AP World History Chapter 4 Flashcards
| 4833809790 | Harrappan Civilization | Also known as the Indus River Valley Civilization, was a Bronze Age civilization that thrived from roughly 2600 BCE - 1900 BCE which centered in northwestern India and Pakistan along the Indus River. Their major cities included Harappa and Mohenjo-dara | 0 | |
| 4833819558 | Aryans | Groups of people who spoke the Indo-European Sanskrit language. They probably invaded India from the northwest during the 2nd millennium BCE, spreading east and south over the succeeding centuries. By about 500 BCE their language was probably common over most of the Indian subcontinent. Some credit them with laying the foundations of Hinduism | 1 | |
| 4833828407 | Hinduism | The common religion of India, having an extremely diversified character with many school of philosophy and theology, many popular cults and a large pantheon of deities, symbolizing the many attributes of a single god | 2 | |
| 4833832573 | Caste system | The rigid Hindu system of hereditary social distinctions based on castes (classes) | 3 | |
| 4833833988 | Untouchables | A member of a large formerly segregated hereditary group in India having in traditional Hindu belief the quality of defiliing by contact a member of a higher caste. They are often considered even being outside the caste system all together | 4 | |
| 4833844009 | Chandragupta Maurya | Founder of the Maurya dynasty and the first emperor (321 - 297 BCE) to unify most of India under one administration. He expanded his empire east to the borders of Persia, south to India's tip, and north to the Himalayas and the Kabul River valley | 5 | |
| 4833847916 | Maurya Empire | An empire founded by Chandragupta Maurya after the death of Alexander the Great, that encompassed most of the Indian subcontinent | 6 | |
| 4833850456 | Ashoka | Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all off the Indian subcontinent from 269 - 232 BCE. One of India's greatest emperor, reigned over most of present day India after a number of military conquests. He was one of the first Indian emperors to embrace Buddhism | 7 | |
| 4833855140 | Gupta Dynasty | Rulers of an empire in northern and parts of central and western India from 320 - 550 CE. This period is noted for the flourishing of Sanskrit literature, sophisticated metal coins, advanced mathematics and astronomical advances | 8 |
AP World History: Ancient World Flashcards
First set of words in the AP World History book by the Princeton Review.
| 6805356735 | Agriculture | The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain. | 0 | |
| 6805356736 | Agrarian | pertaining to land or its cultivation; Ex. agrarian reform, agrarian society | 1 | |
| 6805356737 | Bands/ Clans | extended family groups that generally lived together | 2 | |
| 6805356738 | Barbarian | without civilizing influences | 3 | |
| 6805356739 | Bureaucracy | system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials (not elected) | 4 | |
| 6805356740 | Civilization | a society in an advanced state of social development (e.g., with complex legal and political and religious organizations) | 5 | |
| 6805356741 | City-States | different sections of land owned by the same country but ruled by different rulers (e.g. Greece) | 6 | |
| 6805356742 | Classical | of or characteristic of a form or system felt to be of first significance before modern times | 7 | |
| 6805356743 | Domestication | process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans | 8 | |
| 6805356744 | Economy | system by which goods and services are produced and distributed to meet people's needs | 9 | |
| 6805356745 | Egalitarian | a person who believes in the equality of all people | 10 | |
| 6805356746 | Emperor | supreme ruler of an empire | 11 | |
| 6805356747 | Empire | many territories, countries, or peoples controlled by one government (also just any territory ruled by an emperor) | 12 | |
| 6805356748 | Feudalism | a political system and a social system where by a powerful lord would offer "protection" in return for "service" | 13 | |
| 6805356749 | Foraging | the process of scavenging for food | 14 | |
| 6805356750 | Hierarchy | a series of ordered groupings of people or things within a system | 15 | |
| 6805356751 | Hierarchical | Of, relating to, or arranged in a hierarchy | 16 | |
| 6805356752 | Hunter-Gatherer | A hunter-gatherer society is one whose primary subsistence method involves the direct procurement of edible plants and animals from the wild, foraging and hunting without significant recourse to the domestication of either plants nor animals | 17 | |
| 6805356753 | Irrigation | supplying dry land with water by means of ditches, sprinklers, etc. | 18 | |
| 6805356754 | Monarchy | a government in which power is in the hands of a single person who usually inherits their power | 19 | |
| 6805356755 | Monotheism | belief in a single God | 20 | |
| 6805356756 | Neolithic | The New Stone Age from circa 8500 to 4500 BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution(s) | 21 | |
| 6805356757 | Nomadic | (of groups of people) tending to travel and change settlements frequently | 22 | |
| 6805356758 | Pastoral | relating to shepherds or herdsmen or devoted to raising sheep or cattle (e.g. pastoral peoples) | 23 | |
| 6805356759 | Paleolithic | The Old Stone Age from circa 750,00 to 500,000 years BCE to 8,500 years BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans and the development of minor tools | 24 | |
| 6805356760 | Philosophy | the rational investigation of questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics | 25 | |
| 6805356761 | Polytheism | belief in multiple Gods | 26 | |
| 6805356762 | River Valley | the fertile land surrounding a river- the first civilizations arose near them | 27 | |
| 6805356763 | Sedentary | remaining in one place | 28 | |
| 6805356764 | Settlement | the act of colonizing or a small group of people in a sedentary position | 29 | |
| 6805356765 | Subsistence | the necessities of life, the resources of survival | 30 | |
| 6805356766 | Surplus | a quantity much larger than is needed | 31 | |
| 6805356767 | Sustenance | the act of sustaining life by food or providing a means of subsistence | 32 | |
| 6805356768 | Theocracy | government run by religious leaders | 33 | |
| 6805356769 | Traditional | consisting of or derived from tradition; customary practices | 34 | |
| 6805356770 | Urbanization | the social process whereby cities grow and societies become more urban | 35 | |
| 6805356771 | Vassals | lesser lords who pledged their service and loyalty to a greater lord -- in a military capacity | 36 | |
| 6805356772 | Alexander the Great | king of Macedon, conqueror of Greece, Egypt, and Persia; founder of Alexandria (356-323 BC) | 37 | |
| 6805356773 | Analects of Confucius | "something that is repeated" - a collection of Confucius' famous sayings | 38 | |
| 6805356774 | Bronze Age | a period between the Stone and Iron ages, characterized by the manufacture and use of bronze tools and weapons | 39 | |
| 6805356775 | Byzantium | the civilization that developed from the eastern Roman Empire following the death of the emperor Justinian (C.E. 565) until the fall of Constantinople (C.E.1453) | 40 | |
| 6805356776 | Calendar | a system of timekeeping that defines the beginning and length and divisions of the year | 41 | |
| 6805356777 | Code of Hammurabi | the set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi dating to the 18th century BC, the earliest legal code known in its entirety | 42 | |
| 6805356778 | Cuneiform | One of the first written languages known: A system of writing in which wedge-shaped symbols represented words or syllables. It originated in Mesopotamia and was used initially for Sumerian and Akkadian but later was adapted to represent other languages of western Asia. | 43 | |
| 6805356779 | Democracy | a political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them | 44 | |
| 6805356780 | Eight Fold Path | Eight steps to end suffering and attain enlightenment according to Buddhist tradition. | 45 | |
| 6805356781 | Four Noble Truths | as taught by the Buddha, the four basic beliefs that form the foundation of Buddhism | 46 | |
| 6805356782 | Gothic Migrations | The Migration period, also called the Barbarian Invasions or German: Völkerwanderung (wandering of the peoples), was a period of human migration that occurred roughly between the years 300 to 700 CE in Europe, marking the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. These movements were catalyzed by profound changes within both the Roman Empire and the so-called 'barbarian frontier'. Migrating peoples during this period included the Goths, Vandals, Bulgars, Alans, Suebi, Frisians, and Franks, among other Germanic and Slavic tribes. | 47 | |
| 6805356783 | Great Wall | a fortification 1,500 miles long built across northern China in the 3rd century BC | 48 | |
| 6805356784 | Han Dynasty | imperial dynasty that ruled China (most of the time from 206 BC to AD 220) and expanded its boundaries and developed its bureaucracy | 49 | |
| 6805356785 | Hellenism | The ideals and principles that spread from Greece through much of the ancient world. Much of its influence such as philosophy, athletics, and architecture penetrated the Middle East. | 50 | |
| 6805356786 | The Huns | Fierce warriors from Central Asia- First invaded southeastern Europe and then launched raids on nearby kingdoms | 51 | |
| 6805356787 | Indian Ocean Trade | connected to Europe, Africa, and China.; worlds richest maritime trading network and an area of rapid Muslim expansion. | 52 | |
| 6805356788 | Iron Age | the period following the Bronze Age; characterized by rapid spread of iron tools and weapons | 53 | |
| 6805356789 | Jewish Diaspora | A "scattering" of the Jewish people | 54 | |
| 6805356790 | Legalism | In Chinese history, Legalism was one of the main philosophic currents during the Warring States Period- A philosophy of focusing on the text of written law to the exclusion of the intent of law, elevating strict adherence to law over justice, mercy and common sense | 55 | |
| 6805356791 | Pax Romana | A period of peace and prosperity throughout the Roman Empire, lasting from 27 B.C. to A.D. 180. | 56 | |
| 6805356792 | Pyramids | Huge stone tombs with four triangle-shaped walls that met in a point on top | 57 | |
| 6805356793 | Roman Republic | The period from 507 to 31 B.C.E., during which Rome was largely governed by the aristocratic Roman Senate. | 58 | |
| 6805356794 | Roman Senate | a council of wealthy and powerful Romans that advised the city's leaders | 59 | |
| 6805356795 | Shang Civilization | China's first dynasty almost 2000 BCE | 60 | |
| 6805356796 | Shi Huang Di | harsh ruler who united China for the first time and used legalism in ruling (Qin China) | 61 | |
| 6805356797 | Siddhartha Gautama | founder of Buddhism; born a prince; left his father's wealth to find the cause of human suffering; also know as Buddha | 62 | |
| 6805356798 | Silk Road Trade | The most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the Chinese, Indian, Persian, and Mediterranean civilizations; transmitted goods and ideas among civilization. | 63 | |
| 6805356799 | The Torah | the most sacred text of Judaism | 64 | |
| 6805356800 | The Vedas of Hinduism | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books from the 6th century B.C.E. | 65 | |
| 6805356801 | Ziggurats | a temple or tomb of the ancient Assyrians, Sumerians, or Babylonians, having the form of a terraced pyramid of successively receding stories | 66 |
Unit 3 600-1450 AP World History Flashcards
| 8005562419 | Silk Roads | the most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the European, Indian, and Chinese; transmitted goods and ideas among civilizations | 0 | |
| 8005562420 | Black Death | The common name for a major outbreak of plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century, carrying off vast numbers of persons. | 1 | |
| 8005562421 | Indian Ocean trading network | The world's largest sea-based system of comunication and exchange before 1500 C.E., Indian Ocean commerce stretched from southern China to eastern Africa and included not only the exchange of luxury and bulk goods but also the exchange of ideas and crops. |  | 2 |
| 8005562425 | Swahili civilization | an East African civilization that emerged in the 8th century ce from a blending of Bantu, Islamic, and other Indian Ocean trade elements |  | 3 |
| 8005562426 | Great Zimbabwe | City, now in ruins (in the modern African country of Zimbabwe), whose many stone structures were built between about 1250 and 1450, when it was a trading center and the capital of a large state. | 4 | |
| 8005562427 | Sand roads | The system of roads that led across the Sahara desert in Africa. |  | 5 |
| 8005562432 | Sui dynasty | The short dynasty between the Han and the Tang; built the Grand Canal, strengthened the government, and introduced Buddhism to China |  | 6 |
| 8005562433 | Tang dynasty | 618-907 CE. Much like the Han using Confucianism. had the equal field system, a bureaucracy based on merit and a Confuciansim education system. Trained strong armies of almost a million troops to fight off nomadic powers from Asia. Made story cultural influence over Korea and Vietnam. |  | 7 |
| 8005562434 | Song dynasty | During this Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 AD) China saw many important inventions. There was a magnetic compass; had a navy; traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton); paper money, gun powder; landscape black and white paintings |  | 8 |
| 8005562437 | foot binding | Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household. | 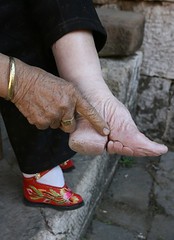 | 9 |
| 8005562438 | tribute system | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people's that assumed the subordination of all non-Chinese authorities and required the payment of tribute --produce of value from their countries--to the Chinese emperor(although the Chines gifts given in return were often much more valuable). | 10 | |
| 8005562447 | Chinese Buddhism | China's only large-scale cultural borrowing before the 20th century. Buddhism entered China from India in the first and second centuries C.E but only became popular between 300-800 C.E through a series of cultural accommodations. At first supported by the state, Buddhism suffered persecution during the 9th century but continued to play a role in Chinese society. | 11 | |
| 8005562448 | Emperor Wendi | a Chinese general, who secured his Emperor position by killing 59 princes of the Zhou royal house, and founded the Sui Dynasty. Presented himself as a Buddhist Cakravartin King, that is, a monarch who uses military force to defend the Buddhist faith. | 12 | |
| 8005562449 | Quran | The holy book of Islam | 13 | |
| 8005562450 | umma | The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a community. | 14 | |
| 8005562451 | Pillars of Islam | The five core practices required of Muslims: a profession of faith, regular prayer, charitable giving, fasting during Ramadan, and a pilgrimage to Mecca (if physically and financially possible). | 15 | |
| 8005562453 | sharia | Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life | 16 | |
| 8005562456 | Umayyad Caliphate | (661-750 CE) The Islamic caliphate that established a capital at Damascus, conquered North Africa, the Iberian Pennisula, Southwest Asia, and Persia, and had a bureaucracy with only Arab Muslims able to be a part of it. |  | 17 |
| 8005562457 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Mulim could be a part of. |  | 18 |
| 8005562458 | Sufism | A branch of Islam, defined by adherents as the inner, mystical dimension of Islam; others contend that it is a perennial philosophy of existence that pre-dates religion, the expression of which flowered within Islam |  | 19 |
| 8005562461 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period. |  | 20 |
| 8005562471 | Byzantine Empire | (330-1453) The eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived after the fall of the Western Empire at the end of the 5th century C.E. Its capital was Constantinople, named after the Emperor Constantine. |  | 21 |
| 8005562472 | Constantinople | A large and wealthy city that was the imperial capital of the Byzantine empire and later the Ottoman empire, now known as Istanbul | 22 | |
| 8005562474 | caesarpapism | a political-religious system where the secular ruler is also the head of the religious establishment (Byzantine Empire) | 23 | |
| 8005562475 | Eastern Orthodox Christianity | Eastern branch of Christianity that evolved following the division of the Roman Empire and the subsequent development of the Byzantine Empire in the east and the medieval European society in the west. The church recognized the primacy of the patriarch of Constantinople | 24 | |
| 8005562477 | Prince Vladimir of Kiev | converted to Orthodox Christianity, and allowed Byzantine influence in his realm | 25 | |
| 8005562478 | Kievan Rus | A monarchy established in present day Russia in the 6th and 7th centuries. It was ruled through loosely organized alliances with regional aristocrats from. The Scandinavians coined the term "Russia". It was greatly influenced by Byzantine | 26 | |
| 8005562482 | Western Christendom | Western Europe was on the margins of world history for most of the postclassical millennium; It was far removed from the growing world trade routes; European geography made political unity difficult; Coastlines and river systems facilitated internal exchange; | 27 | |
| 8005562484 | Crusades | Armed pilgrimages to the Holy Land by Christians determined to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule. The Crusades brought an end to western Europe's centuries of intellectual and cultural isolation. |  | 28 |
| 8005562485 | pastoralism | A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter. | 29 | |
| 8005562487 | Turks | 6th-10th centuries C.E. •Pastoral ethnic group that originated in northern Eurasia and spread into Central Asia and the Middle East •Had significant cultural and political interactions with China, Persia, Byzantium •Conversion to Islam 10th-14th centuries •Diffused Islam throughout Middle East, India, Anatolia(Turkey) | 30 | |
| 8005562489 | Temujin | leader of the largest Mongol clans; he unites them all(plans to conquer Asia); and receives title Genghis Khan(universal ruler) | 31 | |
| 8005562490 | the Mongol world | Eurasia, 13th-15th centuries •50-year period of Mongol conquests across Eurasia that created the Mongol empire •Subjected huge populations to Mongol rule •Military strength allowed for rapid conquest •Mongol rule created interactions between diverse groups •Served to diffuse technology, culture, political and economic systems |  | 32 |
| 8005562491 | Yuan Dynasty | (1279-1368 CE) The dynasty with Mongol rule in China; centralized with bureaucracy but structure is different: Mongols on top->Persian bureaucrats->Chinese bureuacrats. | 33 | |
| 8005562492 | Kublai Khan | (1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China. | 34 |
MICROSCOPE Flashcards
| 7161059067 | EYEPIECE LENS | Eyepiece is the lens, present at the top and is used to see the objects under study. Eyepiece lens usually has a magnification of 10X or 15X. |  | 0 |
| 7161062409 | OBJECTIVE LENS | Generally, three or four objective lenses are found on a microscope, with ranges of 10X, 40X, 100X powers. Lenses are colour coded, the shortest lens is of the lowest power, and the longest lens is high power. |  | 1 |
| 7161062410 | REVOLVING NOSEPIECE | has holders for the different objective lenses. It allows the rotation of the lenses while viewing. |  | 2 |
| 7161067337 | DIAPHRAGM | This helps in controlling the amount of light that is passing through the opening of the stage. It is helpful in the adjustment of the control of light that enters. |  | 3 |
| 7161069665 | COARSE ADJUSTMENT KNOB | Used for APPROXIMATE focus on scanning. Usually the low power lens is used enabling the movement of the tube. |  | 4 |
| 7161070969 | FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB | Used for fine adjustment to make the image really clear. Moves the body tube for focusing the high power lens. |  | 5 |
| 7161078598 | ARM | It supports the tube of the microscope and connects to the base of the microscope. |  | 6 |
| 7161079719 | BASE | Provides support for the microscope. | 7 | |
| 7161082432 | STAGE | The flat platform used for placing the slides under observation. |  | 8 |
| 7161083628 | STAGE CLIP | Hold the slides in proper place. |  | 9 |
AP World History Chapter 23 Flashcards
| 6052581635 | Age of Revolution | Period of political upheaval beginning roughly with the American Revolution in 1775 and continuing through the French Revolution of 1789 and other movements for change up to 1848 | 0 | |
| 6052581636 | Albert Einstein | German physicist who developed the theory of relativity, which states that time, space, and mass are relative to each other and not fixed. | 1 | |
| 6052581637 | American Civil War | 1861-1865: War between North (union states) and South (confederate states) over slavery and succeeding. | 2 | |
| 6052581638 | American Revolution | This political revolution began with the Declaration of Independence in 1776 where American colonists sought to balance the power between government and the people and protect the rights of citizens in a democracy. | 3 | |
| 6052581639 | Balkan Nationalism | Movements to create independent nations within the Balkan possessions of the Ottoman empire; provoked a series of crises within the European alliance system; eventually led to World War I. | 4 | |
| 6052581640 | Benjamin Disraeli | A British Prime Minister, parliamentarian, Conservative statesman and literary figure. Only Prime Minister of Jewish heritage. He played an instrumental role in the creation of the modern Conservative Party after the Corn Laws schism of 1846. | 5 | |
| 6052581641 | Charles Darwin | English naturalist. He studied the plants and animals of South America and the Pacific islands, and in his book On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859) set forth his theory of evolution. | 6 | |
| 6052581642 | Chartist Movement | Attempt by artisans and workers in Britain to gain the right to vote during the 1840s; demands for reform beyond the Reform Act of 1832 were incorporated into a series of petitions; movement failed | 7 | |
| 6052581643 | Congress of Vienna | Following Napoleon's exile, this meeting of European rulers in Austria established a system by which the balance of power would be maintained, liberal revolutions would be repressed, as would imperial expansion, and the creation of new countries in Europe. | 8 | |
| 6052581644 | Conservatism | A political or theological orientation advocating the preservation of the best in society and opposing radical changes. | 9 | |
| 6052581645 | Count Camillo di Cavour | Architect of Italian unification in 1858; formed an alliance with France to attack Austrian control of Northern Italy; resulted in creation of constitutional monarchy under Piedmontese king. | 10 | |
| 6052581646 | Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen | French Revolution document that outlined what the National Assembly considered to be the natural rights of all people and the rights that they possessed as citizens | 11 | |
| 6052581647 | Factory System | This new system gradually replaced localized cottage industry. Workers were paid by the hour instead of for what they produce. On one hand it decreased the need for skilled labor, but in other ways it increased the amount of specialization due to labor being concentrated in factories. | 12 | |
| 6052581648 | Feminist Movement | Sought various legal and economic gains for women, including equal access to professions and higher education; came to concentrate on right to vote; won support particularly from middle-class women; active in Western Europe at the end of the 19th century; revived in light of other issues in the 1960s. | 13 | |
| 6052581649 | French Revolution | The revolution that began in 1789, overthrew the absolute monarchy of the Bourbons and the system of aristocratic privileges, and ended with Napoleon's overthrow of the Directory and seizure of power in 1799. | 14 | |
| 6052581650 | French Revolution of 1830 | Banquet was held to discuss ideas, but the government banned it à revolt for UMS and a new constitution. Workers revolted also when the National Workshops were close | 15 | |
| 6052581651 | French Revolution of 1848 | Banquet was held to discuss ideas, but the government banned it à revolt for UMS and a new constitution. Workers revolted also when the National Workshops were close | 16 | |
| 6052581652 | Greek Revolution | Rebellion in Greece against the Ottoman Empire in 1820; key step in gradually dismantling the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans. | 17 | |
| 6052581653 | Guillotine | device used during the Reign of Terror to execute thousands by beheading | 18 | |
| 6052581654 | Imperialism | A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically. | 19 | |
| 6052581655 | Industrial Revolution | A period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production that began in the mid-1700s | 20 | |
| 6052581656 | James Watt | invented the condenser and other improvements that made the steam engine a practical source of power for industry and transportation. The watt, an electrical measurement, is named after him. | 21 | |
| 6052581657 | Karl Marx | 1818-1883. 19th century philosopher, political economist, sociologist, humanist, political theorist, and revolutionary. Often recognized as the father of communism. Analysis of history led to his belief that communism would replace capitalism as it replaced feudalism. Believed in a classless society. | 22 | |
| 6052581658 | Liberalism | A political ideology that emphasizes the civil rights of citizens, representative government, and the protection of private property. This ideology, derived from the Enlightenment, was especially popular among the property-owning middle classes. | 23 | |
| 6052581659 | Louis Pasteur | French chemist and biologist whose discovery that fermentation is caused by microorganisms resulted in the process of pasteurization (1822-1895) | 24 | |
| 6052581660 | Louis XVI | King of France (r.1774-1792 CE). In 1789 he summoned the Estates-General, but he did not grant the reforms that were demanded and revolution followed. Louis and his queen, Marie Antoinette, were executed in 1793. | 25 | |
| 6052581661 | Luddites | Any of a group of British workers who between 1811 and 1816 rioted and destroyed laborsaving textile machinery in the belief that such machinery would diminish employment. | 26 | |
| 6052581662 | Mass Leisure Culture | an aspect of the later Industrial Revolution; decreased time at work and offered opportunities for new forms of leisure time, such as vacation trips and team sports. | 27 | |
| 6052581663 | Napoleon Bonaparte | (1769-1821) Emperor of the French. Responsible for many French Revolution reforms as well as conquering most of Europe. He was defeated at Waterloo, and died several years later on the island of Saint Helena. | 28 | |
| 6052581664 | Nationalism | A sense of unity binding the people of a state together; devotion to the interests of a particular country or nation, an identification with the state and an acceptance of national goals. | 29 | |
| 6052581665 | Otto von Bismarck | Chancellor of Prussia from 1862 until 1871, when he became chancellor of Germany. A conservative nationalist, he led Prussia to victory against Austria (1866) and France (1870) and was responsible for the creation of the German Empire (714) | 30 | |
| 6052581666 | Population Revolution | Huge growth in population in western Europe beginning about 1730; prelude to Industrial Revolution; population of France increased 50 percent, England and Prussia 100 percent. | 31 | |
| 6052581667 | Proto-Industrialization | preliminary shift away from an agricultural economy; workers become full or part-time producers who worked at home in a capitalist system in which materials, work, orders, and sales depended on urban merchants; prelude to the Industrial Revolution. | 32 | |
| 6052581668 | Radicals | those who favor extreme change | 33 | |
| 6052581669 | Reform Bill of 1832 | Gave vote to all men who paid ten pounds in rent a year; eliminated the rotten boroughs | 34 | |
| 6052581670 | Revisionism | Socialist movements that at least tacitly disavowed Marxist revolutionary doctrine; believed social success could be achieved gradually through political institutions. | 35 | |
| 6052581671 | Revolutions of 1848 | Democratic and nationalist revolutions that swept across Europe during a time after the Congress of Vienna when conservative monarchs were trying to maintain their power. The monarchy in France was overthrown. In Germany, Austria, Italy, and Hungary the revolutions failed. | 36 | |
| 6052581672 | Romanticism | 19th-century western European artistic and literary movement; held that emotion and impression, not reason, were the keys to the mysteries of human experience and nature; sought to portray passions, not calm reflection. | 37 | |
| 6052581673 | Sigmund Freud | 1856-1939; Field: psychoanalytic, personality; Contributions: id/ego/superego, reality and pleasure principles, ego ideal, defense mechanisms (expanded by Anna Freud), psychoanalysis, transference | 38 | |
| 6052581674 | Social Question | Issues relating to repressed classes in western Europe during the Industrial Revolution, particularly workers and women, became more critical than constitutional issues after 1870 | 39 | |
| 6052581675 | Socialism | A system in which society, usually in the form of the government, owns and controls the means of production. | 40 | |
| 6052581676 | Transformismo | Political system in late 19th century Italy that promoted alliance of conservatives and liberals; parliamentary deputies of all parties supported the status quo. | 41 | |
| 6052581677 | Triple Alliance | Alliance among Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy at the end of the 19th century; part of European alliance system and balance of power prior to World War I. | 42 |
AP World History: The Fall of Rome (Unit 3) Flashcards
| 7073155214 | What were the 7 reasons for the Fall of Rome? | Corruption Heavy taxes Instability Over expansion Increased warfare Overuse of slaves Barbarians (Extra: They also couldn't afford to pay their soldiers, they paid them with grain and many quit because of this) | 0 | |
| 7073160279 | What did emperor Diocles do in an effort to stop Rome from falling? | Divided the Roman Empire into eastern and western sections | 1 | |
| 7073165546 | What was the western side of Rome called and why did it fall? | The Roman Empire, fell to invasions | 2 | |
| 7073169430 | What was the eastern side of Rome called and how long did it last? | The Byzantine empire lasted an additional 1,000 years | 3 | |
| 7073171887 | What did Rome pass on to the world? | Government, law, architecture, and customs | 4 |
Ap world history Unit 3 Flashcards
| 7798437318 | Abbasid | The dynasty that came after the Umayyads, devoted their energy to trade, scholorship, and the arts | 0 | |
| 7798439738 | Angkor Wat | The largest Hindu temple in the world, built by King Suryavarman II in present-day Angkor, and dedicated to the Hindu god of Vishnu | 1 | |
| 7798475853 | Astrolabe | instrument used to determine latitude by measuring the position of the stars | 2 | |
| 7798590377 | Bantu migration | The expansion of the Bantu speaking people from Cameroon and Eastern Nigeria into East, Central, and Southern Africa. | 3 | |
| 7798674818 | bubonic plague | A bacterial disease of fleas that can be transmitted by flea bites to rodents and humans; humans in late stages of the illness can spread the bacteria by coughing. High mortality rate and hard to contain. Disastrous. (280) | 4 | |
| 7798709879 | Cahokia | an ancient settlement of southern Indians, located near present day St. Louis, it served as a trading center for 40,000 at its peak in A.D. 1200. | 5 | |
| 7798921688 | Caravanserais | inns offering lodging for caravan merchants as well as food, water, and care for their animals | 6 | |
| 7798983167 | Catholicism | the faith, practice, and church order of the Roman Catholic Church. | 7 | |
| 7799015050 | Chinampas | Raised fields constructed along lake shores in Mesoamerica to increase agricultural yields | 8 | |
| 7799182589 | Christendom | Christianity split into Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholicism based on church leadership, languages, and religious images. | 9 |
AP World History: Ch. 10 Civilization in Eastern Europe: Byzantium and Orthodox Europe, Pt. 2 Flashcards
| 5256852868 | Cyril | Missionary sent by Byzantine government to eastern Europe and the Balkans who was successful converting southern Russia and the Balkans to Orthodox Christianity, and responsible for the creation of a written script in his name. | 0 | |
| 5256852869 | Methodius | Missionary sent by Byzantine government to eastern Europe and the Balkans to Orthodox Christianity. | 1 | |
| 5256852870 | Cyrillic | A Slavic language derived from Greek letters which is the Slavic alphabet. | 2 | |
| 5256852871 | Jews | Group who fled to eastern Europe to get away from the intolerance faced in Western Europe, who became proficient at commerce after being barred from agriculture. | 3 | |
| 5256852872 | Local Language | Encouraged to be used in churches by Byzantine missionaries--a distinct contrast with western Catholicism. | 4 | |
| 5256852873 | Kiev | Trade city in southern Russia established by Scandinavian traders in the 9th century that became a focal point that flourished unto the 12th century. | 5 | |
| 5256852874 | Rurik | Legendary Scandinavian who is regarded as the founder of the first kingdom on Russia based in Kiev in 855 C.E. | 6 | |
| 5256852875 | Kievan Rus' | The predecessor to Modern Russia that existed from the 9th through 13th centuries including parts of modern Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia. | 7 | |
| 5256852876 | Russia | Term coined in the 12th century, possibly taken from the Greek "red" based on the hair color of Norse traders. | 8 | |
| 5256852877 | Vladimir I | Ruler of Russian kingdom of Kiev from 980 to 1015, who converted his kingdom to Christianity. | 9 | |
| 5256852878 | Russian Orthodox | Brach of Christianity that arose largely because, like the Byzantine Church, the king controlled major appointments. | 10 | |
| 5256852879 | Yaroslav | Last of the great Kievan monarchs who issued legal codification based on formal codes developed in Byzantium. | 11 | |
| 5256852880 | Illuminated Manuscripts | Example of how Russian culture and art were heavily influenced by Christianity | 12 | |
| 5256852881 | Boyars | Russian aristocratic landlords who held less political power than their western counterparts. | 13 | |
| 5256852882 | Dneiper | Important river that was a substantial artery facilitating trade. | 14 | |
| 5256852883 | Wait for it... The Mongols | In 1237-1238 and 1240-1241, Kiev was raided when these central Asian invaders who wanted to add the whole of Europe to their empire. | 15 | |
| 5256852884 | Tatars | Turkic people living in Asia and Europe who were one of the five major tribal confederations in the Mongolian plateau in the 12th century CE. | 16 |
Flashcards
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

