People of AP World History Flashcards
Here are some key people to remember for AP World History. They come from the back of the book "The Earth And Its Peoples."
| 9910385715 | Akbar I | Most illustrious sultan of the Mughal Empire (r. 1556-1605). He expanded the empire and pursued a policy of concilation with Hindus. | 0 | |
| 9910385716 | Akhenaten | Egyptian pharaoh (r. 1353-1335 BCE). He built a new capital at Amarna, fostered a new style of naturalistic art, and created a religious revolution by imposing worship of the sun-disk. | 1 | |
| 9910385717 | Alexander the Great | King of Macedonia in northern Greece, Between 334 and 323 BCE, he conquered the Persian Empire, reached the Indus Valley, founded many Greek-style cities, and spread Greek culture across the Middle East. | 2 | |
| 9910385719 | Richard Arkwright | English inventor and entrepreneur who became the wealthiest and most successful textile manufacturer of the early Industrial Revolution. He invented the water frame. | 3 | |
| 9910385720 | Ashoka | Third ruler of the Mauryan Empire in India (r. 270-232 BCE). He converted to Buddhism and broadcast his precepts on inscribed stones and pillars, the earliest surviving Indian writing. | 4 | |
| 9910385721 | Atahualpa | Last ruling Inca emperor of Peru. He was executed by the Spanish. | 5 | |
| 9910385722 | Octavian | Founder of the Roman Principate. After defeating all rivals between 31 BCE and 14 CE, he laid the groundwork for several centuries of stability and prosperity in the Roman Empire. Also called Augustus. | 6 | |
| 9910385723 | Emiliano Zapata | Revolutionary and leader of peasants in the Mexican Revolution. He mobilized landless peasants in south-central Mexico in an attempt to seize and divide the lands of the wealthy landowners. Though successful for a time, he was ultimately defeated and assassinated. | 7 | |
| 9910385724 | Zheng He | An imperial eunuch and Muslim, entrusted by the Ming emperor Yongle with a series of state voyages that took his gigantic ships though the Indian Ocean, from Southeast Asia to Africa. | 8 | |
| 9910385725 | Faisal I | Arab prince, leader of the Arab Revolt in World War I. The British made him king of Iraq in 1921, and he reigned under British protection until 1933. | 9 | |
| 9910385726 | Benjamin Franklin | American intellectual, inventor, and politician. He helped negotiate French support for the American Revolution. | 10 | |
| 9910385727 | Thomas Edison | American inventor best known for inventing the electric lightbulb, acoustic recording on wax cylinders, and motion pictures. | 11 | |
| 9910385728 | Albert Einstein | German physicist who developed the theory of relativity. | 12 | |
| 9910385730 | Yongle | He sponsored the building of the Forbidden City, a huge encyclopedia project, the expeditions of Zheng He, and the reopening of China's borders to trade and travel. | 13 | |
| 9910385731 | Yuan Shikai | Chinese general and first president of the Chinese Republic (1912-1916). He stood in the way of Sun Yat-sen's movement. | 14 | |
| 9910385732 | Ibn Battuta | Moroccan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. | 15 | |
| 9910385734 | Napoleon Bonaparte | Overthrew French Directory in 1799 and became emperor of the French in 1804. Failed to defeat Great Britain and abdicatd in 1914. Returned to power briefly in 1815 but was defeated and died in exile. | 16 | |
| 9910385736 | Jawaharlal Nehru | Indian statesman. He succeeded Gandhi as the leader of the Indian National Congress. He negotiated the end of British colonial rule in India and became India's first prime minister (1947-1964). | 17 | |
| 9910385737 | Alexander Nevskii | Prince of Novgorod (r. 1236-1263). He submitted to the invading Mongols in 1240 and received recognition as the leader of the Russian princes under the Golden Horde. | 18 | |
| 9910385738 | Hammurabi | Amorite ruler of Babylon (r. 1792-1750 BCE). He conquered many city-states in southern and northern Mesopotamia and is best known for a code of laws, inscribed on a black stone pillar, illustrating the principles to be used in legal cases. | 19 | |
| 9910385739 | Hatshepsut | Queen of Egypt (r. 1473-1458 BCE). She dispatched a naval expedition down the Red Sea to Punt, the faraway source of myrrh. There is evidence of opposition to a woman as a ruler, and after her death her name and image were frequently defaced. | 20 | |
| 9910385740 | Henry the Navigator | Portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of Africa. | 21 | |
| 9910385741 | Herodotus | Heir to the technique of historia ("investigation") developed by Greeks in the late Archaic period. He came from a Greek community in Anatolia and traveled extensively, collecting information in western Asia and the Mediterranean lands. He traced the antecedents of and chronicled the Persian Wars, thus originating the Western tradition of historical writing. | 22 | |
| 9910385742 | Theodor Herzl | Austrian journalist and founder of the Zionist movement urging the creation of a Jewish national homeland in Palestine. | 23 | |
| 9910385744 | Adolf Hitler | Born in Austria, he became a radical German nationalist during World War I. He led the Nazi party in the 1920s and became dictator of Germany in 1933. He led Europe into World War II. | 24 | |
| 9910385745 | Saddam Hussein | President of Iraq from 1979 until overthrown by an American-led invasion in 2003. Waged war on Iran from 1980-1988. His invasion of Kuwait in 1990 was repulsed in the Persian Gulf War in 1991. | 25 | |
| 9910385746 | Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini | Shiite philosopher and cleric who led the overthrow of the shah of Iran in 1979 and created an Islamic republic. | 26 | |
| 9910385747 | Khubilai Khan | Last of the Mongol Great Khans (r. 1260-1294) and founder of the Yuan Empire. | 27 | |
| 9910385749 | Pancho Villa | A popular leader during the Mexican Revolution. An outlaw in his youth, when the revolution started, he formed a cavalry army in the north of Mexico and fought for the rights of the landless in collaboration with Zapata. He was assassinated in 1923. | 28 | |
| 9910385750 | George Washington | Military commander of the American Revolution. He was the first elected president of the United States (1789-1799). | 29 | |
| 9910385751 | James Watt | Scot who invented the condenser and other improvements that made the steam engine a practical source of power for industry and transportation. The watt, an electrical measurement, is named after him. | 30 | |
| 9910385753 | Woodrow Wilson | President of the United States (1913-1921) and the leading figure at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. He was unable to persuade the US Congress to ratify the Treaty of Versailles or join the League of Nations. | 31 | |
| 9910385754 | Wilbur and Orville Wright | American bicycle mechanics; the first to build and fly an airplace, at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, December 7, 1903. | 32 | |
| 9910385755 | Margaret Sanger | American nurse and author; pioneer in the movement for family planning; organized conferences and established birth control clinics. | 33 | |
| 9910385757 | Shah Abbas I | The fifth and most renowned ruler of the Safavid dynasty in Iran. He moved the royal capital to Isfahan in 1598. | 34 | |
| 9910385758 | Shi Huangdi | Founder of the short-lived Qin dynasty and creator of the Chinese Empire (ca. 221-210 BCE). He is remembered for his ruthless conquests of rival states, standardization of practices, and forcible organization of labor for military and engineering tasks. His tomb, with its army of life-size terracotta soldiers, has been partially excavated. | 35 | |
| 9910385759 | Socrates | Athenian philosopher (ca. 470-399 BCE) who shifted the emphasis of philosophical investifation from questions of natural science to ethics and human behavior. He attracted young disciples from elite families but made enemies by revealing the ignorance and pretensions of others, culminating in his trial and execution by the Athenian state. | 36 | |
| 9910385760 | Josef Stalin | Bolshevik revolutionary, head of the Soviet Communist Party after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928-1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush all opposition. | 37 | |
| 9910385761 | Henry Morton Stanley | British-American explorer of Africa, famous for his expeditions in search of Dr. David Livingstone. He helped King Leopold II establish the Congo Free State. | 38 | |
| 9910385762 | Suleiman the Magnificent | The most illustrious sultan of the Ottoman Empire (r. 1520-1566); also known as Kanuni ("Lawgiver"). He significantly expanded the empire in the Balkans and eastern Mediterranean. | 39 | |
| 9910385763 | Sun Yat-sen | Chinese nationalist revolutionary, founder and leader of the Kuomintang until his death. He attempted to create a liberal deemocratic political movement in China but was thwarted by military leaders. | 40 | |
| 9910385764 | Tecumseh | Shawnee leader who attempted to organize an Amerindian confederacy to prevent the loss of additional territory to American settlers. He became an ally of the British in the War of 1812 and died in battle. | 41 | |
| 9910385765 | Timur | Member of a prominent family of the Mongols' Jagadai Khanate. He through conquest gained control over much of Central Asia and Iran. He consolidated the status of Sunni Islam as orthodox, and his descendants maintained his empire for nearly a century and founded the Mughal Empire in India. | 42 | |
| 9910385766 | Tupac Amaru II | Member of Inca aristocracy who led a rebellion against Spanish authorities in Peru in 1780-1781. He was captured and executed along with his wife and other members of his family. | 43 | |
| 9910385767 | Ramses II | A long-lived ruler of New Kingdom Egypt (r. 1290-1224 BCE). He reached an accomodation with the Hittites of Anatolia after a standoff in battle at Kadesh in Syria. He built on a grand scale throughout Egypt. | 44 | |
| 9910385769 | Cecil Rhodes | British entrepreneur and politician involved in the expansion of the British Empire from South Africa into Central Africa. The colonies of Zimbabwe and Zambia were originally named after him. | 45 | |
| 9910385770 | Maximilien Robespierre | Young provincial lawyer who led the most radical phases of the French Revolution. His execution ended the Reign of Terror. | 46 | |
| 9910385771 | Bartolome de Las Casas | First bishop of Chiapas, in southern Mexico. He devoted most of his life to protecting Amerindian peoples from exploitation. His major achievement was the New Laws of 1542, which limited the ability of Spanish settlers to compel Amerindians to labor for them. | 47 | |
| 9910385772 | Vladimir Lenin | Leader of the Bolshevik (later Communist) Party. He lived in exile in Switzerland until 1917, then returned to Russia to lead the Bolsheviks to victory during the Russian Revolution and the civil wars that followed. | 48 | |
| 9910385773 | Leopold II | King of Belgium (r. 1865-1909). He was active in encouraging the exploration of Central Africa and became the ruler of the Congo Free State (to 1908). | 49 | |
| 9910385775 | Toussaint L'Ouverture | Leader of the Haitian Revolution. He freed the slaves and gained effective independence for Haiti despite military interventions by the British and French. | 50 | |
| 9910385776 | Andrew Jackson | First president of the US to be born in humble circumstances. He was popular among frontier residents, urban workers, and small farmers. He had a successful political career as judge, general, congressman, senator, and president. After being denied the presidency in 1824 in a controversial election, he won in 1828 and was reelected in 1832. | 51 | |
| 9910385777 | Jesus | A Jew from Galilee in northern Israel who sought to reform Jewish beliefs and practices. He was executed as a revolutionary by the Romans. Hailed as the Messiah and Son of God by his followers, he became the central figure in Christianity, a belief system that developed in the centuries after his death. | 52 | |
| 9910385778 | Muhammad Ali Jinnah | Indian Muslim politician who founded the state of Pakistan. A lawyer by training, he joined the All-India Muslim League in 1913. As leader of the League from the 1920s on, he negotiated with the British and the Indian National Congress for Muslim participation in Indian politics. From 1940 on, he led the movement for the independence of India's Muslims in a separate state of Pakistan, founded in 1947. | 53 | |
| 9910385779 | Benito Juarez | President of Mexico (1858-1872). Born in poverty in Mexico, he was educated as a lawyer and rose to become chief justice of the Mexican supreme court and then president. He led Mexico's resistance to a French invasion in 1863 and the installation of Maximilian as emperor. | 54 | |
| 9910385780 | Darius I | Third ruler of the Persian Empire (r. 521-486 BCE). He crushed the widespread initial resistance to his rule and gave all major government posts to Persians rather than to Medes. He established a system of provinces and tribute, began construction of Persepolis, and expanded Persian control in the east (Pakistan) and west (northern Greece). | 55 | |
| 9910385781 | Deng Xiaoping | Communist Party leader who forced Chinese economic reforms after the death of Mao. | 56 | |
| 9910385783 | Bartolomeu Dias | Portuguese explorer who in 1488 led the first expedition to sail around the southern tip of Africa from the Atlantic and sight the Indian Ocean. | 57 | |
| 9910385784 | Osama bin Laden | Saudi-born Muslim extremist who funded the al Qaeda organization that was responsible for several terrorist attacks, including those on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon in 2001. | 58 | |
| 9910385785 | Otto von Bismarck | Chancellor of Prussia from 1862-1871, when he became chancellor of Germany. A conservative nationalist, he led Prussia to victory against Austria (1866) and France (1870) and was responsible for the creation of the German Empire in 1871. | 59 | |
| 9910385786 | Simon Bolivar | The most important military leader in the struggle for independence in South America. Born in Venezuela, he led military forces there and in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. | 60 | |
| 9910385788 | Siddhartha Gautama | An Indian prince alternately known as the Buddha, who renounced his wealth and social position. After becoming "enlightened" he enunciated the principles of Buddhism. This doctrine evolved and spread throughout India and to Southeast, East, and Central Asia. | 61 | |
| 9910385789 | Vasco da Gama | Portuguese explorer. In 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from Europe to sail to India, opening an important commercial sea route. | 62 | |
| 9910385790 | Mahatma Gandhi | Leader of the Indian independence movement and advocate of nonviolent resistance. After being educated as a lawyer in England, he returned to India and became the leader of the Indian National Congress in 1920. He appealed to the poor, led nonviolent demonstrations against British colonial rule, and was jailed many times. Soon after independence he was assassinated for attempting to stop Hindu-Muslim rioting. | 63 | |
| 9910385791 | Giuseppe Garibaldi | Italian nationalist and revolutionary who conquered Sicily and Naples and added them to a unified Italy in 1860. | 64 | |
| 9910385792 | Genghis Khan | The title of Temujin when the ruled the Mongols (1206-1227). It means the "oceanic" or "universal" leader. He was the founder of the Mongol Empire. | 65 | |
| 9910385793 | Mikhail Gorbachev | Head of the Soviet Union from 1985-1991. His liberalization effort improved relations with the West, but he lost power after his reforms led to the collapse of communist governments in eastern Europe. | 66 | |
| 9910385796 | Pericles | Aristocratic leader who guided the Athenian state through the transformation to full participatory democracy for all male citizens, supervised construction of the Acropolis, and pursued a policy of imperial expansion that led to the Peloponnesian War. He formulated a strategy of attrition but died from the plague early in the war. | 67 | |
| 9910385797 | Eva Duarte Peron | Wife of an Argentinian president. Champion of the poor in Argentina. She was a gifted speaker and popular political leader who campaigned to improve the life of the urban poor by founding schools and hospitals and providing other social benefits. | 68 | |
| 9910385798 | Juan Peron | President of Argentina (1946-1955, 1973-1974). As a military officer, he championed the rights of labor. His wife played a major role in his 1946 election. He built up Argentinian industry, became very popular among the urban poor, but harmed the economy. | 69 | |
| 9910385799 | Peter the Great | Russian tzar (r. 1689-1725). He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg. | 70 | |
| 9910385800 | Francisco Pizzarro | Spanish explorer who led the conquest of the Inca Empire of Peru in 1531-1533. | 71 | |
| 9910385801 | Ferdinand Magellan | Portuguese navigator who led the Spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to sail around the world. | 72 | |
| 9910385802 | Thomas Malthus | 18th century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production. | 73 | |
| 9910385803 | Mansa Kankan Musa | Ruler of Mali (r. 1312-1337). His pilgrimage through Egypt to Mecca in 1324-1325 established the empire's reputation for wealth in the Mediterranean world. | 74 | |
| 9910385804 | Mao Zedong | Leader of the Chinese Communist Party (1927-1976). He led the Communists on the Long March (1934-1935) and rebuilt the Communist Party and Red Army during the Japanese occupation of China (1937-1945). After World War II, he led the Communists to victory over the Kuomintang. He ordered the Cultural Revolution in 1966. | 75 | |
| 9910385805 | Karl Marx | German journalist and philosopher, founder of the Marxist branch of socialism. He is known for two books: "The Communist Manifesto" and "Das Kapital." | 76 | |
| 9910385806 | Menelik II | Emperor of Ethiopia (r. 1889-1911). He enlarged Ethiopia to its present dimensions and defeated an Italian invasion at Adowa. | 77 | |
| 9910385807 | Moctezuma II | Last Aztec emperor, overthrown by the Spanish conquistador Hernan Cortes. | 78 | |
| 9910385809 | Muhammad | Arab prophet; founder of the religion of Islam. | 79 | |
| 9910385810 | Muhammad Ali | Leader of Egyptian modernization in the early 19th century. He ruled Egypt as an Ottoman governor, but had imperial ambitions. His descendants ruled Egypt until overthrown in 1952. | 80 | |
| 9910385811 | Benito Mussolini | Fascist dictator of Italy (1922-1943). He led Italy to conquer Ethiopia (1935), joined Germany in the Axis pact (1936), and allied Italy with Germany in World War II. He was overthrown in 1943 when the Allies invaded Italy. | 81 | |
| 9910385813 | Charlemagne | King of the Franks (r. 768-814); emperor (800-814). Through a series of military conquests he established the Carolingian Empire, which encompassed all of Gaul and parts of Germany and Italy. Though illiterate himself, he sponsored a brief intellectual revival. | 82 | |
| 9910385814 | Chiang Kai-shek | Chinese military and political leader. Succeeded Sun Yat-sen as head of the Kuomintang in 1923; headed the Chinese government from 1928-1948; fought against the Chinese Communists and Japanese invaders. After 1949 he headed the Chinese Nationalist government in Taiwan. | 83 | |
| 9910385815 | Cixi | Empress of China and mother of Emperor Guangxi. She put her son under house arrest, supported antiforeign movements, and resisted reforms of the Chinese government and armed forces. | 84 | |
| 9910385816 | Christopher Columbus | Genoese mariner who in the service of Spain led expeditions across the Atlantic, reestablishing contact between the peoples of the Americas and the Old World and opening the way to Spanish conquest and colonization. | 85 | |
| 9910385817 | Confucius | Western name for the Chinese philosopher Kongzi. His doctrine of duty and public service had a great influence on subsequent Chinese thought and served as a code of conduct for government officials. | 86 | |
| 9910385818 | Constantine | Roman emperor (r. 312-337). After reuniting the Roman Empire, he moved the capital to Constantinople and made Christianity a favored religion. | 87 | |
| 9910385819 | Hernan Cortes | Spanish explorer and conquistador who led the conquest of Aztec Mexico in 1519-1521 for Spain. | 88 | |
| 9910385820 | Cyrus | Founder of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Between 550 and 530 BCE, he conquered Media, Lydia, and Babylon. Revered in the traditions of both Iran and the subject peoples, he employed Persians and Medes in his administration and respected the institutions and beliefs of subject peoples. | 89 |
AP World History Strayer Chapter 8 Vocabulary Flashcards
Unit Three Part Three
| 8299893072 | Sui Dynasty | *Definition:* Short dynasty between Han and Tang. *Significance:* Built Grand Canal, strengthened government, and introduced Buddhism to China. |  | 0 |
| 8299893073 | Tang Dynasty | *Definition:* Dynasty often referred to as "China's Golden Age". (618 CE - 907 CE) *Significance:* China expands to Vietnam, Imperial examination perfected. New technologies (paper money, gunpowder, junks, etc...) through silk road. | 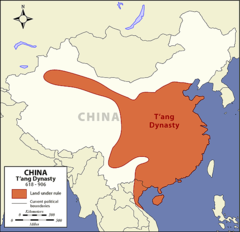 | 1 |
| 8299893074 | Song Dynasty | *Definition:* (960 CE - 1279 CE) Started by Tai Zu. *Significance:* Million people there. Foot binding, magnetic compass, navy, and traded with India and Persia. |  | 2 |
| 8299893075 | Hangzhou | *Definition:* Capital of later Song Dynasty. *Significance:* Permitted overseas trading with population exceeding 1 million. |  | 3 |
| 8299893076 | Economic Revolution | *Definition:* Rapid population growth, economic speculation, increase in industrial production and innovations (Song dynasty). *Significance:* Made China "by far the richest, most skilled, and most populous country on Earth." |  | 4 |
| 8299893077 | Foot Binding | *Definition:* Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet to make them smaller. *Significance:* It was associated with images of female beauty and eroticism. |  | 5 |
| 8299893078 | Tribute System | *Definition:* Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people that assumed subordination of all non-chinese authorities. They required all foreigners wanting access to China to pay tribute. *Significance:* System the attempted to regulate their relationships with Northern Nomads. |  | 6 |
| 8299893079 | Khitan/Jurchen People | *Definition:* Nomadic people who established a state that included parts of Northern China. *Significance:* Was a nomadic group who "picked up the pieces" after collapse of Tang Dynasty. |  | 7 |
| 8299893080 | Silla Dynasty (Korea) | *Definition:* First ruling dynasty to bring a measure of political unity to Korean Peninsula. *Significance:* Allied with China to bring political unity to the peninsula for the first time. |  | 8 |
| 8299893081 | Hangul | *Definition:* Phonetic alphabet in Korea (14th century). *Significance:* Helped Korea move toward greater cultural independence. | 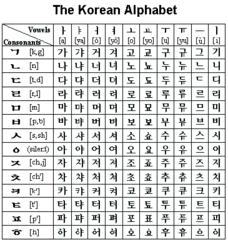 | 9 |
| 8299893082 | Shotoku Taishi | *Definition:* Japanese statesman who launched the drive to make Japan into centralized bureaucratic state modeled on China. *Significance:* Launched a series of large-scale missions to China. |  | 10 |
| 8299893083 | Bushido | *Definition:* "Way of the Warrior". *Significance:* A distinct set of values for Samurais. |  | 11 |
| 8299893084 | Chinese Buddhism | *Definition:* Entered China through cultural accommodations. *Significance:* Useful to helping nomadic rulers govern northern China because it was foreign. |  | 12 |
| 8299893085 | Emperor Wendi | *Definition:* Sui Emperor who patronized Buddhism. *Significance:* He was responsible for the monasteries constructed at the base of China's 5 sacred mountains. |  | 13 |
| 8299893087 | Chu nom | *Definition:* The writing system of Vietnam *Significance:* United Vietnam even during times of civil war |  | 14 |
| 8299898215 | Xinongnu | - an empire with a peace treaty keeping xiugnu from deploying military forces, | 15 |
World History 1 The World of Islam Flashcards
| 7347447722 | Arabian Peninsula | Region of the world that has the largest sand desert in the world |  | 0 |
| 7347456408 | Makkah (Mecca) | The birthplace of Muhammad. The home of the Kaaba. |  | 1 |
| 7347462015 | Muhammad | Arab prophet; founder of religion of Islam. |  | 2 |
| 7347465037 | Islam | the religion of Muslims based on the teachings of the prophet Muhammad. The world Islam means Peace through submission to the will of Allah |  | 3 |
| 7347469275 | Submission | the act of yielding to the authority of another | 4 | |
| 7347470633 | Madinah | "city of the prophet"; city to which Muhammad and his supporters went in 622 |  | 5 |
| 7347475268 | Hijrah | the journey of Muhammad and his followers to Madinah |  | 6 |
| 7347478729 | Abū Bakr | Wealthy merchant and Muhammad's father in law who will take Muhammad place when he dies. |  | 7 |
| 7347485417 | Caliph | successor to Muhammad as political and religious leader of the Muslims | 8 | |
| 7347491564 | Damascus | Muʿāwiyah I moved the capital of the Arab Empire here when he became caliph and established the Umayyad dynasty |  | 9 |
| 7347502320 | Bagdad | In 762, the Abasids built a new capital city here, on the Tigris River. | 10 | |
| 7347506204 | Sultan | "Holder of Power" In 1055 a Turkish leader captured Baghdad and took command of the empire. | 11 | |
| 7347513620 | Ibn Sina | wrote the Canon on Medicine, an encyclopedia of medicinal cures. He showed how diseases could be spread by contaminated water supplies. Also a well know philosopher |  | 12 |
AP World History Chapter 20 Terms Flashcards
| 9323580726 | In Japan in the 1920s: | the populace became politicized | 0 | |
| 9323580727 | Which of the following is NOT a reason why the German people tolerated Hitler's leadership during the mid-1930s? | His persecution of the Jews purged Germany of a legitimate threat to national security | 1 | |
| 9323580728 | Fascism does NOT stand for: | individual rights | 2 | |
| 9323624534 | Which of the following was NOT a tactic utilized by Mussolini in his efforts to claim power in Italy? | rational debate | 3 | |
| 9323624535 | The League of Nations responded to Mussolini's invasion of Ethiopia by: | doing almost nothing | 4 | |
| 9323624536 | Japan had a high rate of economic growth during the two decades preceding World War II | True | 5 | |
| 9323624537 | Adolf Hitler: | Laid out his political program in Mein Kampf | 6 | |
| 9323624538 | After World War I, Japan's industrial development: | succeeded in integrating large-scale factory production with small-scale cottage industries | 7 | |
| 9323624539 | The Gestapo was established in 1936 to eliminate (through murder or internment) opposition leaders who advocated anti-Hitler ideologies | True | 8 | |
| 9337961030 | The League of Nations: | was a forum for resolving international conflicts through negotiations | 9 | |
| 9337961031 | Which of the following aggressive actions occurred before World War II had officially begun? | Japan invaded China | 10 | |
| 9337961032 | Hitler invaded which of the following on 1 September 1939, opening the European theater in World War II? | Poland | 11 | |
| 9337961033 | Which of the following was annexed by Germany in Hitler's Anschluss? | Austria | 12 | |
| 9337961034 | Pablo Picasso painted Guernica to protest: | Aerial bombardment of civilians | 13 | |
| 9337961035 | Which of the following did NOT support General Francisco Franco during the Spanish Civil War? | Soviet Union | 14 | |
| 9337961036 | World War II started when Germany invaded Czechoslovakia. | False | 15 | |
| 9337961037 | Which of the following was NOT a part of the famed "Maginot Line"? | elevated gun turrets | 16 | |
| 9337961038 | Which of the following was NOT a part of Japan's "Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere"? | open trade with the West | 17 | |
| 9353569017 | Which of the following was NOT included in the "Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere" by 1942? | Fiji | 18 | |
| 9353569018 | Mohandas Gandhi argued that: | the civilization was on the path to self-destruction | 19 | |
| 9353569019 | The turning point in the Eastern front came at the battle of: | Stalingrad | 20 | |
| 9363871323 | Hitler believed in a racial hierarchy and placed blacks at the bottom. | False | 21 | |
| 9363871324 | The Soviet Union suffered the highest casualty rate in World War II: about 20 million dead. | True | 22 | |
| 9363871325 | "Island hopping" was: | the U.S. strategy of sequential liberation of Japan's holdings in the Pacific | 23 | |
| 9363871326 | The first atomic bomb was dropped on: | Hiroshima | 24 | |
| 9363871327 | In 1941, hundreds of thousands of Serbs and other "undesirables" were murdered by: | the Ustasa | 25 | |
| 9363871328 | Women did much of the factory work in America during World War II. | True | 26 | |
| 9363871329 | Which of the following achieved the highest level of aircraft production by 1944? | USA | 27 | |
| 9365315738 | According to Albert Camus, the only serious philosophical question is: | Whether to commit suicide | 28 | |
| 9365315739 | Which of the following was NOT one of the aims of the United Nations, according to the preamble of the organization's charter? | establish democratic governments throughout the world | 29 | |
| 9365315740 | According to the preamble to the charter of the United Nations, the world is encouraged to practice tolerance. | True | 30 | |
| 9365315741 | The Terror House in Budapest memorializes: | Hungary's occupations by the Germans and by the Soviets | 31 | |
| 9365315742 | The atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima: | was the first nuclear weapon used in war | 32 | |
| 9365315743 | At the Nuremberg Trials: | 22 Nazis were tried for criminal acts against humanity | 33 | |
| 9365315744 | The United Nations: | was envisioned primarily as a vehicle to promote peace | 34 | |
| 9365315745 | This is NOT part of the United Nations: | International Monetary Fund | 35 |
AP World History Strayer Chapter 4 Vocabulary Flashcards
| 7349890583 | Legalism | *Definition:* Chinese Philosophy distinguished by clear laws with vigorous consequences. *Significance:* Rulers and governments used to control the people and had laws for the people. |  | 0 |
| 7349890584 | Confucianism | *Definition:* Chinese Philosophy first enunciated by Confucius. The moral example of superiors. (Education is key). *Significance:* First body of thought followed as a cultural belief rather than a religion. (Meant to unite China after warring time.) |  | 1 |
| 7349890585 | Ban Zhao | *Definition:* Female Confucian author of Han Dynasty China. *Significance:* Works gave insight into implication of China thinking for women. |  | 2 |
| 7349890586 | Daoism | *Definition:* (opposite of Confucianism) Education was useless and urged unification into the world of nature. Governs all natural phenomenon. *Significance:* Provided ideology to peasant rebellions (Yellow Turban Rebellion). Better than being sad about education. Shaped ordinary people. |  | 3 |
| 7349890587 | Vedas | *Definition:* Earliest Religious text of India. Collection of poems, hymns, and rituals. *Significance:* Lead to religions such as Buddhism and Hinduism. |  | 4 |
| 7349890588 | Upanishads | *Definition:* Mystical, philosophical works that developed in response to dissatisfaction with Brahmins. *Significance:* Gave way to introspective thinking. "Brahman"- world soul. Escape from earth and gods. |  | 5 |
| 7349890589 | Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) | *Definition:* Indian prince who founded Buddhism. *Significance:* Teached Buddhism as "Enlightened one", reflecting on being selfless with no material wants. Focusing on self and morals. |  | 6 |
| 7349890590 | Theravada/Mahayana | *Definition:* "Teachings of elders", early form of Buddhism that portrayed the Buddha as a wise teacher, but not divine. *Significance:* Emphasized practices rather than beliefs. |  | 7 |
| 7349890591 | Bhagavad Gita | *Definition:* A great Hindu epic text. (part of the much larger Mahabharata). *Significance:* Affirmed the performance of caste duties as a path of religious liberation. (reason to do caste duties.) |  | 8 |
| 7349890593 | Judaism | *Definition:* (Hebrews) History recorded in Torah (old testament in Bible) Monotheistic religion. Emphasizing sole personal god: Yahweh with concerns for social justice. *Significance:* Foundation of Christianity and Islam. Big part in Israel and Palestine conflicts of the world due to failure of assimilation. |  | 9 |
| 7349890594 | Greek Rationalism | *Definition:* Secularizing system of scientific, philosophic thought that developed in classical Greek. *Significance:* Emphasized the power of education, and human reason to understanding the world in non-religious terms. Stepped away from supernatural reasoning. |  | 10 |
| 7349890595 | Socrates, Plato, Aristotle | *Definition:* 3 different philosophers who believed in reason and rational thought (Students of each other). *Significance:* Rationalism appearance. Turning Rationalism toward questions of human existence. |  | 11 |
| 7349890596 | Jesus of Nazareth | *Definition:* He came from a lower class family, taught lessons to large crowds and performed miracles. Saviour of Christians. *Significance:* The New Testament in the bible. Christianity is still a major religion today. |  | 12 |
| 7349890597 | Saint Paul | *Definition:* 1st great popularizer of Christianity. *Significance:* Spread Christianity and taught it after Jesus. Convinced people why it was good and needed. | 13 | |
| 7349890598 | Church of the East | *Definition:* Branch of the church in Persia and active in missions to reject China the chalcedonian creed on the grounds that it did not accurately affirm the human nature of Jesus. *Significance:* Spreading of this segment of Christianity. Allowed different forms (even religions) to take shape because of this. |  | 14 |
| 7349890599 | Perpetua | *Definition:* Christian Martyr from an upper class Roman family in Carthage. *Significance:* She refused to renounce her faith and made her an inspiration for other early Christians who were prosecuted. |  | 15 |
| 7349892087 | moksha | unity between the individual soul and world soul; part of Hinduism | 16 | |
| 7349893015 | nirvana | Buddhist term meaning freedom from the "painful" cycle of rebirth (samsara) | 17 |
AP World History-Rome Flashcards
| 5081211639 | Paul of Tarsus | -55 CE Roman guards transported prisoner from port of Caesarea of Palestine to city of Rome -Party boarded ship with grain and 276 passengers -Ship encountered severe storm -For 2 weeks crew and passengers worked to keep the ship afloat -Ship eventually reached the island of Malta where the storm waves destroyed the ship -Most of the people survived including Paul who spent 3 months on Malta before getting on another ship to Rome | 0 | |
| 5081211640 | Christianity | -Sect of Judaism accepted only by few people who believed Jesus of Nazareth was savior of the Jewish Community -mid first century CE Christianity attracted many converts throughout the Mediterranean basin -Paul was a devote Jew from Anatolia who accepted Christian teachings and became a missionary looking for converts from outside as well as inside the Jewish community -Crowd of Paul's enemies attacked him in Jerusalem when he promoted Christianity -Disturbance became so big that Roman imperial government authorities intervened to restore order | 1 | |
| 5081211641 | Roman Empire | -Established close links between other Mediterranean regions -As they conquered other lands the Romans enabled merchants, missionaries, and others to travel throughout the Mediterranean basin and parts of southwest Asia -The early Christians encountered harsh opposition and persecution from Roman officials -Eventually Christianity became official religion of the Roman empire | 2 | |
| 5081211642 | Kingdom to Republic | - Founded in 8th century BCE the city of Roman was originally a small state ruled by a single king -In the late 6th century BCE the city's aristocrats ended the monarchy and created a republic -The Roman republic survived for more than 500 years -Rome was dominant power in Mediterranean basin | 3 | |
| 5081211643 | Romulus and Remus | -Twins-Almost did not survive infancy because their evil uncle abandoned them by the flooded Tiber river expecting them to drown or die from exposure -She-wolf found them and nursed them to health -In 753 BCE Romulus founded Rome and established himself as the first king | 4 | |
| 5081211644 | Etruscans | -Italy underwent rapid political and economic development -dynamic people who dominated much of Italy between the 8th and 5th centuries BCE -Migrated to Italy from Anatolia -Built thriving cities and established political and economic alliances between their settlements -Manufactured high-quality bronze and iron goods and worked gold and silver into jewelry -Etruscan merchants drew a large volume of traffic to Rome | 5 | |
| 5081211645 | Establishment of Republic | -509 BCE Roman nobility got rid of the last Etruscan king -Replaced with aristocratic republic | 6 | |
| 5081211646 | Roman Forum | -Political and civic center filled with temples and public buildings where leading citizens tended to government business | 7 | |
| 5081211647 | Consuls | -Elected by an assembly dominated be hereditary aristocrats and wealthy classes (Patricians) -Senate advised the consuls and ratified all major decisions -Constant tension between the wealthy classes and the common people (Plebeians) | 8 | |
| 5081211648 | Conflicts between Patricians and Plebeians | -Relations between the classes became strained that the plebeians threatened to secede from Rome and establish a rival settlement -The patricians granted plebeians the right to elect officials (tribunes) who represented their interests in the Roman government -Originally plebeians chose 2 tribunes but then that changed to 10 -Problems continued to rise and eventually broadened to the base of political participation -In early 5th century Plebeians threatened to secede Plebeians were granted right to elect Tribunes -2-10 tribunes elected -Had power to intervene in politics -Given veto power | 9 | |
| 5081211649 | The legend | -Aeneas, a refugee from Troy, escapes during the Trojan War -Migrates to Italy - and Remus were left by the Tiber River to die -"Suckled" by a she-wolf -753 B.C.E. Romulus founded the city of Rome and became the first king | 10 | |
| 5081211650 | The real story | -Indo-European origins -Adopted agriculture -Tribal structure of society | 11 | |
| 5081211651 | The Etruscans | -Lived in Italy 8th-5th centuries B.C.E. -Probably from Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) -Built cities -Declined -Greeks attacked at sea -Gauls attacked on land | 12 | |
| 5081211652 | Kingdom of Rome | -Influenced by Etruscans -Monarchy like Etruscans -Many of the first kings were Etruscans -Provided paved streets, public buildings, defensive walls -Rome was well-situated for trade -Easy access to Mediterranean via Tiber River -Protected because it was not on the coast | 13 | |
| 5081211653 | Roman Republic | -509 B.C.E. Etruscan king deposed -Aristocratic republic created -Built public Forum -Government -2 consuls (presidents) -Elected by Patricians -Served 1 year terms -Senate -All early leaders were wealthy Patricians | 14 | |
| 5081211654 | Roman Republic Expansion | -Established military colonies -Often exempted conquered peoples from taxation -Allowed self-rule in a lot of regions -Had right to trade / marry Roman citizens -Possibility of gaining citizenship -Had to provide soldier | 15 | |
| 5081211655 | Punic Wars | -264 - 146 B.C.E. -First Punic War 264-241 BCE -Fought over Sicily -Rome won -Second Punic War 218 BCE -General Hannibal attacked from North -Crossed Alps on elephants -Had to return to Carthage - Rome won -Third Punic War 149 - 146 BCE -Rome attacked/ Burned Carthage -Rome Won | 16 | |
| 5081211656 | Imperial Expansion and Domestic Problems | -Acquired lands fell to wealthy -Elites organized plantations known as LATIFUNDIAS -Enjoyed economies of scale (Think Wal-Mart) -Gracchi Brothers -Tiberius and Gaius -Worked to limit individual landholding -Both were assassinated | 17 | |
| 5081211657 | Civil War | -Generals recruited their own private armies from landless & urban poor -Men were intensely loyal to generals, who fed them -In 87 BCE Gaius Marius (who advocated redistribution of land) marched on Rome Sulla, an aristocrat, gained control after his death -Killed 10,000 people during his reign of terror -Conservative government weakened power of the poor | 18 | |
| 5081211658 | Julius Caeser | -Nephew of Marius -Liberal, favored social reform -Led Roman army in conquering Gaul (France) -In 46 B.C.E. he named himself Dictator for life -Centralized power -Redistributed land to his men and supporters -Large-scale building projects for employment -Extended Roman citizenship to imperial provinces -Was attacked and killed in 44 B.C.E. in the forum | 19 | |
| 5081211659 | Augustus | -13 years of civil unrest after Caesar's death -Octavian (Augustus) was the nephew/son of Caesar -Defeated Marc Antony & Cleopatra in 31 B.C.E. -Ruled for 45 years | 20 | |
| 5081211660 | Augustus' Government | -Monarchy disguised as a republic -Centralized political and military power -Kept traditional offices -Allowed elites to participate in government -Reorganized government -Standing army loyal to him -Appointed people loyal to him -Head of everything in government | 21 | |
| 5081211661 | Effects of Expansion | -Sparsely populated areas quickly grew w/ Roman soldiers, merchants, diplomats and governors -Stimulated local economies -Cities emerged -Paris -London -Toledo | 22 | |
| 5081211662 | Pax Romana | -Within Roman boundaries, long era of peace -1st century C.E. - middle of 3rd century C.E. -Facilitated trade and communication | 23 | |
| 5081211663 | Roman Roads | -Deep roads -Curbs -Drainage -Paved w/ stone -Large enough for 2 way traffic -Milestones -Stations for couriers | 24 | |
| 5081211664 | Roman Law | -Twelve Tables -450 B.C.E. -Argued: -Defendant innocent until proven guilty -Defendants could challenge accusers before a judge -Unfair laws should be repealed | 25 | |
| 5081211665 | Trade and Agriculture | -Greece -Olives and vines -Syria & Palestine -Fruits, nuts, wool -Gaul -Grain, copper, vines Italy -Pottery, glassware, bronze | 26 | |
| 5081211666 | Mediterranean Trade | -Roman military and naval power protected Mediterranean Sea -Called it "Mare nostrum" -"Our Sea" | 27 | |
| 5081211667 | City of Rome | -Statues, pools, monuments -Temples, bathhouses, public buildings -Aqueducts brought in fresh water -Underground sewers | 28 | |
| 5081211668 | Entertainment | -Circuses -Oval structures for chariot races -Circus Maximus sat 250,000 people -Colosseum -Gladiators -Humans & wild animals | 29 | |
| 5081211669 | Pater Families | -Patriarchal tradition of eldest male ruling family -Women had some power within the home, especially in wealthy families -Pater Familias had authority to: -Arrange marriages -Punish family members -Sell relatives into slavery -Execute family | 30 | |
| 5081211670 | "Bread and Circuses" 1st Century B.C.E. | -Many poor farmers moved into city -Often unemployed, they would riot or join personal armies -Imperial authorities tried to distract them with "Bread and Circuses" -Subsidized grain -Spectacular entertainment | 31 | |
| 5081211671 | Slavery in Roman Empire | -2nd Century C.E. 1/3 of population of Roman empire enslaved -Spartacus led the most famous slave rebellion in 73 B.C.E. -Chained together to work on Latifundia -Conditions better in the cities -House slaves -Tutors Some urban slaves manumitted at age 30 | 32 | |
| 5081211672 | Roman Religions | -Influenced by the Greeks -Renamed Greek gods / goddesses -Stoicism -Cicero followed Stoic values -Individuals must live in accordance w/ nature and reason -Religions of Salvation -Sense of purpose and optimism for the future | 33 | |
| 5081211673 | Mithaism | -Zoroastrian mythical god -Identified w/ sun and light -Romans redeveloped Mithras as a god of strength, courage and discipline -Popular among military -Beliefs -Human life divine -Moral behavior -Rewarded w/ reunion w/ Mithras for believers | 34 | |
| 5081211674 | Cult of Isis | -Allowed both men and women followers -Most popular religion of salvation prior to Christianity -Egyptian goddess was benevolent and protective | 35 | |
| 5081211675 | Jews and the Empire | -From 10th century B.C.E. -Jews were first monotheistic religion -Only recognized Yahweh as divine -Refused to worship any other gods, emperors, etc. | 36 | |
| 5081211676 | The Essenes | -A sect of Judaism -Wrote the "Dead Sea Scrolls," discovered in 1947 -Strict moral code -Baptism by water -Community meals -Searched for a savior | 37 | |
| 5081211677 | Jesus of Nazarth | -A Jew -Peaceful, taught devotion to God and love for fellow man -Alarmed Romans because he taught "the kingdom of God is at hand" -Executed around 30 C.E. -Became more popular after death -"Christ" means "anointed one" | 38 | |
| 5081211678 | Christianity | -Paul of Tarsus was disciple of Jesus -Appealed his case -Traveled to spread the word of Jesus -Argued that faith must come before individual or family | 39 |
AP World History ( The Enlightenment, Scientific Revolution, Salons) Flashcards
| 7174485896 | Enlightenment | An intellectual movement in 17~18 CE. Decline in the power of absolute monarchies, reduction of church authorities | 0 | |
| 7174489113 | Francis Bacon. | Father or empiricism from the UK. A creator of the scientific method. Encouraged an empirical approach through his own example and philosophy. He believed that science is precious and people should constantly look for more. | 1 | |
| 7174493831 | Rene Descartes | A philosopher in France. Wrote Discourse on method. His main idea was to think for ourselves, doubt everything. Break down the hard problem into easy problems. I think, therefore I am. He tried to change people's mind who were just believing things without questioning it. LOGICAL PROCESS. | 2 | |
| 7174552205 | Thomas Hobbes | He wrote Leviathan. He thinks human nature is bad and the nature of men is to fight and the only one who can prevent and stop this chaos is the king. THERE IS A KING BECAUSE PEOPLE WANTS IT. | 3 | |
| 7174499002 | John Locke | A philosopher in the UK. Wrote Two Treatises on Government. He thought that no one can be ruled without their consent. He thought people are wonderful and they make the government because they want freedom. He tried to change the absolute monarch in the Europe | 4 | |
| 7174558027 | Adam Smith | An author of An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth Nations. He promoted freedom of the market. The government should not interfere with the market and let people sell and buy what they want. With this, the people will be rich and eventually make the country rich too. | 5 | |
| 7174505460 | Sir Isaac Newton | A mathematician in the UK. Wrote Principia Mathematica and Pricipia. He developed the new laws of mechanics, gravity, and laws of motion. He also led the framework for the Scientific Revolution. He also believed in God through science. | 6 | |
| 7174511259 | Voltaire | A critic in France. He wrote Treatise on Toleration and Candide. He argued for religious tolerance and freedom of speech even though people might disagree with it. He also argued for more chance of education. He tried to change religious wars and persecution. | 7 | |
| 7174521286 | Jean-Jacques Rousseau | A political philosopher in France; born in Swizz. He wrote SOCIAL CONTRACT and CONFESSIONS and EMILE. He promoted more equalitarian; people who are all equal form of government. He promoted originality. He thought that direct democracy is the only form of government where people can get freedom. However, in order to get freedom, the citizens should actively participate and be engaged in the politics. He promoted the exclusion of women in the political realm. He thought women's gentle softness distracted men from their duties. He thought is was the nature's decsion that made women weak. He thought women were too weak mentally and physically so women should not do science | 8 | |
| 7174527948 | Benjamin Franklin | A scientist and politician in the USA. He supported colonial unity in the states. He also proved that lightning and electricity is the same thing. He found positive and negative charges. | 9 | |
| 7174532665 | Thomas Jefferson | He is an American founding father. He wrote The Declaration of Independence. He supported ending slavery. | 10 | |
| 7174545747 | Scientific Revolution | Beginning of experimentation in the 17 to 18 CE | 11 | |
| 7174548741 | Ptolemaic | Also known as Geocentric; The Earth is the center of the universe. People believed this until the 1500s | 12 | |
| 7174550303 | Heliocentric | Sun is the center of the universe. Founded by Copernicus. | 13 | |
| 7174569200 | Baron de Montesquieu | The author of the Spirit of the Laws. He distinguished the main form of the governments: - Republics, monarchies, and despotisms. He says that in order for a government to succeed, it requires them to get support from the citizens. He also says women are good rulers as their weakness shows more gentleness. | 14 | |
| 7174575759 | Monarchy | Ruled by the king, queen, royal families. The authorities get passed down to the king's eldest son | 15 | |
| 7174577562 | Despotism | A monarch who uses their absolute power for evil | 16 | |
| 7174578055 | Republic | Representatives of the government | 17 | |
| 7174581168 | Constitutional monarchy | It says what the government should look like. It limits the power of different people. Also known as the limited monarchy | 18 | |
| 7174583387 | Glorious Revolution | An event where the Parliament exiled Catholic king James II as he tried to take some rights away from the Englishmen. There was no blood shed during this event. The crown was replaced by his daughter, Mary and William. | 19 | |
| 7174587489 | John Wesley | He is a Methodist minister. His opinion about the Lisbon Earthquake is biased. He thinks this is the punishment from God as the people became more greedy during the course of time. | 20 | |
| 7174590466 | Salons | A place in Europe (Paris) where woman and men congregated for intellectual discourse. This reduced marginalization of women in Paris. Also allowed common people to interact with the nobility | 21 | |
| 7174594762 | Salonniere | A leader in the salon. A person who hosts the salon and organizes the conversation. Decides the topic to talk about. | 22 | |
| 7174597608 | Saint-Gabriel | A saint. He thought that France should not rule like a male-dominated country but peacefully. Said the government can function under the goodness of the governance of the ladies. | 23 | |
| 7174602521 | Buffon | A scientist. He promoted gender equality. He suggested women should play a prominent role in the salons. He also gave the reasons of volcanic eruption is that the gas trapped inside the Earth creates the volcanic eruption. | 24 | |
| 7174610767 | Lady Mary Wortley Montague | A very rare exception women in the Enlightenment era. She ran off to the Ottoman Empire and brought small pox vaccination to Europe | 25 | |
| 7174619693 | Mary Wollstonecraft | An author of Vindication of the Rights of Women. She argues that it is not that women are weak to learn but they weren't even given a chance to learn. She thinks women has potential as long as they were given an opportunity. She also says women would be better if they were educated | 26 |
AP World History Flashcards
Ch. 1-6
| 7554849836 | China- class stratification | 1. An elite of officials (selected administrators; scholars) 2. Landlords (people that held land) 3. Peasants (viewed as the 'backbone') 4. Merchants (not favorable) | 0 | |
| 7554849837 | Varna theory- caste system | The idea that society is divided in 4 classes 1. Brahmins (priests) 2. Kshatriya (rulers and warriors) 3. Vaisya (commoners) 4. Sudras (servants) | 1 | |
| 7554849838 | Persian government influence | An imperial system from the Babylonian and Assyrian empires but surpassed them in size and splendor. | 2 | |
| 7554849839 | Christianity in Rome- date | Early fourth century C.E | 3 | |
| 7554849840 | Buddhism against Hindu belief | Buddhism 1. Had a founder 2. Reflects Hindu traditions 3. Against Hindu rituals and sacrifices (seen as irrelevant) 4. Ignored the caste 5. Missionary religion Hindu 1. Vedas and upanishads 2. Rebirth/ reincarnation 3. Women seen as 'unclean' | 4 | |
| 7554849841 | The 2 expressions of Buddhism | Mahayana (great vehicle): help is available for strenuous voyage Theravada (teaching of the elders): intense self-effort for enlightenment | 5 | |
| 7554849842 | Influence of Zoroastrianism | First monotheistic religion (founded in Persia). One unique god and a force of evil. Gained support in Persia and some parts in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Anatolia but never an active missionary religion. Sooner vanished from place of origin. Christianity and Islam adopted some of its core beliefs. | 6 | |
| 7554849843 | First Christian kingdom- state religion | Christianity adopted by the Axum Empire (located in the 'horn of Africa'). Conversion took place around the same time Constantine also converted. | 7 | |
| 7554849844 | Beliefs that appealed to the lower class | Buddhism and Christianity | 8 | |
| 7554849845 | Forms of government- Greek and Rome | Democracy: ruled by popular vote Monarchy: one person with absolute power Republic: authority given to a patrician assembly | 9 | |
| 7554849846 | India- difficulty in empire building | No centralized gov. Initially (political fragmentation). Mauryan empire: 1st of 2. Political structure equivalent to others (not as long-lasting however). Policies did not preserve its empire Gupta empire: art, lit., science, math, etc. large Indian commerce (this empire came much later and didn't last as long) | 10 | |
| 7554849847 | Legalism | a Chinese philosophy that stressed the importance of laws | 11 | |
| 7554849848 | Principles of Confucianism | Not laws, but that superiors should set a moral example that can restore social harmony (6-5 century) | 12 | |
| 7554849849 | Principles of Daoism | Withdrawal into the world of nature and encourage behavior that was spontaneous, individualistic, and natural. (6-3 century BCE) | 13 | |
| 7554849850 | Axum- language and writing | A commerce language is Ge'ez. Agaw-speaking people It's written language was on a smaller scale with the 2nd wave civ | 14 | |
| 7554849851 | Niger valley- growth | People came for more accessible water. Jenne-jeno houses 40,000 at its high point | 15 | |
| 7554849852 | Teotihuacán- key relevance | 10,000 sq Mel's of a core region was administered from the city itself, seen in performing diplomatic relationships, and had vast armies that showed opposition to Maya | 16 | |
| 7554849853 | Sumer | Regarded with the worlds first written language (first used for economics) | 17 | |
| 7554849854 | Epic of Gilgamesh | An epic poem from Mesopotamia, and among the earliest known works of literary writing. | 18 | |
| 7554849855 | Leadership of Solon | Credited for having laid the foundations of Athenian democracy | 19 | |
| 7554849856 | first empire | Akkadian Empire (or the Babylonian empire) | 20 | |
| 7554849857 | Mesopotamian Cities | Babylon, Ninevah, Lagash, Nippur, Ur | 21 | |
| 7554849858 | How the early cities were developed | They were developed/ organized near river like the Nike or the Ganges | 22 | |
| 7554849859 | Inca- artifacts | Monumental ceremonial structures, ritual calendar. And hieroglyphic writing | 23 | |
| 7554849860 | Zhou Dynasty- political | Politics ideology known as the son of heaven, meaning that the monarch served as an intermediary between heaven and earth as long as he governed with benevolence and maintained social harmony. | 24 | |
| 7554849861 | Trung sisters | Leaders in a failed revolt for Vietnam from Chinese rule | 25 | |
| 7554849862 | Greeks- defeat of Persia and after | The defeat of Persia unified the Greeks under one rule (Alexander the great) and it continued to grow after the defeat of Persia. It's culture become diverse throughout the region | 26 | |
| 7554849863 | Spartan- gender roles | Council of Elders (28 men over the age of 60) Slaves were conquered people | 27 | |
| 7554849864 | The spread of Greek culture- regions | Persia (Assyria, Mesopotamia, Anatolia) Egypt Parthia Bactria Gedrosia Sogdriana India Syria | 28 | |
| 7554849865 | Naval power- Rome & Carthage | A series of Punic Wars (Rome winning all) extended Rome's mighty naval power in the Mediterranean | 29 | |
| 7554849866 | Kushan empire conflict with who- geography | Located Central Asia (interacted with all others) | 30 | |
| 7554849867 | Rome- geography | Located Mediterranean, on a peninsula. This gave them oceanic trade advantage | 31 | |
| 7554849868 | Keeping power- china and Rome | Both empires had the same a unified religion, practiced traditions, and assimilated their people so that opposition was almost nonexistent | 32 | |
| 7554849869 | Spread of empire- china and Rome | Both empires had goals to encompass the world with their influence. They did it through force and religion | 33 | |
| 7554849870 | China empire building- compared to Rome | Not creating something g new, but restoring something old (dif. In how to make an empire) The Qin dynasty unified the warring states of China together under a monarchy rule like the romans. | 34 | |
| 7554849871 | Qin state- agriculture | Rapidly increased of the growing population | 35 | |
| 7554849872 | Aboriginal people of Australia | Created a way of gathering and hunting that was used up to modern times. Had a complex outlook on the world (called dreamtime) | 36 | |
| 7554849873 | Moche- date | 100-800 CE | 37 | |
| 7554849874 | The Bhakti movement | Intense adoration and identification with a particular deity through songs, prayers, and rituals | 38 | |
| 7554849875 | Greek intellectual tradition | Gods of mount Olympus Physical reality governed by natural laws | 39 |
AP World History: Athens (Unit 2) Flashcards
| 7014220209 | Who was Solon? | An aristocrat that pushed for democracy | 0 | |
| 7014251656 | What did Pericles do? | Set up the first direct democracy in which adult male citizens could vote in the legislative body called the assembly. This only accounted for 20% of the population | 1 | |
| 7014260877 | What is a golden age? | A time of peace and prosperity and advancements in the arts and sciences | 2 | |
| 7014265417 | What does Greek art reflect? What does Greek art pay special attention to? | Beauty, balance, and order. Pays special attention to the human body | 3 | |
| 7014273738 | What were the 3 styles of columns? | Doric, ionic, and Corinthian | 4 | |
| 7014276377 | What is an acropolis? | A fortified part of an ancient Greek city, typically built on a hill | 5 | |
| 7014277124 | What is the Parthenon? | A giant Athenian temple built on top of the acropolis | 6 | |
| 7014285384 | What did Greek religion look like? What did Greeks do to celebrate their religion? | Polytheistic in faith and played games to honor their gods (Olympics) | 7 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

