| 9358646120 | Core-Periphery Model | A model that describes the core countries have overall power, and the semi-peripheral and peripheral have lower political, economic, and social power
Peripheral and Semi-Peripheral depend on developed core countries for the capital while, Core countries use cheap labor from semi-peripheral and peripheral. All centered around the core. |  | 0 |
| 9358646121 | Peters Projection | maintains the area, but distorts the shape.
The area accurate map maintains the land size of countries but creates a shape not true to the actual shape of the land. |  | 1 |
| 9358646122 | Mercator Projection | the direction is true, but the size and shape are distorted. |  | 2 |
| 9358646123 | Goodes Homosline | Maintains area but divides the oceans up distorting the direction |  | 3 |
| 9358646124 | Robinson | Equally distorts direction, distance, shape, and area (SADD) principles. | | 4 |
| 9358646125 | Scale | Scale is the relationship between a distance portrayed on a map and the same distance on the Earth. | | 5 |
| 9358646126 | Fuller Projection | The shape and size are accurate but the direction is completely lost |  | 6 |
| 9358646127 | Isoline Map | Map that shows lines or area connecting points of equal value |  | 7 |
| 9358646128 | Cartogram | size of the map equals the value | 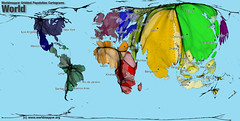 | 8 |
| 9358646129 | Dot Density Map | number of dots equals the frequency of the data. more dots, more frequently it occurs in the area and vice versa |  | 9 |
| 9358646130 | Proportional Symbol map | Symbol size equal value. Bigger dots typically mean larger value and vice versa |  | 10 |
| 9358646131 | Chloropleth Map | Shade of the map indicated the density or value (colors too) |  | 11 |
| 9358646132 | Malthus Population Catastrophe | He predicted that global population increase and the food available could not sustain the growing population |  | 12 |
| 9358646133 | Neo Malthusians | Theory that agrees with Malthus but also says that we are also depleting natural resources with the growing population and accounts for the massive population growth in least developed countries. And says we need to control population growth but is hard in LDCs because of lack of medical resources. CONTRACEPTION | | 13 |
| 9358646134 | Boserup's Hypothesis of Population (anti-Malthusian) | Population growth stimulates the advances is agriculture meaning that more food will be produced when faced with the challenge of a growing population. Contradicts malthusians |  | 14 |
| 9358646135 | Population Pyramid Components | -shows the age and genders of a given population in bar graph form. Age groups typically show five years (known as cohorts) . -Shape of the graph can vary due to birth rates and death rates.
-dependency ratio can be determined ( this is the number of too young or too old compared to the working class cohorts, the working class cohorts have to support the too young or too old.) |  | 15 |
| 9358646136 | Population Pyramid Example Shapes | There are five stages to the population pyramid that make unique shapes.
1. Stage one is rapid expansion and has high birth rates and high death rates, mostly found super least developed countries. life expectancy is very low
2. Stage two is still expansion at higher rates characterized by still high birth rate but fall in death rate by medical supplies becoming more common. Still is more least developed countries transitioning into a more stable country
3. declining birth rate and lower death rate, more people are starting to live to an older age
4. Low birth rate and low death rate, starting to level out more and will have high dependency ratio
5. Birth rate has fallen below death rate and the population has started declining in the lower cohorts
STAGE 1 AND 2 CAN BE COMBINED AS ONE |  | 16 |
| 9358646137 | Demographic Transition Model | It is used to explain and predict human population growth. It assumes that ALL countries go through four stages of population growth. It measures crude birth rate, crude death rate, and the population of a country.
Stage 1-low growth- because of the high death rate even though it has a high birth rate. (all countries have passed this)
Stage2- high growth-High birth rate, declining death rate, increasing rate of natural increase (African countries)
Stage 3-moderate growth- declining birth rates, declining death rates, decreasing rate of natural increase but still population growth (latin America countries)
stage 4- low growth- birth rate equals death rate==
usually service based industries, stable rate of growth (Western European Nations)
stage 5- declining rate of natural increase | | 17 |
| 9358646138 | Demographic Transition Model Visual | The visual in one graph through the five stages |  | 18 |
| 9358646139 | Epidemiologic Transition Model | Focuses on the cause of each step in the Demographic transition model
Stage 1-infectious diseases and famine- ((plague in the1300s killed 40 percent of Europeans))
Stage 2- epidemic and contagious diseases by overcrowding. Less pandemics because semi-improved health conditions (19th-century cholera)
Stage 3- Human created diseases like cardio and cancer
stage 4- humans live longer with the same diseases from stage three because better, longer treatments | | 19 |
| 9358646140 | Epidemiologic Transition Model | The visuals for ETM
As the stages increase in picture, the death rates decrease due to medical advances |  | 20 |
| 9358646141 | Gravity Model of Spatial Interaction | 1)Measures the interactions between two places
2) Compares the distance between two cities to figure how much pulls for migration
MAIN IDEA
-big places have a larger pull
-places closer together have a greater attraction so more migration between the two
The formula is
POP 1 * POP 2 / distance between two cities (subtract) ^2 ( then raise two second power) |  | 21 |
| 9358646142 | Ravenstein's Laws of Migration | created by english geographer, stated his principles are the basic principles for all migrations
1. most migrants go short distances if traveling in the same country. this refers back to distance decay( interactions increase or decrease when the distance between two places decreases or increases)
2. If a migrant is going to travel a long distance, it is most likely for a large city )this refers to gravity model because bigger places have a bigger pull)
3. rural populations are most likely to move to urban populations for better opportunities especially with jobs
4. individuals are more likely to migrate then families. Easier to pick yourself up and move then with family ( young children and older people)
5. every migration to a place causes a counterstream (movement that runs opposite of migration)
6. most migrants are young males (looking for work to support their families ) |  | 22 |
| 9358646143 | Zelinsky Model of Migration Transition | Based on the demographic transition model !
each stage in the DTM has a unique pattern of migration.
Stage 1: no migration, just movement that is cyclic or seasonal
Stage 2: has the MOST migration because people are moving from rural farms to urban cities in search of work and people will move internationally. Usually people from stage two will move to stage three and four nations
Stage 3 and 4: internal migration (within the nation), From cities to suburbs! |  | 23 |
| 9358646144 | Zelinsky Model of Migration Transition Visual | Shows three stages around the world and their chain migrations movements |  | 24 |
| 9358646145 | Indo-European Language | Indo European is the worlds largest family in languages
There are 8 branches in the indo european family.
1. Indo-Iranian (south Asia)- HAS THE MOST SPEAKERS IN THE WORLD
2. Romance (Southwest Europe and Latin America)- MEANS IT COMES FROM LATIN
3. Germanic (Northwestern Europe and North America)-
4. Balto-Slavic (Eastern Europe)
5. Albanian
6. Armenian
7. Greek
8. Celtic
English comes from the west germanic group. |  | 25 |
| 9358646146 | I-E Language Diffusion Theories (Agriculture, Conquest) | -- believed the Indo-European languages all came from Proto-Indo-European---
Two theories of diffusion:
1. Conquest theory - from the Kurgan hearth in steppe regions ( warriors who conquered asia and europe spreading the language)
2. Agricultural migration theory - from the Anatolian hearth in Turkey (peaceful farmers, spread language by trade and agriculture) | | 26 |
| 9358646147 | Domino Theory | It was thought if one region became communistic, then the ideal would diffuse to the surrounding countries and then those countries would become communistic and so on. PROMOTED BY THE US | | 27 |
| 9358646148 | Heartland Theory | Theory proposed that whoever controls eastern Europe controls the heartland, who then controls the world island. PRO WORLD DOMINATION
Ultimately it's whoever controlled eurasia, would then control its peripheral countries and then the entire world island (Asia, europe) |  | 28 |
| 9358646149 | Rimland Theory | The opposite of heartland theory, not the heart of the world island! whoever controls the coastal area will control the world island, which in then says will control the world. |  | 29 |
| 9358646150 | Rank Size Rule | Helps determine the urban hierarchy
-The nth largest city's population size in a region is 1/n the size of the region's largest city population | | 30 |
| 9358646151 | World Systems Theory (Wallerstein) | The theory that stated if the developed world changed, it would ultimately cause a change in the developing world. (HAS A THREE TIER SYSTEM THAT SHOWS THIS)
Core / semi-peripheral/ peripheral
Core exploits peripheral by using their labor and natural materials
peripheral are dependent core for MONEYYYY | | 31 |
| 9358646152 | WST visual | Shows the ranking and hierarchy |  | 32 |
| 9358646153 | von Thünen's Agricultural Model | Model that shows products and their proximity to the market. It's located in rings with the central city the inner core. ITS BASICALLY HOW THE FARMLAND WILL BE USED IN PROXIMITY TO THE CITY. The order the rings are in are based on how perishable the products is (needs to be super close to market) and how expensive it was to transport.
Inner-market
1st ring-dairy and market gardening
2nd ring- forestry (heavy logs)
3rd ring- field crops(didn't spoil and light to transport)
4th ring- animal grazing cause land is cheap
FIRST THREE RINGS ARE INTENSIVE
LAST RING IS EXTENSIVE | | 33 |
| 9358646154 | von Thunen visual | CONCENTRIC RINGSSSS |  | 34 |
| 9358646155 | First Agricultural Revolution | AKA KNOWN AS NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION
the switch 12,000 years ago from hunting and gathering (very nomadic)
to settling down and growing crops (also using animals for livestock) and they realized that seeds could be used to grow foooood |  | 35 |
| 9358646156 | Second Agricultural Revolution | Around the 17th century Europe AGRICULTURE BOOMED
****was before the industrial revolution
innovations made it easier for farmers to use less land and labor but produce the same amount of food. (tractor, cotton gin, plows) |  | 36 |
| 9358646157 | Third Agricultural Revolution | AKA GREEN REVOLUTION
1960s-1970s-enough food to feed the whole world
-science advances (better fertilizers, better seeds)
-Genetically modified foods came into play- created desirable traits in seeds by altering genes to make the "perfect crop"
-big agribusiness helping globalize the world
-poor countries got behind though because they could not afford the technologies
- |  | 37 |
| 9358646158 | Liberal Models of Development (self-sufficiency / international trade | *All nations can develop theory *
1. Self Sufficiency spin on LMD-
(used by China, India, Eastern European and African Nations)
-money within the country will be spent EVENLY within all sectors of the country so the country will grow together.
-businesses are kept LOCAL or NATIONAL
-NO INTERNATIONAL TRADE
-USES TRADE BARRIERS TO PREVENT INTERNATIONAL TRADE
2. International Trade spin on LMD
-countries see what they have in abundance of and trade with other nations that want it. SUPPLY AND DEMAND ON INTERNATIONAL LEVEL | | 38 |
| 9358646159 | Structuralist Model of Development (dependency theory) | Theory that the world will never let the Least developed nations fully develop like the current modern day countries. KEEPING THEM DOWN
-says that they will never be able to catch up with the big boys resource and tech wise | | 39 |
| 9358646160 | New International Division of Labor | the process of developed countries' jobs going to least developed countries because they have cheaper labor and fewer regulations.
-Multinational companies- are focusing on low-cost production in LDCs and high profits in MDCs
-Outsourcing- allows a company to relocate some or all of its production to cheaper locations (DOESNT HAVE TO BE OUT OF THE COUNTRY)
-Offshore companies- do the vast majority of their business (production) outside of their home nation |  | 40 |
| 9358646161 | Rostow's Stages of Growth (Modernization Model) | The model that shows how each country develops when it goes through the stages (stages of the DTM similar)
1. STAGE ONE-TRADITIONAL SOCIETY
-not started development
-money is focused on military and religion
-subsistence (feed your own family) agriculture
2. STAGE TWO-PRECONDITIONS FOR TAKEOFF
-external influences start up some economic activity
-country follows educated elitist and invest in technology and infrastructure
-making the bones of a country
3. STAGE THREE-TAKE OFF
-rapid growth in one area BUT other areas remain the same ole same ole
4. STAGE FOUR-DRIVE TO MATURITY
-workers are skilled and educated
-economic activities spread to all sectors of industry and market
5. STAGE FIVE-MASS CONSUMPTION
-economic shift from industry to services |  | 41 |
| 9358646162 | Fordism | Transformed industrial ways--MASS PRODUCTION---
one task is done by one person in a process over and over again |  | 42 |
| 9358646163 | Post-Fordism | TEAM WORK MAKES THE DREAM WORK
modern day spin on fordism where a team of people are assigned a task
-very flexible
-team performs a variety of task |  | 43 |
| 9358646164 | Location Interdependence Theory (Hotelling) | PROFIT MAXIMIZATION THEORY
-Best location was next to competitors or IN THE MIDDLE OF THE MARKET because it draws a larger amount of customers in because customers will go to the closest market possible |  | 44 |
| 9358646165 | Weber Model of Industrial Location (Least Cost Theory) | FOCUSED ON PRODUCTION PRICE MINIMIZATION
-Model that showed where industries should locate their factories relative to the market or source of raw materials.
-three parts that affect where it should locate 1. labor 2. transportation 3. agglomeration
1. labor-locate where labor is the cheapest
2. bulkgaining industries should locate closer to the market because the heaviest material will be at the end of production.......bulk reducing industries locate near the raw material because it loses weight as production goes on
3. agglomeration helps by having similar industries to share similar equipment, talent, and workers | | 45 |
| 9358646166 | Weber visual | ITS LOCATED NEAR THE HEAVIER MATERIAL< WATER |  | 46 |
| 9358646167 | Profit Maximization (Losch's Zone of Maximization) | CALCULATES WHAT REGION WILL CREATE THE MOST PROFIT. AREA WITH THE GREATEST AMOUNT OF INCOME-COST OF PRODUCTION .
-zone of profitability is where the business can make money
-doesn't always work due to the substitutional principle |  | 47 |
| 9358646168 | Bid-Rent Theory (Land Rent) | -BIG BUSINESSES (RETAIL) WILL SPEND LOTS OF MONEEEY TO GET THE BEST SPOT NEAR THE CENTRAL BUSINESS DISTRICT.
-manufacturing doesn't need to be close to CBD so they will pay cheaper prices of land farther away from CBD
-suburbs pay the cheapest price because they are farthest away from CBD |  | 48 |
| 9358646169 | Bid-Rent visual | Farther away? lower price
closer to the CBD? mpre expensive |  | 49 |
| 9358646170 | Borchert's Model of Urban Evolution | Predict the growth and evolution of cities based on innovative ideas around five phases of transportation
STAGE 1:sailboats and wagons! main way of transportation from 1790-1830
STAGE 2: iron horse transportation 1830-1870
STAGE 3: steel horse transportation 1870-1920
STAGE 4: auto and air 1920-1970(planes, cars)
STAGE 5: high technology (jets, supercars, rockets) | | 50 |
| 9358646171 | Central Place Theory (Christaller) | Explained the patterns of urban land use!!
-CENTRAL PLACES PROVIDED FOR PEOPLE IN THE SURROUNDING RURAL AREA
-THRESHOLD is the minimum amount of people needed to exist in that area
-range is the maximum distance a person will travel to go to the business
-more unique a business is, the higher the threshold and range
-have a hierarchy of village, town , city and central place (hence the dots within the hexagons) | | 51 |
| 9358646172 | CPT Visual | red dot is central city surrounded by the city, towns, and villages in HEXAGON shape |  | 52 |
| 9358646173 | Concentric Circle (Burgess) | Theory that has concentric rings around the central business district.
-each ring has consistently the same type of things in them
-2nd ring is industry and slums (real close to the central business district)
-3rd ring is the working class ring (easy travel distance to factories)
-4th ring is middle-class house, farther away from city because they have enough money to pay for commute but are not quite in the commuter zone
-rich people zone or commuter zone, people can afford to commute and typically have nice houses | | 53 |
| 9358646174 | Concentric Model visual | rings grow out from central business district |  | 54 |
| 9358646175 | Sector Model (Hoyt) | City grows out from the central business district in wedges. Usually due to transportation advances
-middle class around the high end people
-low class people around the manufacturing and industry sector | | 55 |
| 9358646176 | Sector model visual | Central district is in the middle
-wedges grow out from the CBD |  | 56 |
| 9358646177 | Peripheral Model | central business district is surrounds by suburbs and businesses all tied together by a beltway that surrounds the city, suburbs, and businesses.
beltway will lead out to a commerical strip and edge cities | | 57 |
| 9358646178 | Peripheral model visual | EDGE CITIES ON THE PERIPHERAL |  | 58 |
| 9358646179 | Multiple-Nuclei Model | The central business district is not the only focal point that people will surround around. There will be other multiple nodes like airports and universities.
-people will move towards some nodes while avoiding others | | 59 |
| 9358646180 | Multiple-Nuclei visual | SEE THE MULTIPLE NODES THAT PEOPLE WILL CROWD AROUND |  | 60 |
| 9358646181 | Urban Realms Model | how a metropolis is spread out, realms link together and surround the central city which forms this gigantic metropolis
-each realm is a seperate political, social, and economic entity linked together | | 61 |
| 9358646182 | Urban realms visual | multiple realms hook onto another and form the glob of a metropolis in picture |  | 62 |
| 9358646183 | Latin American Cities Model | The center is the central business district
the spine that comes off the central business district is for the wealthy, usually contains commercial residentials. Zone of maturity is the surrounding part of the central business district that has "matured" meaning all the infrastructure is complete and is well functioning. Zone of Situ accretion is the middle between the zone of maturity and the squatter settlements. It isn't really poor, but it's not fully developed. Zone of peripheral squatter settlements is the outermost ring farthest away from the central business district. It usually has little to no infrastructure and is a very poor region consisting of squatter homes | | 63 |
| 9358646184 | Latin American cities visual | Middle class usually surronds both sides of the elite spine. |  | 64 |
| 9358646185 | SE Asian Cities Model | This model lacks a central business district, but it does have a port that shares many characteristics of a central business district. Zones surrounding the port are western commercial zone, government zone, alien commercial zone, and high-class zones. Mainly in the most developed parts of the city. Then there are squatter areas and suburbs on the next to last ring of the model, and finally on the outer level gardening zone (because land it cheapest away from port) Some industries are building on the very peripheral of the city | | 65 |
| 9358646186 | SE Asian cities visual | Mixed land use zones are usually a mixture of commercial and "tradition central business district" |  | 66 |
| 9358646187 | African Cities Model | Contains three main central business districts that cluster in the middle of the city : traditional-single story buildings with traditional arch, colonial-vertical development, and market-open air, informal. Lack a lot of infrastructures so there are few roads but the main one does go through the three CBDs. Ethnic and mixed neighborhoods surround three CBDs which are then the squatter settlements are the informal townships. | | 67 |
| 9358646188 | African cities visual | Moves from the richest in the center to the poorest on the peripheral part of the city |  | 68 |


























































































































