Flashcards
Flashcards
AP World Final Review Flashcards
This took me hours but I hope it helps you, and many others pass this AP World final. There's a lot, yes, but in the end it can prove itself worth it for the AP Exam as well (that way you don't have to pay 20 bucks for a 1,000 term one!)
| 5716798904 | What were early humans known for being? | Hunters and gatherers, moved around a lot (nomadic). | 0 | |
| 5716798905 | What revolution had the development of farming? | The Neolithic Revolution. | 1 | |
| 5716798906 | What was the cause of job specializations in 8000 BCE? | Due to farming, animal breeding, settlements, stability, and food surplus. | 2 | |
| 5716798907 | What was part of the craft industry? | Pottery, metallurgy, textiles. | 3 | |
| 5716798908 | What's the early beginnings of metal? | Copper was the earliest, lead to bronze (tin and copper, 3000 BCE), and iron. Carbon came around 1000 BCE. | 4 | |
| 5716798909 | When did civilizations start to develop? | 3500 BCE, which led to population growth and cities. | 5 | |
| 5716798910 | What did early civilizations, overtime, have? | Organized governments, complex religions, social structures, writing, job specialization, and marketplaces. | 6 | |
| 5716798911 | Where were early civilizations developed? | Along rivers. | 7 | |
| 5716798912 | Which classical civilizations considered organization to a high level? | Greece, Rome, China, and India. | 8 | |
| 5716798913 | What caused collapses for early civilizations? | Internal - Corrupt government, high taxes, poor leaders External - Famine, over extensions | 9 | |
| 5716798914 | For classical civilizations, what order was the recovery rate for each civilization? | China (quickest), India, and Rome (most severe). | 10 | |
| 5716798915 | Where was Mesopotamia? | Tigris and Euphrates river, fertile crescent. | 11 | |
| 5716798916 | What was the first civilization? | Sumer (3500 BCE). | 12 | |
| 5716798917 | What did Sumer use first? | The wheel. | 13 | |
| 5716798918 | What were Sumerian temples called? | Ziggurats. | 14 | |
| 5716798919 | What writing system did Sumerians use? | Cuneiform. | 15 | |
| 5716798920 | In Sumer, who ruled their city states? What was their social class system? | Kings ruled. Then, priests, commoners, and slaves were below. | 16 | |
| 5716798921 | What currency did Sumerians use? | Silver. | 17 | |
| 5716798922 | What did Sumerians contribute to history? | Calendar and astronomy. | 18 | |
| 5716798923 | What code did Babylonians contribute? | Hammurabi's Code 1st written law: eye for an eye. | 19 | |
| 5716798924 | Where were early Egyptian's located? | Along the Nile River. | 20 | |
| 5716798925 | What were Egyptian rulers called? | Pharaohs, or god-like kings. | 21 | |
| 5716798926 | What were tombs in early Egyptian civilizations? | Tombs. | 22 | |
| 5716798927 | What was mummification? | The preservation of human or animal remains, a common practice for Egyptian rituals. | 23 | |
| 5716798928 | How did the Egyptian calendar contribute to history? | The Egyptian calendar is similar to our modern calendars, 12 months with 30 day incriments, following up with about 365 days in their years. | 24 | |
| 5716798929 | What are hieroglyphics? | Ancient Egyptian writings made up of stylized pictures of an object representing a word, syllable, or sound. | 25 | |
| 5716798930 | When did the Phoenicians reign? | 1300 BCE. | 26 | |
| 5716798931 | What was the language of Phoenicians? | Simplified alphabet, predecessor to Greek and Latin. | 27 | |
| 5716798932 | What nomadic group moved from Mesopotamia to Palestine? | Early Judaism followers. | 28 | |
| 5716798933 | What religion from 2000 BCE follows a monotheistic belief? | Judaism. | 29 | |
| 5716798934 | What religion had a "covenant" with God? | Judaism. | 30 | |
| 5716798935 | What did the ten commandments emphasize? | Living a moral life. | 31 | |
| 5716798936 | When did the Romans drive out Jewish settlers? | The Diaspora, 135 CE. | 32 | |
| 5716798937 | What is the Torah? | The law of God as revealed to Moses and recorded in the first give books of the Hebrew scriptures. | 33 | |
| 5716798938 | Origins of Jesus? | He was Jewish, born in Judea. | 34 | |
| 5716798939 | What did Jesus preach? | He preached the Kingdom of God at hand. | 35 | |
| 5716798940 | What is Christian teachings derived from? | Jewish teachings. | 36 | |
| 5716798941 | What did the Old Testament teach? | Equality of souls came before God, and emphasized eternal life. | 37 | |
| 5716798942 | According to the bible, who crucified Jesus? | Romans in 30 CE. | 38 | |
| 5716798943 | How was Christianity spread? | Apostle Paul. | 39 | |
| 5716798944 | Where was the Shang Dynasty? | Along the Huang He (Yellow) River in China. | 40 | |
| 5716798945 | What writing system was used during the Shang Dynasty (1500 BCE)? | Oracle bones, developed ideographic symbols, or pictograph writing. | 41 | |
| 5716798946 | True or False: The Zhou Dynasty was considered a "long lasting" dynasty. | True! | 42 | |
| 5716798947 | Where did the Zhou emperor received power from? | The Mandate of Heaven. | 43 | |
| 5716798948 | Where did the Zhou Dynasty expand to? | The Middle Kingdom, between the Huanghe and Yangtze rivers. | 44 | |
| 5716798949 | True or False: The Zhou dynasty had a strong central government. | False, the dynasty's government was not powerful. | 45 | |
| 5716798950 | Who was Confucius? | A philosopher who wanting to bring order to end warring states. | 46 | |
| 5716798951 | What did Confucianism entail for "order to warring states"? | 1. Ren (appropriate feelings) 2. Li (correct actions) 3. Filial piety (respect for parents, elders, need to know proper role and relationship to others) | 47 | |
| 5716798952 | What were five key Confucian relationships? | Ruler-subject, father-son, husband-wife, older brother-younger brother, friend-friend. | 48 | |
| 5716798953 | Who was the founder of Daoism (Taoism)? | Laozi, the founder of "School of Thought". | 49 | |
| 5716798954 | What was the main belief in Daoism? | Humans should coexist in harmony; a way of nature. | 50 | |
| 5716798955 | Which concept were Daoists taught? | Act by not acting -Wu Wei | 51 | |
| 5716798956 | Which of the following did Daoists believe in regards to war? a. War is the best method for harmony. b. War should never be used. c. Defensive tactics are important, shouldn't involve war. d. War can only be used for defensive purposes. | D! | 52 | |
| 5716798957 | Who was the first emperor of the Qin dynasty? | Shi Huangdi. | 53 | |
| 5716798958 | True or False: Shi Huangdi was known for being extremely brutal. | True. | 54 | |
| 5716798959 | What did Shi Huangdi help with in early Chinese civilization history? | He brought order after the Era of Warring States. | 55 | |
| 5716798960 | Which Chinese emperor started the Great Wall? | Shi Huangdi. | 56 | |
| 5716798961 | Which Chinese emperor built the Terracotta army? | Shi Huangdi. | 57 | |
| 5716798962 | Which Chinese emperor used Legalism to teach his people? | Shi Huangdi | 58 | |
| 5716798963 | What did Shi Huangdi enforce for a better society? | Strict laws, punishment to behave, strong central government, an absolute leader, and heavy taxes. | 59 | |
| 5716798964 | Which rule did the Han dynasty retain? | Imperial rule. | 60 | |
| 5716798965 | Which important Chinese emperor built roads and started civil service exams based on Confucianism? | Wu Di (Wu Ti). | 61 | |
| 5716798966 | Which dynasty started the flourish for the silk road? | The Han Dynasty. | 62 | |
| 5716798967 | True or False: the Han dynasty was a patriarchal society. | True. | 63 | |
| 5716798968 | What inventions were created during the Han dynasty? | Wheel barrow, watermills, rudder, compass, and paper. | 64 | |
| 5716798969 | When did Polynesian people reach Fiji and Samoa? | 1000 BCE. | 65 | |
| 5716798970 | How did Polynesian people reach Hawaii? | Outrigger canoes. | 66 | |
| 5716798971 | What did Polynesian people bring to Hawaii? | Pigs and a caste system ruled by local kings. | 67 | |
| 5716798972 | What was formed along the Indus river in 2500 BCE? | The River Valley civilization, which supported several large cities including Harrapa and Mohenjo Daro. | 68 | |
| 5716798973 | Were river valley civilizations monotheistic or polytheistic? | Polytheistic - belief in more than one God. | 69 | |
| 5716798974 | Where did Nomadic Aryan migrants enter from? | The north. | 70 | |
| 5716798975 | What did Nomadic Aryans bring to the North? | Hymns, songs, prayers (Vedas). | 71 | |
| 5716798976 | What language were Vedas written in? | Sanskirt. | 72 | |
| 5716798977 | What did the Vedas lead to? | A caste system. 1. Varnas ; Brahmins (priests and scholars) 2. Ksatriyas (rulers and warriors) 3. Vaisyas (merchants) 4. Shudras (servants) 5. The Untouchables. | 73 | |
| 5716798978 | True or False: Hinduism has a founder. | False, no known founder of Hinduism. | 74 | |
| 5716798979 | What do Hindus have to do? | Dharmas, or duties to perform in life. | 75 | |
| 5716798980 | What happens if Hindus perform their Dharma? | Good Karma, allows them to move up level of Samsara in next life because of reincarnation after death. | 76 | |
| 5716798981 | What is reincarnation? | The rebirth after death in Hindu religion. | 77 | |
| 5716798982 | What is the ultimate goal of Hinduism? | Moksha - oneness with the universe. |  | 78 |
| 5716798983 | What are some gods in the Hindu faith? | Brahma (creator) Vishnu (preserver) Shiva (destroyer) | 79 | |
| 5716798984 | Who was the founder of Buddhism? | Siddhartha Gautama. | 80 | |
| 5716798985 | What encouraged Siddhartha Guatama towards enlightenment? | The amount of suffering he saw in everyday life. | 81 | |
| 5716798986 | What are the four noble truths of Buddhism? | 1. All life is suffering. 2. Suffering is caused by desire. 3. There is always a way out of suffering. 4. The way out of suffering is to follow the 8 fold path and live in a righteous manner. | 82 | |
| 5716798987 | What's the goal of Buddhism? | Nirvana, similar to the ultimate goal of Hinduism which is Moksha. | 83 | |
| 5716798988 | True or False: Buddhism thrives on the cycle of rebirth. | False, Buddhism's goal is to reach Nirvana and not worry about the rebirth cycle. | 84 | |
| 5716798989 | What are some beliefs of Buddhism? | You don't need Gods and you will seek enlightenment on your own. | 85 | |
| 5716798990 | What is one thing Buddhism had about their believers that was different from other religions? | There was equality of all believers. | 86 | |
| 5716798991 | Who spread the message of Buddhism? | Missionaries. | 87 | |
| 5716798992 | After Buddha's death, how did the classes split? | Theravada (way of elders) Hinayana (lesser vehicle) Mahayana (greater vehicle) | 88 | |
| 5716798993 | Who founded the Mauryan Empire? | Chanragupta Maurya | 89 | |
| 5716798994 | What did Chanragupta Maurya end? What did he enforce? | A long period of decentralized rule. He enforced regional kingdoms. | 90 | |
| 5716798995 | Who was the most famous Mauryan ruler? | Ashoka, grandson of Chanragupta Maurya. | 91 | |
| 5716798996 | Which religion did Ashoka convert to, then later spread? | Buddhism. | 92 | |
| 5716798997 | What new found kings established the empire named after them? | The Guptas. | 93 | |
| 5716798998 | What did the Guptas do in their new empire? | Left local government intake and reestablished Hinduism. | 94 | |
| 5716798999 | What did the Mauryan and Gupta empires trade through the silk road? | Cotton and pepper. | 95 | |
| 5716799000 | What math systems did the Guptas use? | Algebra, pi, arabic numbers. | 96 | |
| 5716799001 | Who conquered both the Guptas and the Mauryans? | Nomads (white Huns). | 97 | |
| 5716799002 | What was Sub Saharian Africa made up of? | Mostly stateless cities. | 98 | |
| 5716799003 | What was the most important trade corridor on the Nile? | Nubia. | 99 | |
| 5716799004 | What empire battled Egyptians in the upper Nile? | Kush empire. | 100 | |
| 5716799005 | Which kingdom defeated Kush? | Kingdom of Axum, which eventually fell to Ethiopia. | 101 | |
| 5716799006 | What is Bantu? | An important language based group that emerged in the Niger River Basin, then migrated throughout Africa. | 102 | |
| 5716799007 | What were Greek city states called? | Polis. | 103 | |
| 5716799008 | What type of democracy was found in Athens? | A direct democracy. | 104 | |
| 5716799009 | Who had military rule in Greece (1000 BCE)? | Spartans. | 105 | |
| 5716799010 | Due to fighting together during the Persian war and winning, what was formed? | The Delian League, which was an alliance of Greek city-states led by Athens and formed in 478 BCE to liberate eastern Greek cities from Persian rule. | 106 | |
| 5716799011 | What war caused the Delian League to fight against each other? | Peloponnesian War. | 107 | |
| 5716799012 | Who was the king of Macedonia? | King Phillip II. | 108 | |
| 5716799013 | What did King Phillip II's son contribute to Macedonia? | His son, Alexander, set up empire, spread Greek culture (Hellenism), which was polytheistic. | 109 | |
| 5716799014 | What great philosophers emerged from Greece? | Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. | 110 | |
| 5716799015 | What famous Epic Poem author came from Greece? | Homer, wrote (spoke) the Illiad and the Odyssey. | 111 | |
| 5716799016 | What was the first American civilization? | Olmecs, or the "mother civilization" (1200 - 400 BCE) in Mesoamerica. | 112 | |
| 5716799017 | What was the next society in early American history? | Teotihuacan, near Mexico city. | 113 | |
| 5716799018 | Where did the Mayans establish their empire? | Yucatan peninsula. | 114 | |
| 5716799019 | Where did the Chavins establish? | Andes mountains. | 115 | |
| 5716799020 | What is a republic? | Government in which people elect representatives. | 116 | |
| 5716799021 | Which government changed from a monarchy to a republic? | Rome. | 117 | |
| 5716799022 | What is the name of the wealthy class that dominated Rome? | Patricians. | 118 | |
| 5716799023 | Who were the common people of Rome? | Plebeians. | 119 | |
| 5716799024 | How did Rome gain their position? | By winning the Punic Wars with Cartage. | 120 | |
| 5716799025 | Who lead the conquest of Gaul? | Julius Caesar. | 121 | |
| 5716799026 | Who was claimed as "dictator for life"? | Julius Caesar. | 122 | |
| 5716799027 | Who is Octavian? | The nephew of Julius Caesar who took over Roman rule, earning the title Augustus. | 123 | |
| 5716799028 | What laws did Augustus write? | Twelve Tables. | 124 | |
| 5716799029 | What culture did Rome derive during Augustus's rule? | Greek. | 125 | |
| 5716799030 | What was a great architectural achievement of Romans? | Their roadways. | 126 | |
| 5716799031 | What is the Edit of Milan? | Emperor Constantine's bill to grant legal status for Christians. | 127 | |
| 5716799032 | Due to the collapse of the Roman empire, which two directions did Christianity split into? | Roman Catholic (west_ and Eastern Orthodox. | 128 | |
| 5716799033 | What society did Islam spring from? | Bedouin (nomads) | 129 | |
| 5716799034 | What did the Kaaba's find important? | Idol worship. | 130 | |
| 5716799035 | What is the story of Muhammad? | A merchant who was 40 years old when he was visited by angel Gabriel. He received revelation that Allah was the only true God. He was God's messenger, and preached all equal before god. Said that you must face judgement (heaven or hell). | 131 | |
| 5716799036 | Where did Muhammad flee to? | Medina (Hijra). | 132 | |
| 5716799037 | True or False: Muhammad was the last in the long line of Jewish and Christian prophets. | True! | 133 | |
| 5716799038 | What did Muhammad do when he returned to Mecca? | He captured the city and after his death, his followers wrote down revelations in their holy book, the Quran. | 134 | |
| 5716799039 | What were some attributes of Islam? | It was a universal religion, open to all, appealed to the poor and women. | 135 | |
| 5716799040 | What are the five pillars of Islam? | 1. No God but Allah. 2. Pray 5 times, facing Mecca. 3. Give alms. 4. Fast during Ramadan. 5. Make pilgrimage to Mecca. | 136 | |
| 5716799041 | What happened after Mohammed's death? | There was a battle over the successor (caliph) and Sunni (most worthy) and Shiite (descendant of Ali) split. | 137 | |
| 5716799042 | What did the Sunni begin? | Umayyad Caliphate, moved their capital to Damascus, eventually extending their empire around the Mediterranean. | 138 | |
| 5716799043 | True or False: Jews and Christians (Dhimmi, people of the book) were tolerated as long as they paid taxes. | True! | 139 | |
| 5716799044 | What was the official language of the Muslim world? | Arabic! | 140 | |
| 5716799045 | Who followed the Umayyad Caliphate? | Abbasid Caliphate, moved their capital to Baghdad. | 141 | |
| 5716799046 | What were some highlights in Islamic culture? | Pottery, rugs, Algebra, The Thousand and One Nights, Ibn Battuta, and kept Greek ideas alive. | 142 | |
| 5716799047 | Who captured caliph in 1258 and took over? | The Mongols (Ilkhan, Hulegu). | 143 | |
| 5716799048 | Who reunified at the end of period under Islamic rule? | The Ottomans. | 144 | |
| 5716799049 | What was reunified after 350 year Era of Division? | The Sui Dynasty, under Wendi, which later became Yangdi. | 145 | |
| 5716799050 | What dynasty reestablished the exam system and the Silk Road? | Sui Dynasty. | 146 | |
| 5716799051 | Which dynasty built the Grand Canal? | Sui Dynasty. | 147 | |
| 5716799052 | Which dynasty expanded borders by setting up a tributary system? | Tang Dynasty. | 148 | |
| 5716799053 | What did the Tang Dynasty increase? | The silk industry and trade over the Silk Road and the Indian Ocean trade network. | 149 | |
| 5716799054 | Who is Empress Wu? | She supported and spread Buddhism after her anti Buddhist campaign and growth of Neo-Conficuanism. | 150 | |
| 5716799055 | Who was the famous Chinese poet during the Tang Dynasty? | Li Bou. | 151 | |
| 5716799056 | What was the Song Dynasty? | The most technologically advanced society of its time. | 152 | |
| 5716799057 | What was a difference between the Tang and Song dynasty? | The Song dynasty did not have as strong of a military as the Tang dynasty. | 153 | |
| 5716799058 | What did the Song dynasty develop? | Working compass, paper money, flying cash (credit), gunpowder, and block printing. | 154 | |
| 5716799059 | What is foot binding? | The compressing of the feet of girls with tight bandages (as formerly in China) so as to keep the feet from being over three or four inches long. | 155 | |
| 5716799060 | Who was a great rival of the Song Dynasty? | Neo-Confucianism. | 156 | |
| 5716799061 | What emperor's rule did the Mongols attack under? | Chingis Khan. | 157 | |
| 5716799062 | After Khan's death, who took over? | His grandson, Kublai Khan. | 158 | |
| 5716799063 | What became the official language of the Yuan dynasty? | Mandarin. | 159 | |
| 5716799064 | What religion did the Yuan dynasty adopt? | Buddhism. | 160 | |
| 5716799065 | What other achievements were completed by the Yuan dynasty? | They restarted trade, rebuilt China's roads, canals, and the Great Wall. | 161 | |
| 5716799066 | What explorer (has a game named after him) visited the Yuan dynasty? | Marco Polo. | 162 | |
| 5716799067 | After Kublai Khan's death, what lead to the Yuan dynasty overthrow? | Poor leadership and the bubonic plague. | 163 | |
| 5716799068 | Who was Zhu Yuanzhang? | A soldier who became Emperior Hongwu of the Ming Dynasty. | 164 | |
| 5716799069 | What did Emperior Hongwu revive? | Scholar-gentry: civil servants appointed by the emperor of China to perform day-to-day governance from the Han dynasty to the end of the Qing dynasty in 1912, China's last imperial dynasty. | 165 | |
| 5716799070 | How was did the army of the Ming dynasty? | Very strong, including their navy. | 166 | |
| 5716799071 | Who did the Ming dynasty send on long voyages to Africa? | Zheng He, where he traded porcelain. | 167 | |
| 5716799072 | What was the emperior of the Hein period considered? | Descendant from the Shinto God. | 168 | |
| 5716799073 | What was the Tale of Genji? | A story written by Lady Muraski, who wrote about the court life. | 169 | |
| 5716799074 | What war led to the medieval period in Japan? | Taira-Minamoto war. | 170 | |
| 5716799075 | What is a sho-gun? | A great general, that shared their power with the daimyo (warlords). | 171 | |
| 5716799076 | What are samurais? | The "one who serves", or Japanese warriors. | 172 | |
| 5716799077 | What was the code of Bushito? | A code that held that the true warrior must hold that loyalty, courage, veracity, compassion, and honor as important, above all else. | 173 | |
| 5716799078 | What was the new form of Buddhism? | Zen. | 174 | |
| 5716799079 | What kingdom allied with Tang? | The Silla Kingdom, in order to defeat Koguryo and Paekce kingdoms. | 175 | |
| 5716799080 | What part of Asia fell under Chinese influence? | Vietnam. | 176 | |
| 5716799081 | What's the Khmer civilization? | A civilization that emerged in Cambodia and Laos, the city of Angkor Wat. | 177 | |
| 5716799082 | What was Malacca? | An economic powerhouse in the Indian Ocean Sea trading network. | 178 | |
| 5716799083 | When did Polynesians reach New Zealand? | The 8th century, the Maori. | 179 | |
| 5716799084 | When did India disunite? | 600-1200. | 180 | |
| 5716799085 | What did Muslim invaders unite? | A large part to Establish Delhi Sultanate. | 181 | |
| 5716799086 | Who was Timur? | A Mongol warlord that conquered part of India, Middle East, and Russia. | 182 | |
| 5716799087 | What were the three zones of the Indian Ocean Trade Network and what did they trade at each post? | Arab - goods from Africa (ivory, timber, gold, slaves) to the Middle East - (textiles, carpets, glass, horses) The middle zone offered Indian gems, elephants, salt, cotton cloth, and cinnamon (Sri Lanka). The east had wood (Indonesia) and silk, porcelain, paper, (China), and silver (Japan). | 183 | |
| 5716799088 | In Africa, what was most common? | Stateless societies. | 184 | |
| 5716799089 | What were small community characteristics in Africa? | Hunting, gathering, metalwork, lineage that was sometimes matrilineal, animistic, and had oral tradition. | 185 | |
| 5716799090 | Who eventually fell to Muslim invaders? | Ghana. | 186 | |
| 5716799091 | Who were the most dedicated converts? | Berbers (desert nomads, jihad). | 187 | |
| 5716799092 | What became a strong Muslim empire along the Niger River? | Mali, which was founded by Sundiata. | 188 | |
| 5716799093 | Who was the most power ruler of Mali? | Mansa Musa, who went on a famous hajj spreading gold, also bringing back Muslim scholars and artisans to Timbuktu. | 189 | |
| 5716799094 | How was East Africa part of Indian Ocean Trading Network? | Through Swahili city states. | 190 | |
| 5716799095 | What did Central Africa have? | Great Zimbabwe, a city of 20,000 people. | 191 | |
| 5716799096 | Which empire centered around Constantinople? | The Byzantine Empire. | 192 | |
| 5716799097 | What was the center of Eastern orthodox church? | The Byzantine Empire. | 193 | |
| 5716799098 | Which missionaries spread religion? | Cyril and Methodius, who spoke Greek. | 194 | |
| 5716799099 | Who was Justinian? | The most famous Byzantine emperor, who issued a code based off the Roman 12 tables. | 195 | |
| 5716799100 | What were Justinian's achievements? | The Hagia Sophia and used Greek fire. | 196 | |
| 5716799101 | Who took the Byzantine land? | Seljuk Turks, that eventually lost it to the Ottoman Empire. | 197 | |
| 5716799102 | Who established Kiev Rus? | Danish Prince Rurik. | 198 | |
| 5716799103 | Who as Vladimir I? | A man who began a separate Russian Orthodox church, who was highly decentralized under Boyars (aristocrats). | 199 | |
| 5716799104 | Who was Yaroslav? | The last great Kievan prince, who established law codes. | 200 | |
| 5716799105 | Who were under Batu and the golden horde? | Mongols (Taters). | 201 | |
| 5716799106 | Who did the power shift to as Mongol's increased trade? | Moscow. | 202 | |
| 5716799107 | What battle defeated the Golden Horde? | The Battle of Kulikova in 1380. | 203 | |
| 5716799108 | Who followed the Mayans? | The Toltecs. | 204 | |
| 5716799109 | What was Tenochtitlan? | The chief city, that was built on a lake with little floating islands called chinampas to feed their people. | 205 | |
| 5716799110 | What was built for human sacrifice in Mesoamerica? | Pyramids. | 206 | |
| 5716799111 | Where did the Incas live? | Rugged terrain (Andes Mountains) | 207 | |
| 5716799112 | What were contributions from the Incas? | Built roads with way stations called tambos, terrace farming, irrigation, bred Llamas, large cities like Machu Picchu, used labor tribute system (mita). | 208 | |
| 5716799113 | True or False: The Incas had a written language. | False. | 209 | |
| 5716799114 | What are quipu? | Knotted strings the Incas used to record information. | 210 | |
| 5716799115 | When were the dark ages? | 50-1000. | 211 | |
| 5716799116 | Who awarded land (fiefs) to loyal vassals? | Monarchs and Lords (nobles). | 212 | |
| 5716799117 | What was manorialism? | Serfs worked the land and a portion had to be given to the lord in exchange for protection. | 213 | |
| 5716799118 | Who controlled learning in Western Europe? | Monks. | 214 | |
| 5716799119 | What Pope launched crusades to recapture the Holy Land? | Pope Urban II. | 215 | |
| 5716799120 | Who was Charles Martel? | A man who defeated Muslims in Spain and Portugual (Battle of Tours, 732) | 216 | |
| 5716799121 | Who was crowned the Holy Roman Emperor? | Charlemagne. | 217 | |
| 5716799122 | What was a trade later in Western Europe? | Urbanization. | 218 | |
| 5716799123 | What is the Renaissance? | A cultural rebirth in Western Europe that had an emphasis on humanism and classicism. | 219 | |
| 5716799124 | Who is Prince Henry? | The man who established of navigation school and sponsored voyages. | 220 | |
| 5716799125 | What was the Colombian Exchange? | A global trade network in America where goods, diseases, and culture was traded. | 221 | |
| 5716799126 | What did the Sultan Memed II lead? | The capture of Constantinople, which expanded after Mongols declined. | 222 | |
| 5716799127 | Who is Suleyman? | The most famous Sultan in the Middle East. | 223 | |
| 5716799128 | Who led troops in battle of Chaldiran? | Ismail, lost because he had no muskets for his army. | 224 | |
| 5716799129 | What did Abbas the Great contribute to the Safavid empire? | Gunpowder, built public work projects, mosques, and school. | 225 | |
| 5716799130 | What did European's establish in China? | trading ports, trading with silver. | 226 | |
| 5716799131 | What caused revolts in China? | Ming rulers being weak, famine, Manchus (;ed by Nurhaci) | 227 | |
| 5716799132 | In China, what did Canton have at their trade port? | Silk, porcelain, and tea. | 228 | |
| 5716799133 | Most famous ruler from East China? | Kangxi - skilled general and lawgiver. | 229 | |
| 5716799134 | Who gained influence in Japan? | European missionaries such as Francis Xavier. | 230 | |
| 5716799135 | Who reunified Japan after they went to chaos? | Tokugawa Ieyasu, who appointed himself shogun and moved capital to Edo. | 231 | |
| 5716799136 | In southeast Asia and Oceania, what were dominant religions? | Buddhism and Hinduism were dominant religions, with Islam import and in Indonesia and the southern part of the Philippines. | 232 | |
| 5716799137 | What happened to Indonesia's economic importance? | European's came and conquered what they could, traded elsewhere. | 233 | |
| 5716799138 | Who was Babur? | A mongol warlord who began the Mughal empire and led a multitude of invasions. | 234 | |
| 5716799139 | When did south asia reach its peak? | During the rule of Akbar, the grandson of Babur. | 235 | |
| 5716799140 | Who built the Taj Mahal? | Shah Jahan, in memory of his wife. | 236 | |
| 5716799141 | Who is Aurangzeb? | Akbar's great grandson, who was extremely intolerant of non-Muslim. | 237 | |
| 5716799142 | What happened in West Africa? | Portuguese pushed down the coast of west Africa and established forts and trading posts with African merchants. | 238 | |
| 5716799143 | What was El Mina? | The most important factory on the Gold coast. | 239 | |
| 5716799144 | What did Europeans do in Africa? | Changed character of slave trade form east (Arab, Female) to West (Atlantic, Male), working with local powerful kingdoms named Asante and Dahomey. | 240 | |
| 5716799145 | What did east africa trade? | Gold, ivory, and slaves. | 241 | |
| 5716799146 | Where was the Dutch East India company? | The cape of good hope, where Boers (Settlers) began to arrive. | 242 | |
| 5716799147 | What was done by Ivan the Great? What about Ivan the Terrible? | Helped end Mongol rule and free moscow. Ivan the terrible killed many boyars. | 243 | |
| 5716799148 | What happened with Spanish conquistadors? | They led invasion of Aztecs (Hernan Cortes) and Incas (Francisco Pizarro), and eventually created New Spain. | 244 | |
| 5716799149 | What happened to Native American Populations? | Many died due to diseases such as smallpox and measles and others died because of forced labor in gold and silver mines. | 245 | |
| 5716799150 | What's an encomienda? | A system that forced natives to work as slaves, which reduced their numbers and led to escalation of the Atlantic slave trade for workers. | 246 | |
| 5716799151 | How did the system for New Spain go? | 10 audiencias, peninsularies, creoles, then mestizos, mulattos, and zambos. The bottom had slaves as well. | 247 | |
| 5716799152 | Who were some explorers from Western Europe? | Christopher Columbus - sponsored by King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain. Ferdinand Magellan - goes around the world Vasco da Gama - reached India from Portugual | 248 | |
| 5716799153 | How did Renaissance affect the North? | It spread influence, such as intellectual thought, human reason, and accumulated in the Scientific revolution. | 249 |
AP World History: Chapter 12 (The Silk Road) Flashcards
| 3606475017 | Zhang Qian | sent by Han wudi to make allies, ends up being captured by the Xiongnu twice, but returns to Wudi with stories and the need for commerce and international trade in China | 0 | |
| 3606475018 | monsoon system | used to determine different sea routes to use throughout the year | 1 | |
| 3606475019 | Periplus maris erythraei | Red Sea, African coast, Indian Ocean ports | 2 | |
| 3606475020 | roads and bridges | built by the Romans, helped to create a world of trade | 3 | |
| 3606475021 | buffer zones | helped peace, protected two powerful countries' land from each other | 4 | |
| 3606475022 | long distance trade | cost decreases as volume increases | 5 | |
| 3606475023 | stabilized governments | no one wanted to trade in an unsafe region; stable governments were much more attractive to merchants and facilitated trade | 6 | |
| 3606475024 | Silk road range | Antioch to Chang'an | 7 | |
| 3606475025 | areas connected by the Silk road | Africa, Europe, Middle East, India, Indonesia, China | 8 | |
| 3606475026 | sea lanes | travel by sea not easy, man cannot swim, no boats seaworthy (except Chinese who did not engage heavily in trade) | 9 | |
| 3606475027 | Taklamakan desert | "land from which no one returns" | 10 | |
| 3606475028 | trade goods | wine, olive oil, art, pottery, jewelry, glass (only Romans made clear), cinnamon, cotton (India), nutmeg, jade, pearls, ivory | 11 | |
| 3606475029 | Buddhism | brought by foreign merchants and diffused among many cultures | 12 | |
| 3606475030 | Indian influence | raja = king, Indian relation | 13 | |
| 3606475031 | Hinduism | popular mainly only in India | 14 | |
| 3606475032 | Christianity | primarily in Mediterranean | 15 | |
| 3606475033 | Nestorians | emphasized the human quality of Christ | 16 | |
| 3606475034 | Mani | prophet orignally or Zoroastrian origins that founded Manichaeism | 17 | |
| 3606475035 | Manichaeism | syncretic blend of 3 religions: Christianity, Buddhism, Zoroastrianism; HATED by Zoroastrians | 18 | |
| 3606475036 | forms of plague | smallpox, measles, bubonic plague | 19 | |
| 3606475037 | Marcus Aurelius | killed by smallpox | 20 | |
| 3606475038 | epidemic weakened 2 empires | Han Dynasty and roman empire | 21 | |
| 3606475039 | Fall of the Han | crop shortage + disease, Yellow Turban Uprising, gone by 220 CE | 22 | |
| 3606475040 | sinicization, sino | Chinese | 23 | |
| 3606475041 | nomads assimilate | adopt Chinese settlements, marry Chinese, take Chinese names; ancestry between native and nomads becomes muddled | 24 | |
| 3606475042 | Confucian scholars | not very popular | 25 | |
| 3606475043 | Daoism | popular with the nomads | 26 | |
| 3606475044 | Fall of Rome | 476 CE, no single cause. internal problems: lack of money + disease. external problems: Attila the Hun. | 27 | |
| 3606475045 | barracks emperors | 26 of them, all assassinated by their own men except for 1. Horrible at leading, good at military | 28 | |
| 3606475046 | Diocletian | DIVIDES. splits rome into two and assigns 4 tetrarchs: his officials leading under him. tried to make reforms to administration and economy. | 29 | |
| 3606475047 | Constantine | CONSOLIDATES. Constantinople, unity, Christianity, promoted Edict of Milan. | 30 | |
| 3606475048 | The Huns | Attila attacking the Visigoths, Vandals and Franks; sent them all packing to Rome | 31 | |
| 3606475049 | Visigoths | people on the outskirts of Rome | 32 | |
| 3606475050 | Alaric | sacks rome in 410 CE, goes back on his word to maintain friendliness with the romans in exchange for safety from the Huns | 33 | |
| 3606475051 | Odovacer | in 476 CE, Rome falls to him and he defeats Romulus Augustus (14 yrs old) the last roman emperor | 34 | |
| 3606475052 | most influential thing to survive Rome | Christianity | 35 | |
| 3606475053 | Theodosius | made Christianity the official religion of the Roman empire | 36 | |
| 3606475054 | St. Augustine | the bishop of Hippo, instrumental in bringing Christianity to the people of the Mediterranean | 37 | |
| 3606475055 | Council of Nicaea | Jesus is both fully divine and fully human | 38 | |
| 3606475056 | Edict of Milan | practice of Christianity is ok | 39 | |
| 3606475057 | Byzantine empire | Eastern roman empire, Constantinople | 40 |
Flashcards
Medical Terminology Chapter 1-3 Flashcards
| 7300850548 | Cell Membrane | Structure surrounding and protecting the cell. It determines what enters and leaves the cell | 0 | |
| 7300850549 | Nucleus | Control center of the cell. It contains chromosomes and directs the activities of the cell. | 1 | |
| 7300850550 | Chromosomes | Rod-shaped structures in the nucleus that contain regions of DNA called genes. There are 46 (23 pairs) in every cell except for the egg and sperm cells which contain only 23 individual, unpaired chromosomes | 2 | |
| 7300850551 | Cytoplasm | All of the material that is outside the nucleus and yet contained within the cell membrane | 3 | |
| 7300850552 | Endoplasmic reticulum | Network of canals within the cytoplasm of the cell. Large proteins are made here from smaller protein pieces. | 4 | |
| 7300850553 | Mitochondria | Structures in the cytoplasm that provide the principal source of energy for the cell. Catabolism is the process that occurs here. | 5 | |
| 7300850554 | Anabolism | Process of building up large proteins from small protein pieces called amino acids. | 6 | |
| 7300850555 | Catabolism | Process whereby complex nutrients are broken down to simpler substances and energy is released. | 7 | |
| 7300850556 | DNA | Chemical found within each chromosome. Arranged like a sequence of recipes in code, it directs the activities of the cell. | 8 | |
| 7300850557 | Genes | Regions of DNA within each chromosome. | 9 | |
| 7300850558 | Karyotype | Picture of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell. The chromosomes are arranged in numerical order to determine their number and structure. | 10 | |
| 7300850559 | Metabolism | Total of the chemical processes in a cell. It includes catabolism and anabolism. | 11 | |
| 7300850560 | Digestive System | Mouth, pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, intestines (small and large), liver, gallbladder, pancreas. | 12 | |
| 7300850561 | Urinary or excretory System | Kidneys, ureters (tubes from the kidneys to the urinary bladder), Urinary bladder, urethra (tube from the bladder to the outside of the body). | 13 | |
| 7300850562 | Respiratory System | Nose, pharynx, larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchial tubes, lungs (where the exchange of gases takes place). | 14 | |
| 7300850563 | Reproductive System | Female: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus (womb), vagina, mammary glands Male: Testes and associated tubes, urethra, penis, prostate gland. | 15 | |
| 7300850564 | Endocrine System | Thyroid gland (in the neck), Pituitary gland (at the base of the brain), sex glands (ovaries and testes), adrenal glands, pancreas (islets of Langerhans), parathyroid glands | 16 | |
| 7300850565 | Nervous System | Brain, spinal cord, nerves, and collections of nerves | 17 | |
| 7300850566 | Circulatory System | Heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), lymphatic vessels and nodes, spleen, thymus gland | 18 | |
| 7300850567 | Musculoskeletal System | Muscles, bones, and joints | 19 | |
| 7300850568 | Skin and sense organs | Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous (oil) glands; eye, ear, nose, and tongue. | 20 | |
| 7300850569 | adipose tissue | Collection of fat cells. | 21 | |
| 7300850570 | Cartilage | Flexible connective tissue often attached to bones at joints. Cartilage forms part of the external ear and the nose. Rings of cartilage surround the trachea. | 22 | |
| 7300850571 | Epithelial cells | Skin cells that cover the outside of the body line the internal surfaces of organs | 23 | |
| 7300850572 | Histologist | Specialist in the study of tissues. | 24 | |
| 7300850573 | Larynx | Voice box; located at the upper of the trachea | 25 | |
| 7300850574 | Pharynx | Throat. Serves as the common passageway for food (from the mouth going to the esophagus) and air (going from the nose to the trachea). | 26 | |
| 7300850575 | Pituitary gland | Endocrine gland at the base of the brain. | 27 | |
| 7300850576 | Thyroid gland | Endocrine gland that surrounds the trachea in the neck. | 28 | |
| 7300850577 | Trachea | Windpipe (tube leading from the throat to the bronchial tubes). | 29 | |
| 7300850578 | Ureter | One of the two tubes, each leading from a single kidney to the urinary bladder | 30 | |
| 7300850579 | Urethra | Tube from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body | 31 | |
| 7300850580 | Uterus | Womb; the organ that holds the embryo/fetus as it develops | 32 | |
| 7300850581 | Viscera | Internal organs. | 33 | |
| 7300850582 | Muscle Cell | long and slender and contains fibers that aid in contracting and relaxing. | 34 | |
| 7300850583 | Epithelial Cell | (a lining and skin cell) may be square and flat to provide protection. | 35 | |
| 7300850584 | Nerve cell | may be long and have various fibrous extensions that aid in its job of carrying impulses. |  | 36 |
| 7300850585 | Fat Cell | Contains large, empty spaces for fat storage | 37 | |
| 7300850586 | Epithelial Tissue |  | 38 | |
| 7300850587 | Muscle Tissue |  | 39 | |
| 7300850588 | Connective Tissue (Fat) |  | 40 | |
| 7300850589 | Nerve Tissue |  | 41 | |
| 7300850590 | Cranial Cavity | Space in the head containing the brain & pituitary gland and surrounded by the skull. Cranial= pertaining to the skull | 42 | |
| 7300850591 | Plueral | Is a double folded membrane that surrounds the lungs and protects them. IF inflamed, the cavity may fill with fluid. | 43 | |
| 7300850592 | Thoracic Cavity | Space in chest containing Lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea, bronchial tubes, thymus gland, aorta (large artery). | 44 | |
| 7300850593 | Peritoneum | The double-folded membrane surrounding the abdominal cavity. It attaches the abdominal organs to abdominal muscles and surrounds each organ to hold it in place. | 45 | |
| 7300850594 | Mediastinum (part of thoracic cavity) | centrally located space outside of and between the lungs. | 46 | |
| 7300850595 | Abdominal Cavity | Space below the chest containing organs such as kidneys, stomach, small and large intestines, spleen, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. AKA Abdomen or peritoneal cavity. | 47 | |
| 7300850596 | Pelvic Cavity | Space below the abdomen containing portions of the small and large intestines, rectum, urinary bladder, urethra, and ureters; uterus and vagina in the female. | 48 | |
| 7300850597 | Diaphragm | A muscular wall that divides the abdominal and thoracic cavities. Moves up and down and aids in breathing. | 49 | |
| 7300850598 | Dorsal (posterior) | Pertaining to the back | 50 | |
| 7300850599 | Spinal Cavity | Space within the spinal column (backbones) containing the spinal cord. AKA spinal canal. | 51 | |
| 7300850600 | Pleural Cavity | Space between the pleural layers. | 52 | |
| 7300850601 | Ventral (anterior) | Pertaining to the front. | 53 | |
| 7300850602 | Cervical | Neck Region (C1 to C7) | 54 | |
| 7300850603 | Thoracic | Chest region. 12 Vertebrae (T1 to T12) | 55 | |
| 7300850604 | Lumbar | Loin (waist) or flank region. 5 vertebrae (L1 to L5) | 56 | |
| 7300850605 | Sacral | 5 Bones (S1 to S5) are fused to form one bone, the sacrum | 57 | |
| 7300850606 | Coccygeal | The coccyx (tailbone) is a small bone composed of four fused pieces | 58 | |
| 7300850607 | Hypochondriac | Right and left upper regions | 59 | |
| 7300850608 | epigastric | middle upper region | 60 | |
| 7300850609 | lumbar | right and left middle regions near the waist | 61 | |
| 7300850610 | umbilical | central region near the navel | 62 | |
| 7300850611 | inguinal | right and left lower regions | 63 | |
| 7300850612 | hypogastric | middle lower region | 64 | |
| 7300850613 | RUQ | Right Upper Quadrant | 65 | |
| 7300850614 | LUQ | Left upper quadrant | 66 | |
| 7300850615 | RLQ | Right Lower Quadrant | 67 | |
| 7300850616 | LLQ | Left Lower quadrant | 68 | |
| 7300850617 | Cervical (division of back) | Neck Region (C1-C7) | 69 | |
| 7300850618 | Thoracic (division of back) | Chest Region (T1-T12) | 70 | |
| 7300850619 | Lumbar (division of back) | Loin (waist) region (L1-L5) | 71 | |
| 7300850620 | Sacral (division of back) | Region of the sacrum (S1-S5) | 72 | |
| 7300850621 | Coccygeal (division of back) | Region of the coccyx (tailbone). Composed of 4 fused pieces | 73 | |
| 7300850622 | Vertebra | Single backbone | 74 | |
| 7300850623 | Vertebrae | backbones (plural) | 75 | |
| 7300850624 | Spinal Column | Bone tissue surrounding the spinal cavity | 76 | |
| 7300850625 | Spinal cord | Nervous tissue within the spinal cord | 77 | |
| 7300850626 | Disk (disc) | Pad of cartilage between vertebrae | 78 | |
| 7300850627 | Anterior (ventral) | Front side of the body. EX forehead | 79 | |
| 7300850628 | Posterior (dorsal) | Backside of the body | 80 | |
| 7300850629 | Deep | Away from the surface | 81 | |
| 7300850630 | Superficial | On the surface. EX _________ veins can be seen through skin. | 82 | |
| 7300850631 | Proximal | Near the point of attachment to the trunk or near the beginning of a structure | 83 | |
| 7300850632 | Distal | Far from the point of attachment to the trunk or far from the beginning of a structure | 84 | |
| 7300850633 | Inferior | Below another structure | 85 | |
| 7300850634 | Superior | Above another structure | 86 | |
| 7300850635 | Medial | Pertaining to the middle or nearer the medial plane of the body | 87 | |
| 7300850636 | Lateral | Pertaining to the side. EX when palms are facing outward the thumb is ______ | 88 | |
| 7300850637 | Supine | Laying on the back | 89 | |
| 7300850638 | Prone | Laying on the stomach | 90 | |
| 7300850639 | Frontal (coronal) Plane | Vertical Plane that divides anterior and posterior portions | 91 | |
| 7300850640 | Sagittal (lateral) Plane | Vertical Plane that divides body into left and right sides | 92 | |
| 7300850641 | Transverse (axial) Plane | Horizontal (cross-sectional) plane running across the body parallel to the ground | 93 | |
| 7300850642 | Abdomin/o | Abdomen | 94 | |
| 7300850643 | Adip/o | Fat | 95 | |
| 7300850644 | Anter/o | front | 96 | |
| 7300850645 | Cervic/o | Neck | 97 | |
| 7300850646 | Chondr/o | Cartilage (type of connective tissue) | 98 | |
| 7300850647 | Chrom/o | Color | 99 | |
| 7300850648 | Coccyg/o | Coccyx (tailbone) | 100 | |
| 7300850649 | Crani/o | Skull | 101 | |
| 7300850650 | Cyt/o | Cell | 102 | |
| 7300850651 | Dist/o | far, distant | 103 | |
| 7300850652 | Dors/o | Back portion of the body | 104 | |
| 7300850653 | Hist/o | Tissue | 105 | |
| 7300850654 | Ili/o | Ilium | 106 | |
| 7300850655 | Inguin/o | Groin | 107 | |
| 7300850656 | Kary/o | Nucleus | 108 | |
| 7300850657 | Later/o | Side | 109 | |
| 7300850658 | Lumb/o | Lower back | 110 | |
| 7300850659 | Medi/o | Middle | 111 | |
| 7300850660 | Nucle/o | Nucleus | 112 | |
| 7300850661 | Pelv/i | Pelvis | 113 | |
| 7300850662 | Poster/o | Back, behind | 114 | |
| 7300850663 | Proxim/o | Nearest | 115 | |
| 7300850664 | Sacr/o | Sacrum | 116 | |
| 7300850665 | Sarc/o | Flesh | 117 | |
| 7300850666 | Spin/o | Spine, backbone | 118 | |
| 7300850667 | Thel/o Theli/o | Nipple | 119 | |
| 7300850668 | Thorac/o | Chest | 120 | |
| 7300850669 | Trache/o | Trachea, windpipe | 121 | |
| 7300850670 | Umbilic/o | Navel, umbilicus | 122 | |
| 7300850671 | Ventr/o | Belly side of the body | 123 | |
| 7300850672 | Vertebro | Vertebra(e), backbone(s) | 124 | |
| 7300850673 | Viscer/o | Internal Organs | 125 | |
| 7300850674 | Ana- | up | 126 | |
| 7300850675 | Cata- | down | 127 | |
| 7300850676 | Epi- | Above | 128 | |
| 7300850677 | Hypo- | Below | 129 | |
| 7300850678 | Inter- | between | 130 | |
| 7300850679 | Inter- | within | 131 | |
| 7300850680 | Meta- | change | 132 | |
| 7300850681 | -eal -iac -ior | pertaining to | 133 | |
| 7300850682 | -ism | process, condition | 134 | |
| 7300850683 | -ose | pertaining to, full of | 135 | |
| 7300850684 | -plasm | formation | 136 | |
| 7300850685 | -somes | bodies | 137 | |
| 7300850686 | -type | picture, classification | 138 | |
| 7300850687 | aden/o | Gland. (ex adenoma: tumor of a gland) | 139 | |
| 7300850688 | arthr/o | joint. | 140 | |
| 7300850689 | bi/o | life | 141 | |
| 7300850690 | carcin/o | cancerous/cancer | 142 | |
| 7300850691 | cardi/o | heart | 143 | |
| 7300850692 | cephal/o | head | 144 | |
| 7300850693 | cerebr/o | cerebrum (largest part of the brain) | 145 | |
| 7300850694 | cis/o | to cut | 146 | |
| 7300850695 | crin/o | to secrete (to form and give off) | 147 | |
| 7300850696 | cyst/o | urinary bladder; a sac or a cyst (sac containing fluid) | 148 | |
| 7300850697 | cyt/o | cell | 149 | |
| 7300850698 | derm/o dermat/o | skin | 150 | |
| 7300850699 | electr/o | electricity | 151 | |
| 7300850700 | encephal/o | brain | 152 | |
| 7300850701 | enter/o | intestines (usually the small intestine) | 153 | |
| 7300850702 | erythr/o | red | 154 | |
| 7300850703 | gastr/o | stomach | 155 | |
| 7300850704 | glyc/o | sugar | 156 | |
| 7300850705 | gnos/o | knowledge | 157 | |
| 7300850706 | gynec/o | woman, female | 158 | |
| 7300850707 | hemat/o hem/o | blood | 159 | |
| 7300850708 | hepat/o | liver | 160 | |
| 7300850709 | iatr/o | treatment, physician | 161 | |
| 7300850710 | leuk/o | white | 162 | |
| 7300850711 | log/o | study of | 163 | |
| 7300850712 | nephr/o | kidney | 164 | |
| 7300850713 | neur/o | nerve | 165 | |
| 7300850714 | onc/o | tumor (cancerous) | 166 | |
| 7300850715 | ophthalm/o | eye | 167 | |
| 7300850716 | oste/o | bone | 168 | |
| 7300850717 | path/o | disease | 169 | |
| 7300850718 | ped/o | child | 170 | |
| 7300850719 | psych/o | mind | 171 | |
| 7300850720 | radi/o | x-rays | 172 | |
| 7300850721 | ren/o | kidney | 173 | |
| 7300850722 | rhin/o | nose | 174 | |
| 7300850723 | sarc/o | flesh | 175 | |
| 7300850724 | sect/o | to cut | 176 | |
| 7300850725 | thromb/o | clot, clotting | 177 | |
| 7300850726 | ur/o | urinary tract, urine | 178 | |
| 7300850727 | -ac -al -ic -ical | pertaining to | 179 | |
| 7300850728 | -algia | pain | 180 | |
| 7300850729 | -cyte | cell | 181 | |
| 7300850730 | ectomy | excision, removal | 182 | |
| 7300850731 | -emia | blood condition | 183 | |
| 7300850732 | -genic | pertaining to producing, produced by, or produced in | 184 | |
| 7300850733 | -globin | protein | 185 | |
| 7300850734 | -gram | record | 186 | |
| 7300850735 | -ion | process | 187 | |
| 7300850736 | -ist | specialist | 188 | |
| 7300850737 | -itis | inflammation | 189 | |
| 7300850738 | -logy | process of study | 190 | |
| 7300850739 | -oma | tumor, mass, swelling | 191 | |
| 7300850740 | -opsy | process of viewing | 192 | |
| 7300850741 | -osis | condition, usually abnormal (slight increase in numbers when used in blood cells) | 193 | |
| 7300850742 | -pathy | disease condition | 194 | |
| 7300850743 | -scope | instrument to visually examine | 195 | |
| 7300850744 | -scopy | the process of visually examining | 196 | |
| 7300850745 | -sis | state of; condition | 197 | |
| 7300850746 | -tomy | process of cutting, incision | 198 | |
| 7300850747 | -y | process, condition | 199 | |
| 7300850748 | a- an- | no, not, without | 200 | |
| 7300850749 | aut- auto- | self, own | 201 | |
| 7300850750 | dia- | complete, through | 202 | |
| 7300850751 | endo- | within | 203 | |
| 7300850752 | epi- | above, upon | 204 | |
| 7300850753 | ex- exo- | out, outside of, outward | 205 | |
| 7300850754 | hyper- | excessive, above, more than normal | 206 | |
| 7300850755 | hypo- | deficient, below, under, less than normal | 207 | |
| 7300850756 | in- | into, in | 208 | |
| 7300850757 | peri- | surrounding, around | 209 | |
| 7300850758 | pro- | before, forward | 210 | |
| 7300850759 | re- | back, backward, again | 211 | |
| 7300850760 | retro- | behind | 212 | |
| 7300850761 | sub- | below, under | 213 | |
| 7300850762 | trans- | across, through | 214 | |
| 7300853228 | 215 |
NHA Study Guide for Medical Assistant Flashcards
| 7206806716 | Chief Complaint (CC) | The reason why patient came to see the physician. | 0 | |
| 7206806717 | Dorsal Recumbent Position | Patient is on his/her back with knees flexed and soles of the feet flat on the bed. |  | 1 |
| 7206806718 | History of present illness (HPI) | An explanation of the chief complaint to determine the onset of the illness; associated symptoms; what the patient has done to threat the condition, etc | 2 | |
| 7206806719 | Horizontal Recumbent Position | Used for most physical examination. The patient lies on his/her back with legs extended. |  | 3 |
| 7206806720 | Fowler's Position | Used to promote drainage or to ease breathing. A setting or semi-setting position where the back of the examination tableis elevated to either 45 degrees (Semi-Fowler's) or 90 degrees (High- Fowler's) |  | 4 |
| 7206806721 | Dorsal Lithotomy Position | Used for examination of pelvic organs. Legsare well separated and thighs are acutely flexed. Feet usually placed in stirrups or bath blanket is placed crooswise over thighs and legs. |  | 5 |
| 7206806722 | Prone Position | Used to examine the spine and back. The patient lies on his/her abdomen with head turned to one side for comfort, the arms may ba above head or alongside the body. |  | 6 |
| 7206806723 | Sim's Position | Used for rectal examination. The patient is on his/her left side with right knee flexed against the abdomen and the left knee slightly flexed. |  | 7 |
| 7206806724 | Knee-chest Position | Used for rectal and vaginal examinations and as treatment to bring the uterus into normal position. On his/her knees with his/her chest resting on the bed and elbows resting on the bed or arms above head. |  | 8 |
| 7206806725 | Trendelenburg position | The patient is placed flat on the back, face up, the knees flexed and legs hanging off the end of the table, with the legs and feet supported by a footboard. |  | 9 |
| 7206806726 | Body processes necessary for life: | Body temperature Respiration Heart function | 10 | |
| 7206806727 | Vital signs of body function | Temperature Pulse Respiration Blood pressure | 11 | |
| 7206806728 | Rectal | Normal Range: 98.6F TO 100.6F | 12 | |
| 7206806729 | Oral | Normal Range: 97.6F to 99.6F | 13 | |
| 7206806730 | Axillary | Normal Range: 96.6F to 98.6F | 14 | |
| 7206806731 | Tympanic Membrane | Normal Range: 98.6F | 15 | |
| 7206806732 | Febrile | Presence of fever | 16 | |
| 7206806733 | Afebrile | Absence of fever | 17 | |
| 7206806734 | Intermittent (Fever) | Fluctuating fever that returns to or below baseline then rises again | 18 | |
| 7206806735 | Remittent (Fever) | Fluctuating fever that remains elevated; it does not return to baseline temperature | 19 | |
| 7206806736 | Continuous (Fever) | a fever that remains constant above the baseline; it does not fluctuate | 20 | |
| 7206806737 | Types of fever | Intermittent Remittent Continuous | 21 | |
| 7206806738 | Body Temperature | A balance between heat production and heat loss in conjunction with each other, maintained and regulated by the hypothalamus. | 22 | |
| 7206806739 | normal adult pulse rate | Between 60 to 100 beats per minute | 23 | |
| 7206806740 | normal respiration rate | Between 12 to 20 per minute | 24 | |
| 7206806741 | Apnea | A temporary complete absence of breathing which may be a result of reduction in the stimuli to the respiratory centers of the brain | 25 | |
| 7206806742 | Tachypnea | A respiration rate of greater than 40/min. It is transient in the newborn and maybe caused by the hysteria in the adult. | 26 | |
| 7206806743 | Bradypnea | decrease in numbers of respirations. This occurs during sleep. It may also be due to certain diseases. | 27 | |
| 7206806744 | Hypoventilation | State in which reduced amount of air enters the lungs resulting in decreased oxygen level and increased carbon dioxide level in blood. | 28 | |
| 7206806745 | Hyperventilation | state in which there is an increased amount of air entering the lungs | 29 | |
| 7206806746 | Hyperpnea | abnormal increase in the depth and rate of breathing | 30 | |
| 7206806747 | Cheyne-Stokes | A regular pattern of irregular breathing rate | 31 | |
| 7206806748 | Orthopnea | Difficulty or inability to breath unless in an upright position | 32 | |
| 7206806749 | Blood pressure | The measurement of the amount of force exerted by the blood on the peripheral arterial walls and is expressed in millimeters (mm) of mercury (Hg) | 33 | |
| 7206806750 | Systole | Highest reading in blood pressure | 34 | |
| 7206806751 | Diastole | Lowest reading in blood pressure | 35 | |
| 7206806752 | common errors when taking blood pressure | Improper cuff size The arm is not at heart level Cuff is not completely deflated before use Deflation of the cuff is faster that 2-3 mmHg per second The cuff is re-inflated during the procedure Improper cuff placement Defective equipment | 36 | |
| 7206806753 | Principles of physical examination | Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation | 37 | |
| 7206806754 | Inspection | provides an enormous amount of information | 38 | |
| 7206806755 | Palpation | The examiner uses the sense of touch to determine the characteristics of an organ system. | 39 | |
| 7206806756 | Percussion | Involves tapping or striking the body, usually with the fingers or small hammer to determine the position, size and density of the underlying organ or tissue | 40 | |
| 7206806757 | Auscultation | Involves listening to sounds produced by internal organs. It is usually done to evaluate the heart, lungs, and the abdomen. | 41 | |
| 7206806758 | Medical Assistant's role in the physical examination | Room preparation Patient preparation | 42 | |
| 7206806759 | Physician's sources of utilizing diagnosis | The patient's health history The physical examination Laboratory test | 43 | |
| 7206806760 | Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) | Responsible for the identification of the various hazards present in the workplace and for the creation of rules and regulation to minimize exposure to such hazards. | 44 | |
| 7206806761 | External Hemorrhage | Controlling the bleeding is most effectively accomplished by elevating the affect part above heart level and applying direct pressure to the wound. | 45 | |
| 7206806762 | Shock occurs | Insufficient return of blood flow to the heart, resulting in inadequate supply of oxygen to all organs and tissues of the body. | 46 | |
| 7206806763 | common symptoms of Shock | Pale, cold, clammy skin Rapid, weak pulse, Increased, shallow breathing rate | 47 | |
| 7206806764 | Shock's first aid | -Maintain an open airway -Call for assistance -Keep the victim lying down with the head lower than the rest of the body -Attempt to control bleeding or cause of shock (if known) -Keep the victim warm until help arrives | 48 | |
| 7206806765 | infection control | the transmission of infectious diseases will be prevented or stopped when any level in the chain is broken or interrupted. | 49 | |
| 7206806766 | Agents | Infectious microorganisms that can be classified into groups namely: viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites | 50 | |
| 7206806767 | Portal of exit | the method by which an infectious agent leaves its reservoir | 51 | |
| 7206806768 | Mode of transmission | specific ways in which microorganisms travel from the reservoir to the susceptible host | 52 | |
| 7206806769 | types of mode of transmission | Contact: direct and indirect Droplet Airborne Common vehicle Vectorborne | 53 | |
| 7206806770 | Portal of entry | Allows the infectious agent access to the susceptible host. | 54 | |
| 7206806771 | common portal of entry site | -Broken skin -Mucous membranes -Body system exposed to the external environmental such as respiratory, gastrointestinal and reproductive | 55 | |
| 7206806772 | methods limit the transmission of the infectious agents | -Sterile wound care -Transmission wound precaution -Aseptic technique | 56 | |
| 7206806773 | Susceptible host | The infectious agent enters a person who is not resistant or immune | 57 | |
| 7206806774 | Medical Asepsis | The destruction of pathogenic microorganism after they leave the body | 58 | |
| 7206806775 | methods of medical asepsis | Standard Precautions Transmission-Based Precautions | 59 | |
| 7206806776 | Disinfection | Procedure used in medical asepsis using various chemicals that can be used to destroy many pathogenic microorganisms. | 60 | |
| 7206806777 | What are the limitations when using boiling water (212 F) for disinfection in today's medical setting? | -will not be used in invasive procedures -will not be inserted into body orifices nor be used in a sterile procedure | 61 | |
| 7206806778 | methods of sterilization | -Gas sterilization -Dry Heat sterilization -Chemical sterilization -Steam sterilization | 62 | |
| 7206806779 | Gas sterilization | Often used for wheelchair and hospital beds. | 63 | |
| 7206806780 | Dry Heat sterilization | requires higher temperature that steam sterilization but longer exposure times. Used for instruments that easily corrodes | 64 | |
| 7206806781 | Chemical sterilization | Uses the same chemical used for chemical disinfection, but the exposure is longer | 65 | |
| 7206806782 | Steam sterilization (autoclave) | Uses steam under pressure to obtain high temperature of 250-254F with exposure times of 20-40 minutes defending on the item being sterilized | 66 | |
| 7206806783 | Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | -Masks -Goggles -Face shields -Respirator | 67 | |
| 7206806784 | Standard Precautions | An infection control method designed to prevent direct contact with blood and other body fluids and tissues by using barrier protection and work control practices. | 68 | |
| 7206806785 | Contact Precautions | Designed to reduce the risk of transmission of microorganisms by direct or indirect contact | 69 | |
| 7206806786 | direct-contact transmission | Involves skin-to-skin contact and physical transfer of microorganism to a susceptible host from an infected or colonized person. | 70 | |
| 7206806787 | Indirect-contact transmission | Involves contact with a contaminated intermediate object in the patient's environment | 71 | |
| 7206806788 | Airborne Precautions | Designed to reduce the risk of airborne transmission of infectious agents | 72 | |
| 7206806789 | Required to prevent airborne transmission | -Special air handling -Ventilation | 73 | |
| 7206806790 | Droplet precautions | Designed to reduce the risk of droplet transmission of infectious agent. | 74 | |
| 7206806791 | droplet transmission involves contact | with the conjunctivae or the mucous membranes of the nose or mouth of a susceptible person with large particle droplet generated from the source person primarily during coughing, sneezing or talking | 75 | |
| 7206806792 | PO | by mouth or orally | 76 | |
| 7206806793 | PR | per rectum or by way of the rectum | 77 | |
| 7206806794 | SL | sublingual (under the tongue) | 78 | |
| 7206806795 | IV | intravenous | 79 | |
| 7206806796 | IM | intramuscular (in the muscle) | 80 | |
| 7206806797 | SQ | short of the subcutaneous ( meaning under the skin) | 81 | |
| 7206806798 | qd | every day | 82 | |
| 7206806799 | bid | twice a day | 83 | |
| 7206806800 | tid | three times a day | 84 | |
| 7206806801 | qid | four times a day | 85 | |
| 7206806802 | pc | after meals or not on a empty stomach | 86 | |
| 7206806803 | qhs | each night | 87 | |
| 7206806804 | prn | as needed | 88 | |
| 7206806805 | Endocardium | the innermost layer of the heart | 89 | |
| 7206806806 | function of the endocardium | To prevent blood cells destruction and clotting | 90 | |
| 7206806807 | Myocardium | the middle and contractile layer of the heart | 91 | |
| 7206806808 | Heart skeleton | made up of four rings of thick connective tissues | 92 | |
| 7206806809 | Pericardium | the outermost layer of the heart | 93 | |
| 7206806810 | Four chambers of the heart | Right atria Left atria Right Ventricle Left Ventricle | 94 | |
| 7206806811 | Purpose of heart valves | To prevent backflow of blood thereby assuring uni-directional flow thru the heart | 95 | |
| 7206806812 | Characteristics of AV cusped valves | tough fibrous rings long and strong leaflets (cuspids) Accessory organs such as papillary muscles and chordae tendinae | 96 | |
| 7206806813 | Atrioventricular valves (AV) | located between the atria and ventricles | 97 | |
| 7206806814 | Tricuspid valve | located between the right atrium and the right ventricle | 98 | |
| 7206806815 | Bicuspids Mitral Valve | located between the left atrium and left ventricle | 99 | |
| 7206806816 | Pulmonic Valve | located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk | 100 | |
| 7206806817 | Aortic valve | located between the left ventricle and aorta | 101 | |
| 7206806818 | The first branches coming out of Aorta and supply the heart with oxygenated blood | The right and left coronary arteries | 102 | |
| 7206806819 | Two branches of the left coronary arteries | Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery Left Circumflex (LCX) artery | 103 | |
| 7206806820 | Systole | the period of contractions of both Arial and Ventricles | 104 | |
| 7206806821 | Diastole | The period of relaxation and filling of all cardiac chambers | 105 | |
| 7206806822 | heart sound causes | Closure of the heart valve | 106 | |
| 7206806823 | S1 first heart sound (Lubb) | occurs during ventricle contraction and the closure of AV valves | 107 | |
| 7206806824 | S2 second heart sound (Dupp) | occurs during ventricular relaxation when SL valves (Pulmonary and Aortic Valves) close. | 108 | |
| 7206806825 | heart murmur causes | By diseases of the valves or other structural abnormalities | 109 | |
| 7206806826 | Heart Rate | the number of heart contractions per minute | 110 | |
| 7206806827 | Normal heart rate | between 60 to 100 | 111 | |
| 7206806828 | the heart rate controls | Chemo-receptors(chemical sensors) Baro-receptors (pressure receptors) located in Aortic Arch and Carotid arteries | 112 | |
| 7206806829 | The heart is under the influence by the | Autonomic nervous system (ANS) | 113 | |
| 7206806830 | Autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into | Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Nervous System | 114 | |
| 7206806831 | Heart as a Pump | The blood volume ejected outside the heart is equal to the blood volume returning back into the heart | 115 | |
| 7206806832 | Stroke Volume (preload) | the blood volume ejected outside the ventricle after each contraction | 116 | |
| 7206806833 | The stroke volume depends on | -the volume of blood returning into the heart -the force of the myocardium contraction -Vascular resistance (after load) | 117 | |
| 7206806834 | Starling law | The greater the volume of the blood inside the heart during diastole, the stronger the heart contraction force during the systole | 118 | |
| 7206806835 | Cardiac Output | The amount of blood ejected outside the heart per minute | 119 | |
| 7206806836 | Peripheral Vascular Resistance | The force exerted against the blood flow and is determined by the diameter of the vessel | 120 | |
| 7206806837 | How many minutes do you need to wait when taking an oral temperature in patients who have just finished eating, drinking or smoking? | 30 minutes | 121 | |
| 7206806838 | Oral Temperature | the most common method of measuring the temperature | 122 | |
| 7206806839 | Oral temperature is not taken from the following patients: | -Infants and children less than six years old -Surgery, or facial, neck, nose or mouth injury -Receiving oxygen -with nasogastric tubes -with convulsive seizure -hemiplegic -with altered mental status | 123 | |
| 7206806840 | Rectal Temperature | Taken when oral temperature is not feasible | 124 | |
| 7206806841 | Rectal temperature is not taken from the following patients: | -with heart disease -with rectal disease or disorder or has had rectal surgery -with diarrhea | 125 | |
| 7206806842 | Apical Pulse | more accurate measurement of the heart and it is taken over the apex of the heart by auscultation using the stethoscope | 126 | |
| 7206806843 | Apical pulse is used | For patients with irregular heart rate and for infants and small children | 127 | |
| 7206806844 | counting respiration | It is counted for 30 seconds multiplied by two or for a full minute | 128 | |
| 7206806845 | Counts as one respiration | One inspiration (inhale) and one expiration (exhale) | 129 | |
| 7206806846 | Respiratory rhythm | Refers to the pattern of breathing. | 130 | |
| 7206806847 | Axillary Temperature | least accurate and it is taken only when no other temperature site can be used | 131 | |
| 7206806848 | Tympanic Temperature | useful for children and confused patients because of the speed of operation of the tympanic thermometer | 132 |
Human Anatomy Flashcards
| 8828354431 | human anatomy | The study of the structures that make up the human body and how those structures relate to each other | 0 | |
| 8828354432 | lateral | Farther from the medial plane (midline) | 1 | |
| 8828354433 | medial | Nearer to the medial plane (midline) | 2 | |
| 8828354434 | superficial | Nearer to the surface of the body | 3 | |
| 8828354435 | anterior (ventral) | Nearer to the front | 4 | |
| 8828354436 | posterior (dorsal) | Nearer to the back | 5 | |
| 8828354437 | superior | Nearer to the top of the head (transverse plane) | 6 | |
| 8828354438 | deep | Farther from the surface of the body | 7 | |
| 8828354439 | distal | Farther from the trunk | 8 | |
| 8828354440 | proximal | Nearer to the trunk | 9 | |
| 8828354441 | supine | Laying on your back | 10 | |
| 8828354442 | prone | Laying face down | 11 | |
| 8828354443 | inferior | Nearer to the feet | 12 | |
| 8828354444 | median plane (midsagittal plane) | A vertical plane that bisects the body into right and left halves | 13 | |
| 8828354445 | sagittal plane | Any plane parallel to the median plane | 14 | |
| 8828354446 | frontal plane (coronal plane) | Any vertical plane at the right angles to the median plane (separate anterior and posterior) | 15 | |
| 8828354447 | transverse plane (or horizontal plane) | Any plane at the right angle of both median and frontal plane (separate superior and inferior) | 16 | |
| 8828354448 | sagittal plane movement | Movement that are parallel to the sagittal plane (flexion and extension) | 17 | |
| 8828354449 | frontal plane movement | Movement that are parallel to the front planes (lateral/side-to-side movements) | 18 | |
| 8828354450 | transverse plane movements | Movement that are parallel to the transverse (horizontal) plane (twisting, rotation, etc.) | 19 | |
| 8828354451 | flexion | Reduces the angle between two bones at a joint | 20 | |
| 8828354452 | extension | Increases the angle between two bones at a joint | 21 | |
| 8828354453 | abduction | Movement away from the midline | 22 | |
| 8828354454 | adduction | Movement toward the midline | 23 | |
| 8828354455 | circumduction | A cone-shaped movement that does not include any rotation | 24 | |
| 8828354456 | rotation | The action of rotating around an axis or center. | 25 | |
| 8828354457 | medial (or internal) rotation | Rotational movement toward the midline | 26 | |
| 8828354458 | lateral (external) rotation | Rotational movement away from the midline | 27 | |
| 8828354459 | supination | When the palm is moved to face anteriorly | 28 | |
| 8828354460 | pronation | When the palm is moved to face posteriorly | 29 | |
| 8828354461 | inversion | When the sole of the foot is turned inward | 30 | |
| 8828354462 | eversion | When the sole of the foot is turned outward | 31 | |
| 8828354463 | dorsiflexion | Motion of bringing the top of the foot toward the shin, or movement of the ankle so that the dorsal surface of the foot moves superiorly | 32 | |
| 8828354464 | plantar flexion | Motion of bringing the top of the foot away from the shin, or movement of the ankle so that the dorsal surface of the foot move inferiorly | 33 | |
| 8828354465 | short bone | Type of bone shaped to serve as a good shock absorber (e.g., wrist bone) | 34 | |
| 8828354466 | long bone | Type of bone that has proximal and distal enlargements (e.g., femur) | 35 | |
| 8828354467 | flat bone | Type of bone that largely protects underlying organs and provides areas for muscle attachment (e.g., scapula) | 36 | |
| 8828354468 | irregular bone | Type of bone that performs a special function (e.g., vertebrae) | 37 | |
| 8828354469 | sesamoid bone | Type of bone shaped like a pea and found in tendons (e.g., patella) | 38 | |
| 8828354470 | porous | Bones that have a smaller proportion of calcium phosphate and carbonate, and greater non-mineralized tissue | 39 | |
| 8828354471 | cortical bone | Bone that has a low porosity, it is less flexible and can resist greater stress | 40 | |
| 8828354472 | spongy (cancellous) bone | Bone that has high porosity, a characteristic honeycomb structure and provides move flexibility. | 41 | |
| 8828354473 | axial skeleton | Composed of skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum | 42 | |
| 8828354474 | appendicular skeleton | Composed of pectoral, pelvic girdles, upper and lower limbs. | 43 | |
| 8828354475 | calvaria [skull] | Skullcap, upper part of the skull that covers the brain | 44 | |
| 8828354476 | face [skull] | Give it its individuality and provides protection for the eyes and air passages, as well as allow chewing. | 45 | |
| 8828354477 | parietal bone [calvaria] |  | 46 | |
| 8828354478 | temporal bone [calvaria] |  | 47 | |
| 8828354479 | occipital bone [calvaria] |  | 48 | |
| 8828354480 | sphenoid bone [calvaria] |  | 49 | |
| 8828354481 | epidural hemorrhage [calvaria] | Bleeding between the skull and the meninges, or protective covering of the brain. |  | 50 |
| 8828354482 | nasal bone [facial bones] |  | 51 | |
| 8828354483 | lacrimal bone [facial bones] |  | 52 | |
| 8828354484 | zygomatic bone [facial bones] |  | 53 | |
| 8828354485 | maxilla bone [facial bones] |  | 54 | |
| 8828354486 | mandible bone [facial bones] |  | 55 | |
| 8828354487 | cervical vertebrae [vertebral column] |  | 56 | |
| 8828354488 | atlas [vertebral column] | C1 |  | 57 |
| 8828354489 | axis [vertebral column] | C2 |  | 58 |
| 8828354490 | thoracic vertebrae [vertebral column] |  | 59 | |
| 8828354491 | lumbar vertebrae [vertebral column] |  | 60 | |
| 8828354492 | sacrum [vertebral column] |  | 61 | |
| 8828354493 | coccyx [vertebral column] |  | 62 | |
| 8828354494 | intervertebral discs [vertebral column] | Absorb shock effectively when the load on the column increases and allow the vertebrae to move without causing damage to other vertebrae. |  | 63 |
| 8828354495 | ribs [ribs & sternum] | 12 pairs of ribs, They are curved and slightly twisted, making them ideal to protect the chest area. |  | 64 |
| 8828354496 | true ribs [ribs & sternum] | Upper 7 pairs (1-7), attaching to both of the vertebrae and sternum |  | 65 |
| 8828354497 | false ribs [ribs & sternum] | The next 3 pairs (8-10), attaching to the sternum indirectly. |  | 66 |
| 8828354498 | floating ribs [ribs & sternum] | The attach only to the vertebrae column (11 & 12) |  | 67 |
| 8828354499 | sternum [ribs & sternum] | The midline breastbone. |  | 68 |
| 8828354500 | manubrium [ribs & sternum] |  | 69 | |
| 8828354501 | sternal body [ribs & sternum] |  | 70 | |
| 8828354502 | xiphoid process [ribs & sternum] |  | 71 | |
| 8828354503 | scapula [pectoral girdle] |  | 72 | |
| 8828354504 | clavicle [pectoral girdle] |  | 73 | |
| 8828354505 | humerus [upper limb] |  | 74 | |
| 8828354506 | radius [upper limb] |  | 75 | |
| 8828354507 | ulna [upper limb] |  | 76 | |
| 8828354508 | carpus [upper limb] | Wrist |  | 77 |
| 8828354509 | carpals [upper limb] | Bones of the wrist |  | 78 |
| 8828354510 | scaphoid [upper limb] |  | 79 | |
| 8828354511 | lunate [upper limb] |  | 80 | |
| 8828354512 | trapezium [upper limb] |  | 81 | |
| 8828354513 | trapezoid [upper limb] |  | 82 | |
| 8828354514 | capitate [upper limb] |  | 83 | |
| 8828354515 | hamate [upper limb] |  | 84 | |
| 8828354516 | SLTPTTCH - She Likes To Play, Try To Catch Her [upper limb] | Acronym, representing the carpals from lateral to medial. | 85 | |
| 8828354517 | metacarpal [upper limb] |  | 86 | |
| 8828354518 | phalanges [upper limb] | (phalanx = singular) |  | 87 |
| 8828354519 | os coxae [pelvic girdle] |  | 88 | |
| 8828354520 | acetabulum [pelvic girdle] | Lateral surface of the os coxae is a cup-shaped for the head of the femur. |  | 89 |
| 8828354521 | femur [lower limb] |  | 90 | |
| 8828354522 | patella [lower limb] |  | 91 | |
| 8828354523 | tibia [lower limb] |  | 92 | |
| 8828354524 | fibula [lower limb] |  | 93 | |
| 8828354525 | medial malleolus [lower limb] |  | 94 | |
| 8828354526 | lateral malleolus [lower limb] |  | 95 | |
| 8828354527 | tarsus [lower limb] |  | 96 | |
| 8828354528 | talus [lower limb] |  | 97 | |
| 8828354529 | calcaneus [lower limb] |  | 98 | |
| 8828354530 | navicular [lower limb] |  | 99 | |
| 8828354531 | cuboid [lower limb] |  | 100 | |
| 8828354532 | 1st (medial) cuneiform [lower limb] |  | 101 | |
| 8828354533 | 2nd (intermediate) cuneiform [lower limb] |  | 102 | |
| 8828354534 | 3rd (lateral) cuneiform [lower limb] |  | 103 | |
| 8828354535 | metatarsals [lower limb] |  | 104 | |
| 8828354536 | ligament | Connects bone to bone. |  | 105 |
| 8828354537 | fibrous [joint classification] | Fixed joints where there is no movement between the bones. | 106 | |
| 8828354538 | cartilaginous [joint classification] | Slightly movable joints allow a slight amount of movement. | 107 | |
| 8828354539 | synovial joints [joint classification] | Freely movable joints allow a wide range of movements. | 108 | |
| 8828354540 | hinge (ginglymus) joint | This type of joint has one articulating surface that is convex and another is concave. |  | 109 |
| 8828354541 | pivot joint | One bone rotates around one axis. |  | 110 |
| 8828354542 | condyloid joint | The joint surfaces are usually oval, as in the joint between your third metacarpal and proximal phalanx of your third digit. | 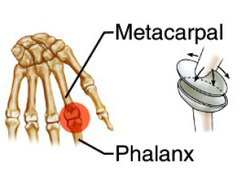 | 111 |
| 8828354543 | saddle joint | The bones are set together as in sitting on a horse. |  | 112 |
| 8828354544 | ball and socket joint | A rounded bone is fitted into a cup like receptacle. |  | 113 |
| 8828354545 | plane (gliding) joint | The joint permits gliding movement. |  | 114 |
| 8828354546 | synovial capsule | An envelope surrounding a synovial joint. | 115 | |
| 8828354547 | synovial membrane | A layer of connective tissue that lines the cavities of joints. It makes the synovial fluid. Secretes the lubrication fluid for the joint. | 116 | |
| 8828354548 | synovial cavity | Space between the bones that is filled with synovial fluid. | 117 | |
| 8828354549 | synovial fluid | Reduce the friction between the connecting cartilage at the joint during movement. Lubricate the joint. | 118 | |
| 8828354550 | Ligaments | Tissue that connects bone to bone. | 119 | |
| 8828354551 | extrinsic ligaments | Support the joint and connecting the articulating bones, outside of capsule and not connected to it. | 120 | |
| 8828354552 | articular discs | Another term for menisci (singular = meniscus), the fibrocartilage pads between opposing surfaces in a joint | 121 | |
| 8828354553 | intracapsular ligaments | Ligaments that prevent anterior/posterior displacement of the articular surfaces & secure bones when standing | 122 | |
| 8828354554 | cartilage | At the end of each bone, helps protect the bone from wearing each other down.Helps reduces friction during movement. | 123 | |
| 8828354555 | humeroradial joint | Between the capitulum of the humerus and the head of the radius | 124 | |
| 8828354556 | humeroulnar joint | Between the trochlea of the humerus and the olecranon process of the ulna | 125 | |
| 8828354557 | radioulnar joint | Between the radius and the ulna | 126 | |
| 8828354558 | Glenohumeral Joint | Is made up of SSIT (the Subscapularis, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, and the Teres minor muscles) that hold the head of the humerus firmly against the glenoid fossa of the scapula | 127 | |
| 8828354559 | radiocarpal joint | Between the radius and the carpals, location where the distal radius articulates with the proximal row of carpal bones | 128 | |
| 8828354560 | carpometacarpal joint | Articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones | 129 | |
| 8828354561 | metacarpophalangeal joint | Is the knuckle between the hand and the finger | 130 | |
| 8828354562 | interphalangeal joint | The hinge joints between the phalanges of the hand | 131 | |
| 8828354563 | iliofemoral (hip) joint | Between the head of the femur and the cup of the hip bone | 132 | |
| 8828354564 | knee (tibiofemoral) joint | 133 | ||
| 8828354565 | triquetral [upper limb] | 134 | ||
| 8828354566 | pisiform [upper limb] | 135 |
Medical Abbreviations Flashcards
| 7387691150 | before |  | 0 | |
| 7387691151 | ac | before meals | 1 | |
| 7387691152 | ad lib | as desired | 2 | |
| 7387691154 | amt | amount | 3 | |
| 7387691156 | bid | twice a day | 4 | |
| 7387691158 | with |  | 5 | |
| 7387691159 | C | Celsius | 6 | |
| 7387691160 | CC | chief complaint | 7 | |
| 7387691161 | cc | cubic centimeter | 8 | |
| 7387691162 | cm | centimeter | 9 | |
| 7387691163 | c/o | complains of | 10 | |
| 7387691164 | CT | computed tomography | 11 | |
| 7387691165 | d | day | 12 | |
| 7387691166 | dc/DC or D/C | discontinue | 13 | |
| 7387691167 | DOB | date of birth | 14 | |
| 7387691168 | Dx | diagnosis | 15 | |
| 7387691169 | ER | emergency room | 16 | |
| 7387691170 | ETA | estimated time of arrival | 17 | |
| 7387691171 | F | Fahrenheit | 18 | |
| 7387691173 | g or gm | gram | 19 | |
| 7387691174 | gtt or gtts | drop or drops | 20 | |
| 7387691175 | h | hour | 21 | |
| 7387691176 | Hg | mercury | 22 | |
| 7387691177 | water |  | 23 | |
| 7387691178 | hydrogen peroxide |  | 24 | |
| 7387691179 | H&P or HxPx | history and physical | 25 | |
| 7387691180 | Ht | height | 26 | |
| 7387691181 | Hx | history | 27 | |
| 7387691182 | ICU | intensive care unit | 28 | |
| 7387691183 | I&D | incision and drainage | 29 | |
| 7387691184 | IP | inpatient | 30 | |
| 7387691185 | K/K+ | potassium | 31 | |
| 7387691186 | kg | kilogram | 32 | |
| 7387691187 | left |  | 33 | |
| 7387691188 | L/l | liter | 34 | |
| 7387691189 | lb or # | pound | 35 | |
| 7387691190 | mg(m) | milligram | 36 | |
| 7387691191 | ml | milliliter | 37 | |
| 7387691192 | mm | millimeter | 38 | |
| 7387691193 | MRI | magnetic resonance imaging | 39 | |
| 7387691194 | Na/Na+ | sodium | 40 | |
| 7387691195 | N/A | not applicable | 41 | |
| 7387691196 | neg | negative | 42 | |
| 7387691197 | NKA | no known allergies | 43 | |
| 7387691198 | NKDA | no known drug allergies | 44 | |
| 7387691200 | OD | overdose | 45 | |
| 7387691202 | OP | outpatient | 46 | |
| 7387691203 | OR | operating room | 47 | |
| 7387691204 | OTC | over-the-counter | 48 | |
| 7387691206 | oz | ounce | 49 | |
| 7387691207 | after |  | 50 | |
| 7387691208 | PE | physical exam | 51 | |
| 7387691209 | per | by or through | 52 | |
| 7387691210 | PET | positron emission tomography | 53 | |
| 7387691212 | pm/PM | between noon and midnight | 54 | |
| 7387691213 | PRN/prn | as needed | 55 | |
| 7387691214 | Pt/pt | patient | 56 | |
| 7387691215 | q | every | 57 | |
| 7387691216 | qd | every day | 58 | |
| 7387691217 | qid | four times a day | 59 | |
| 7387691218 | right |  | 60 | |
| 7387691219 | r/o, R/O | rule out | 61 | |
| 7387691221 | Rx | "take" OR prescription | 62 | |
| 7387691222 | without |  | 63 | |
| 7387691223 | sig | instructions or directions | 64 | |
| 7387691224 | SO | standing order OR significant other | 65 | |
| 7387691226 | S&S | signs and symptoms | 66 | |
| 7387691227 | stat | immediately | 67 | |
| 7387691228 | T | temperature | 68 | |
| 7387691230 | tbsp | tablespoon | 69 | |
| 7387691231 | temp | temperature | 70 | |
| 7387691232 | tid | three times a day | 71 | |
| 7387691233 | TPR | temperature, pulse, and respiration | 72 | |
| 7387691234 | tsp | teaspoon | 73 | |
| 7387691235 | Tx | therapy or treatment | 74 | |
| 7387691237 | VS | vital signs | 75 | |
| 7387691239 | wk | week | 76 | |
| 7387691240 | WNL | within normal limits | 77 | |
| 7387691241 | Wt | weight | 78 | |
| 7387691242 | > | greater than | 79 | |
| 7387691243 | < | less than | 80 | |
| 7387691244 | + | positive | 81 | |
| 7387691245 | - | negative | 82 | |
| 7387691246 | ~ | approximately | 83 | |
| 7387691247 | % | percent | 84 | |
| 7387691248 | increase |  | 85 | |
| 7387691249 | decrease |  | 86 | |
| 7387691252 | change or changed |  | 87 | |
| 7387691253 | @ | at | 88 | |
| 7387691254 | degree |  | 89 | |
| 7387691255 | ♀ | female | 90 | |
| 7387691256 | ♂ | male | 91 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

