for Sumerian and Akkadian but later was adapted to represent other languages of western Asia. |  | 32 |
| 8682114583 | Democracy | a political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them | | 33 |
| 8682114584 | Iron Age | the period following the Bronze Age; characterized by rapid spread of iron tools and weapons | | 34 |
| 8682114585 | Pyramids | Huge stone tombs with four triangle-shaped walls that met in a point on top |  | 35 |
| 8682114587 | Ziggurats | a temple or tomb of the ancient Assyrians, Sumerians, or Babylonians, having the form of a terraced pyramid of successively receding stories |  | 36 |
| 8682114588 | Trans Saharan | route across the sahara desert. Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels played a huge role in the trading |  | 37 |
| 8682114589 | Monsoons | Major winds in the Indian Ocean that blew into India for half the year, and blew away from India for the other half. Helped facilitate trade in the Indian Ocean. |  | 38 |
| 8682114590 | Sumerians | people who dominated Southern Mesopotamia through the end of the 3rd Millennium BCE. Responsible for the creation of irrigation technology, cuneiform, and religious conceptions. |  | 39 |
| 8682114592 | Before agriculture, men and women are believed to have a greater degree of equality. But after the rise of agriculture, most human societies became ________ as a result of greater male strength. | Patriarchal |  | 40 |
| 8682114593 | caste system | a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society, there was virtually no social mobility |  | 41 |
| 8682114594 | Paleolithic | (Old Stone Age) a long period of human development before the development of agriculture |  | 42 |
| 8682114595 | Carthage | This city has existed for nearly 3,000 years, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC into the capital of the Carthaginian Empire. Controlled commerce in the Mediterranean prior to the rise of Roman Power. The expanding Roman Republic took control of many of its outposts after the two Punic Wars. |  | 43 |
| 8682114609 | Norte Chico | A region along the coast of Peru that possessed a highly-developed urban culture as early as 2500 B.C.E. Characterized by massive stepped pyramids and extensive use of cotton. |  | 44 |
| 8682114610 | Indus Valley | 3rd millennium BC, Elaborately planned cities, standardized measures, irrigated agriculture, written language, no temples kings etc., had a lot of land, no political hierarchy, was abandoned because of mass deforestation, low crop yields, famine, environmental deterioration, etc. their influence continued even to this day (i.e. yoga). Important because it shows how we developed in our cities and economy. |  | 45 |
| 8682114611 | Olmec Civilization | earliest known American civilization, located in southern Mexico and known for its pyramids and huge stone heads |  | 46 |
| 8682114615 | Code of Hammurabi | A collection of 282 laws which were enforced under Hammurabi's Rule. One of the first examples of written law in the ancient civilizations. |  | 47 |
| 8682114616 | Patriarchy | A form of social organization in which a male is the family head and title is traced through the male line |  | 48 |
| 8682114617 | Rise of the State | A process of centralization that took place in the First Civilizations, growing out of the greater complexity or urban life in recognition of the need for coordination, regulation, adjudication, and military leadership |  | 49 |
| 8682114618 | Egypt: "the gift of the Nile" | provided annual and predictable flooding that benefited and provided a sustainable lifestyle for this civilization, also gave them a stable and positive worldview, proved unty and independence and security |  | 50 |
| 8682114619 | Nubia | A civilization to the south of Egypt in the Nile Valley, noted for development of an alphabetic writing system and a major iron working industry by 500 BCE |  | 51 |
| 8682114620 | Venus Figurines | Paleolithic carvings of the female form, often with exaggerated breasts, buttocks, hips, and stomachs, which may have had religious significance |  | 52 |
| 8682114624 | shamans | In many early societies, a person believed to have the ability to act as a leasion between living humans and supernatural forces, often by means of trances induced by psychoactive drugs |  | 53 |
| 8682114625 | Paleolithic settling down | The process by which some Paleolithic peoples moved toward permanent settlement in the wake of the last Ice Age. Settlement was marked by increasing storage of food and accumulation of goods, as well as growing inequalities in society |  | 54 |
| 8682114627 | Fertile Crescent | A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates |  | 55 |
| 8682114629 | Diffusion | Is the process by which a characterictic spreads |  | 56 |
| 8682114630 | Bantu Migrations | (1500BCE to 500CE) As the Bantu people migrated, they spread the Bantu family of languages and culture. The Bantu also spread the use of iron, which improved farming techniques and agricultural efficiency, the greater food supply sparked economic development and population growth. The changes instigated by the Bantu migration increased the vitality of sub-Saharan Africa. |  | 57 |
| 8682114631 | Pastoral Societies | Based on the domestication of animals and use their products as main source of food. Groups move where there is foods but they are more settlers than nomads. Independent and warlike. |  | 58 |
| 8682114633 | Chiefdoms | A society that is led by a ruler of decent, but seldom used force to lead their people. They relied on generosity, charisma, and leadership to rule. |  | 59 |
| 8682114636 | Agrarian | relating to cultivated land or the cultivation of land | | 60 |
| 8682114637 | Mesopotamia | the name for the area of the Tigris-Euphrates river system, in modern days roughly corresponding to most of Iraq plus Kuwait, the eastern parts of Syria | | 61 |
| 8682114638 | Phoenicians | dominant traders and merchants who created purple dye and established Carthage. | | 62 |
| 8682114639 | Israelites | a member of the ancient Hebrew nation, especially in the period from the Exodus to the Babylonian Captivity | | 63 |
| 8682114640 | Characteristics of a Civilization | cities, government, trade, social structure, writing and art | | 64 |
| 8682114643 | Hebrews | a member of an ancient people living in what is now Israel and Palestine and, according to biblical tradition, descended from the patriarch Jacob, grandson of Abraham. | | 65 |
| 8682114644 | Mandate of Heaven | is an ancient Chinese belief/theory and philosophical idea that tiān (heaven) granted emperors the right to rule based on their ability to govern well, appropriately and fairly. | | 66 |
| 8682114645 | Horse-drawn chariots | humanities first form of personal transport, used as a technological advancement in warfare and conquest. | | 67 |
| 8682114646 | Babylon | an ancient city of SW Asia, on the Euphrates River, famed for its magnificence and culture: capital of Babylonia and later of the Chaldean empire. | | 68 |
| 8682114647 | Sargon of Akkad | was the first ruler of the Semitic-speaking Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC. | | 69 |
| 8682114648 | Assyrians | an ancient empire in SW Asia: greatest extent from about 750 to 612 b.c. the Capital: Nineveh. | | 70 |
| 8682114650 | Caste System | a class structure that is determined by birth. Loosely, it means that in some societies, if your parents are poor, you're going to be poor, too. Same goes for being rich | | 71 |
| 8682114651 | Patriarchy | A male dominated society |  | 72 |
| 8682114652 | Matriarchal | A female dominated society |  | 73 |
| 8682114653 | Mandate of Heaven | an ancient Chinese belief and philosophical idea that tiān (heaven) granted emperors the right to rule based on their ability to govern well and fairly. |  | 74 |
| 8682114654 | Silk Road | an ancient network of trade and cultural transmission routes that were central to cultural interaction through regions of the Asian continent connecting the West and East by merchants, pilgrims, monks, soldiers, nomads, and urban dwellers from China and India to the Mediterranean Sea | | 75 |
| 8682114655 | Social Heirarchy | how individuals and groups are arranged in a relatively linear ladder |  | 76 |
| 8682114656 | Reincarnation | the rebirth of a soul in a new body. | | 77 |
| 8682114657 | Assimilation | The process by which a person or persons acquire the social and psychological characteristics of a group |  | 78 |
| 8682114658 | Monotheistic | The belief in only one god | | 79 |
| 8682114659 | Eightfold Path | the path to nirvana, comprising eight aspects in which an aspirant must become practiced: right views, intention, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, and concentration. | | 80 |
| 8682114660 | Zoroanstrianism | one of the world's oldest monotheistic religions. It was founded by the Prophet Zoroaster in ancient Iran approximately 3500 years ago. | | 81 |
| 8682114661 | Greek Philosophy | the rational investigation of questions about existence and knowledge and ethics |  | 82 |
| 8682114662 | Polytheistic | The belief in many gods | | 83 |
| 8682114663 | Legalism | strict adherence, or the principle of strict adherence, to law or prescription, especially to the letter rather than the spirit. | | 84 |
| 8682114664 | Confucianism | a system of philosophical and ethical teachings founded by Confucius and developed by Mencius. | | 85 |
| 8682114665 | Buddhism | is a nontheistic religion or philosophy (Sanskrit: dharma; Pali: धम्म dhamma) that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and spiritual practices largely based on teachings attributed to Gautama Buddha, commonly known as the Buddha ("the awakened one"). | | 86 |
| 8682114666 | Islam | the religion of the Muslims, a monotheistic faith regarded as revealed through Muhammad as the Prophet of Allah. | | 87 |
| 8682114667 | Judaism | an ancient monotheistic religion, with the Torah as its foundational text (part of the larger text known as the Tanakh or Hebrew Bible), and supplemental oral tradition represented by later texts such as the Midrash and the Talmud. | | 88 |
| 8682114668 | Christianity | the religion based on the person and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth, or its beliefs and practices. | | 89 |
| 8682114669 | Daoism | a philosophical, ethical or religious tradition of Chinese origin, or faith of Chinese exemplification, that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao. | | 90 |
| 8682114670 | Han Dynasty | an empire in ancient China, that lasted from 206 b.c.e- 24 c.e. | | 91 |
| 8682114671 | Persia | an empire located in modern day Iran but stretched as far as Egypt and Iraq. | | 92 |
| 8682114673 | Ancient Egypt | an empire that lasted for 3000 years | | 93 |
| 8682114674 | Roman empire | located in modern day Italy but expanded to outlying countries throughout its reign, it lasted from 201 b.c.e- 476 c.e. | | 94 |
| 8682114675 | Maya | located in modern day central america, it lasted from 1800 b.c.e- 250 c.e. | | 95 |
| 8682114676 | State | A body of people living in a defined territory who have a government with the power to make and enforce law without the consent of any higher authority | | 96 |
| 8682114677 | Empire | an extensive group of states or countries under a single supreme authority. | | 97 |
| 8682114678 | Hebrew Scriptures | Torah, Old Testament | | 98 |
| 8682114679 | Assyrian Empire | this empire covered much of what is now Mesopotamia, Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and Anatolia; its height was during the seventh and eighth centuries BCE. | | 99 |
| 8682114680 | Babylonian Empire | Empire in Mesopotamia which was formed by Hammurabi, the sixth ruler of the invading Amorites. | | 100 |
| 8682114681 | Roman Empire | Existed from 27 BCE to about 400 CE. Conquiered entire Mediterranean coast and most of Europe. Ruled by an emperor. Eventually oversaw the rise and spread of Christianity. | | 101 |
| 8682114682 | Sanskrit Scriptures | An ancient Indic language of India, in which the Hindu scriptures and classical Indian epic poems are written and from which many northern Indian languages are derived. | | 102 |
| 8682114683 | Vedic Religions | Core beliefs in sanskrit scriptures; Hinduism; influence of Indo-European traditions in the development of the social and political roles of a caste system; importance of multiple manifestations of Brahma to promote teachings about reincarnation. | | 103 |
| 8682114684 | Hinduism | A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms | | 104 |
| 8682114686 | Ashoka | Leader of the Mauryan dynasty of India who conquered most of India but eventually gave up violence and converted to Buddhism. | | 105 |
| 8682114687 | Siddhartha Gautama (The Buddha) | Means "Enlightened One." He is said to have renounced his worldly possessions and taught of a way to overcome suffering. | | 106 |
| 8682114688 | Emperor Constantine | Founded Constantinople; best known for being the first Christian Roman Emperor; issued the Edit of Milan in 313, granting religious toleration throughout the empire. | | 107 |
| 8682114689 | Buddha | |  | 108 |
| 8682114690 | Shiva | |  | 109 |
| 8682114691 | Brahma | |  | 110 |
| 8682114692 | Vishnu | |  | 111 |
| 8682114709 | filial piety | In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors. | | 112 |
| 8682114710 | monasticism | A way of life in which men and women withdraw from the rest of the world in order to devote themselves to their faith | | 113 |
| 8682114712 | animism | Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life. | | 114 |
| 8682114713 | ancestor veneration | Veneration of the dead or ancestor reverence is based on the beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of the living, the worship of deceased ancestors | | 115 |
| 8682114714 | syncretic religion | Combines two religious traditions into something distinctly new, while containing traits of both | | 116 |
| 8682114715 | Persian Empire | Greatest empire in the world up to 500 BCE. Spoke an Indo-European language. A multi-ethnic and multi-religious empire. Fell to Alexander the Great. | | 117 |
| 8682114716 | Qin Dynasty | the Chinese dynasty (from 246 BC to 206 BC) that established the first centralized imperial government and built much of the Great Wall | | 118 |
| 8682114717 | Han Dynasty | (202 BC - 220 AD) dynasty started by Lui Bang; a great and long-lasting rule, it discarded the harsh policies of the Qin dynasty and adopted Confucian principles; rulers chose officials who passed the civil service exams rather than birth; it was a time of prosperity | | 119 |
| 8682114718 | Phoenicia | Semitic-speaking Canaanites living on the coast of modern Lebanon and Syria in the first millennium B.C.E. Famous for developing the first alphabet, which was adopted by the Greeks. | | 120 |
| 8682114719 | Hellenistic | Of or influenced by the Greek Empire. A type of culture typically referred to after the conquests of Alexander the Great. | | 121 |
| 8682114720 | Teotihuacan | A large central city in the Mesoamerican region. Located about 25 miles Northeast of present day Mexico City. Exhibited city planning and unprecedented size for its time. Reached its peak around the year 450. | | 122 |
| 8682114725 | Chang'an | Capital of Tang dynasty; population of 2 million, larger than any other city in the world at that time. | | 123 |
| 8682114727 | Athens | A democratic Greek polis who accomplished many cultural achievements, and who were constantly at war with Sparta. | | 124 |
| 8682114729 | Alexandria | City on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt founded by Alexander. It became the capital of the Hellenistic kingdom of Ptolemy. It contained the famous Library and the Museum and was a center for leading scientific and literary figures in the classical and postclassical eras. | | 125 |
| 8682114730 | Constantinople | A large and wealthy city that was the imperial capital of the Byzantine empire and later the Ottoman empire, now known as Istanbul | | 126 |
| 8682114731 | Silk Roads | trade routes stretching from China to the Mediterranean, which allowed for the exchange of goods and ideas from China to the Roman Empire | | 127 |
| 8682114732 | Trans-Saharan Caravan Route | Islamic trade in West Africa was conducted by caravans of camels. According to Ibn Battuta, the explorer who accompanied one of the caravans, the average size was a thousand camels per caravan, with some being as large as 12,000. | | 128 |
| 8682114733 | Indian Ocean Sea Lanes | lanes throughout the Indian Ocean connecting East Africa, southern Arabia, the Persian Gulf, India, Southeast Asia, and southern China | | 129 |
| 8682114734 | Mediterranean Sea Lanes | Trade routes that connected the Mediterranean civilizations together. The need for a sea rout for trade in the region. Trade increased and diffusion of cultures occurred | | 130 |
| 8682114735 | Qanat System | a traditional system of gravity-fed irrigation that uses gently sloping tunnels to capture groundwater and direct it to low-lying fields | | 131 |
| 8682114736 | Shaduf | a mechanical device that consists of a long pole balanced on a crossbeam. It has a rope and bucket on one end and a weighted balance on the other. It is used for transferring water from the river to the fields. | | 132 |
| 8682114737 | Jesus of Nazareth | a teacher and prophet born in Bethlehem and active in Nazareth; his life and sermons form the basis for Christianity. | | 133 |
| 8682114739 | Greco-Roman Philosophy | Ideas that emphasized logic, empirical observation, and nature of political power and hierarchy. | | 134 |
| 8682114742 | corvee labor | unpaid forced labor usually by lower classes, forced upon them by the government | | 135 |
| 8682114743 | tribute | Money paid by one country to another in return for protection | | 136 |