AP Language Rhetorical Strategies Flashcards
| 7480361264 | Anaphora | Repotition of the FIRST part of the sentense | 0 | |
| 7480361265 | Antithesis | Two contrasting ideas being contrasted in a sentece | 1 | |
| 7480361266 | Paradox | Statement that contradicts itself, ex: Don't go near the water unless you can swim. | 2 | |
| 7480361267 | Apophasis | Passive agressive ex: You didn't study for the quiz, but come on now. | 3 | |
| 7480361268 | Parallelism | Continuing an idea ex: I enjoy walking, running, and jogging. | 4 | |
| 7480361269 | Epistrophe | Repitition of words of phrases at the END of the sentence | 5 | |
| 7480634173 | Anadiplosis | Chain of phrases, Anger leads to hate, hate leads to, etc... | 6 |
AP World History Strayer Chapter 8 Vocabulary Flashcards
Unit Three Part Three
| 7926398137 | Sui Dynasty | A short dynasty between Han and Tang. |  | 0 |
| 7926398138 | Tang Dynasty | A dynasty often referred to as "China's Golden Age". (618 CE - 907 CE) | 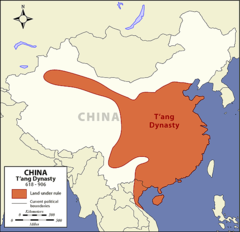 | 1 |
| 7926398139 | Song Dynasty | (960 CE - 1279 CE) Started by Tai Zu. |  | 2 |
| 7926398140 | Hangzhou | Capital of later Song Dynasty. |  | 3 |
| 7926398141 | Economic Revolution | Rapid population growth, economic speculation, increase in industrial production and innovations (Song dynasty). |  | 4 |
| 7926398142 | Foot Binding | Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet to make them smaller. |  | 5 |
| 7926398143 | Tribute System | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people that assumed subordination of all non-chinese authorities. They required all foreigners wanting access to China to pay tribute. |  | 6 |
| 7926398144 | Khitan/Jurchen People | Nomadic people who established a state that included parts of Northern China. |  | 7 |
| 7926398145 | Silla Dynasty (Korea) | First ruling dynasty to bring a measure of political unity to Korean Peninsula. |  | 8 |
| 7926398146 | Hangul | Phonetic alphabet in Korea (14th century). | 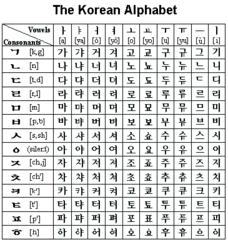 | 9 |
| 7926398147 | Shotoku Taishi | Japanese statesman who launched the drive to make Japan into centralized bureaucratic state modeled on China. |  | 10 |
| 7926398148 | Bushido | "Way of the Warrior". |  | 11 |
| 7926398149 | Chinese Buddhism | Entered China through cultural accommodations. |  | 12 |
| 7926398150 | Emperor Wendi | Sui Emperor who patronized Buddhism. |  | 13 |
| 7926398151 | Chu nom | The writing system of Vietnam |  | 14 |
| 7926398152 | Izumi Shikibu | Japanese poet who had an affair with the two sons of the emperor |  | 15 |
| 7926398153 | Xiongnu | A confederation of nomadic peoples living beyond the northwest frontier of ancient China. HAN Dynasty |  | 16 |
| 7926422271 | Gunpowder | An invention in the Tang and Song dynasty that changed history. |  | 17 |
AP World History, Chapter 22 Flashcards
| 9007797778 | Miguel Lopez de Legazpi | Conquested the Philippines | 0 | |
| 9007806368 | Mindanao | Where a large Muslim community resisted Spanish expansion | 1 | |
| 9007823090 | Manila | multicultural port city for silk | 2 | |
| 9007825888 | Spanish Policy | revolved around Christianity and trade in the Phillipines | 3 | |
| 9007850733 | Conquest of Java | policy founded by Jan Pieterzoon Coen | 4 | |
| 9007853776 | Dutch mariners | Did not focus on spreading Christianity; concentrated on spice trade | 5 | |
| 9007906820 | Monopoly profits from the spice trade | Not only enriched the VOC but also made the Netherlands the most prosperous land in Europe throughout most of the 17th century | 6 | |
| 9007913773 | VOC | Dutch/Indian compnany | 7 | |
| 9007931474 | European people | Built maritime empires | 8 | |
| 9007935348 | Russians | Layed the foundations for a vast land Russian interior | 9 | |
| 9007977461 | Frozen tundras and dense forests of Siberia | Posed formidable challenges | 10 | |
| 9008001626 | Mariners competed for... | trade in Asia and the Americas | 11 | |
| 9008049495 | Seven Years War | It involved every European great power of the time and spanned five continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, India, and the Philippines. The French and Indian War was the North American conflict in a larger imperial war between Great Britain and France known as the Seven Years' War. | 12 | |
| 9015815414 | Who won the Seven Years War | Britain | 13 | |
| 9015839283 | Commercial exchange flourished what? | The wake of the voyages of exploration as European merchants traveled to ports throughout the world in search of trade | 14 | |
| 9015928014 | The infectious/contagious disease hat killed most in the 16th century | Smallpox | 15 | |
| 9016017818 | The Colombian's exchange in food resulted in | Increase in human population | 16 | |
| 9016060333 | Grew well in North America | Wheat | 17 | |
| 9016075155 | Became popular in China because it grew in eco-niches unsuitable for rice and millet production | Maize | 18 | |
| 9016171486 | Manila Galleons | Early workings of global economy in the Pacific Ocean basin-Heavy armed ships | 19 | |
| 9016203810 | Demand for what was high in China | Silver | 20 | |
| 9016409179 | Vasco Da Gama | Planned to go to India by sailing around Africa through the India Ocean Expedition opened door to direct maritime trade between Europe and Asia | 21 | |
| 9016432258 | Projection in European Trade brought | shift in global balance of power | 22 | |
| 9016521194 | Magnetic compass and astrolabe | Important navigation equipment | 23 |
AP World History Chapter 20 Flashcards
| 5877170863 | Zheng He | Chinese Muslim admiral who commanded series of Indian Ocean, Persian Gulf, and Red Sea trade expeditions under third Ming emperor, Yunglo, between 1405 and 1455. | 0 | |
| 5877190136 | Castile | Along with Aragon, a regional kingdom of the Iberian peninsula; pressed reconquest of peninsula from Muslims; developed a vigorous military and religious agenda. | 1 | |
| 5877224909 | Aragon | Along with Castile, a religious kingdom of the Iberian peninsula; pressed reconquest of peninsula from Muslims; developed a vigorous military and religious agenda. | 2 | |
| 5877232397 | Vivaldis | Two Genoese brothers who attempted to find a Western route to the "Indies"; disappeared in 1291; precursors of thrust into southern Atlantic. | 3 | |
| 5877245852 | Renaissance | Cultural and political movement in western Europe; began in Italy c. 1400 rested on urban vitality and expanded commerce; featured a literature and art with distinctly more secular priorities than those of middle ages. | 4 | |
| 5877263498 | Henry the Navigator | Portuguese prince responsible for direction of series of expeditions along the African coast in the 15th century; marked beginning of western European expansion. | 5 |
AP World History Chapter 13 Flashcards
| 8868698259 | Distinguished empires of western europe from other empires | initiated by maritime expansion | 0 | |
| 8868698260 | region experienced the least racial mixing and was least willing to recognize the offspring of interracial unions | british north america | 1 | |
| 8868698261 | Reason that portugal, spain, france, and britain were the first to expand into the new world | these lands were on the atlantic coast and were closer to the americas | 2 | |
| 8868698262 | Some native americans aided the spanish in their initial invasion of the new world bc | to gain an advantage against their own enemies | 3 | |
| 8868698263 | The colonial economy of the spanish empire in former aztec and inca lands was | based on commercial agriculture and mining | 4 | |
| 8868698264 | Many native americans in mesoamerica and peru respond to spanish missionaries efforts to convert them to catholicism | they blended their old customs into catholic practices | 5 | |
| 8868698265 | Motivated europeans to venture across atlantic ocean | rivalries between competing european states | 6 | |
| 8868698266 | Describes slavery in latin america | Large scale importation of new slaves contributed into the 19th century | 7 | |
| 8868698267 | In contrast to the portuguese and spanish colonists in latin america, british colonists in north america | sought to escape rather than re create european traditions in the americas | 8 | |
| 8868698268 | Contributed to higher literacy rates in the british colonies in north america than in the spanish and portuguese colonies in latin america | Protestantism, which was practiced by most british colonists, encouraged reading the bible for oneself | 9 | |
| 8868698269 | Describes a feature of qing chinas policy toward its possessions in central asia | respect for the different cultures of the region | 10 | |
| 8868698270 | Chinese and russian expansion into central asia affected the nomadic ppl inhabiting the steppe lands by | they no longer enjoyed political independence and economic prosperity | 11 | |
| 8868698271 | The mughal ruler akbar favored policies that promoted | a cosmopolitan and hybrid indian persian turkic culture | 12 | |
| 8868698272 | A result of the ottoman empires policy toward the christian population in southwestern europe | christian communities enjoyed considerable autonomy over their own affairs | 13 | |
| 8868698273 | An outcome of the establishment of european empires in the america's | the emergence of an atlantic world connecting four continents | 14 | |
| 8868698274 | Contributed to the great dying in america's | native americas lack of immunity to european and african diseases | 15 | |
| 8868698275 | Intro of domesticated animals into the american made possible | Ranching economics | 16 | |
| 8868698276 | Silver from the mines of mexico and peru affected international commerce by | enabling europeans to buy chinese tea, silk, and porcelain | 17 | |
| 8868698277 | Example of the columbian exchange | Intro of corn and potatoes into the afro-eurasian diet | 18 | |
| 8868698278 | Policy reflects mercantilist thinking | Accumulating precious metals | 19 | |
| 8868698279 | Map 13.3. The addition of mongolia, xinjiang, and tibet to the chinese empire during the qing dynasty led to | creation of the court of colonial affairs | 20 | |
| 8868698280 | Dominated the agricultural economy in british north america | small scale independent farmers working their own land | 21 | |
| 8868698281 | Reason russian expanded beginning in 16th century | to secure its borders from attack | 22 | |
| 8868698282 | Describes what happened to the native populations of the steppes and siberia as a consequence of russian imperial expansion | assimilation | 23 | |
| 8868698283 | Empire did the process of expansion occurred at same time that a distinctive state was taking shape | the russian empire | 24 | |
| 8868698284 | Policy contributed to the growth of hindu opposition to mughal rule by the late 17th century | reinstatement of the jizya | 25 | |
| 8868698285 | Offered christian men a means of upward mobility within the ottoman empire | devshirme | 26 | |
| 8868698286 | Conflict between the islamic and christian worlds, event in 15th century signaled the islamic world held the upper hand | the ottoman conquest of constrantinopoe | 27 | |
| 8868698287 | Resulted from russia's westward expansion in 17th and 18th centuries | a program of westernization in russia | 28 | |
| 8868698288 | Map 13.1 in the textbook shows the Americas in which century? | 18th | 29 | |
| 8868698289 | In self portrait by the chinese emperor . Statement explains why kangxi changed the penalty for hu chien ching imposed by the board of punishment | sometimes people have to be persuaded into morality by the example of an execution | 30 | |
| 8868698290 | Mughal emperor jahangirs memoirs, he quotes his father akbar telling him that the class of whom we are speaking are usefully engaged, class of people discussed | hindus | 31 | |
| 8868698291 | A description of ottoman empire found in a letter written by the diplomat for austrian empire busbecq | honors, high posts, and judgeships are the rewards of the great ability and good service | 32 | |
| 8868698292 | Reflects how louis saw his role as king expressed in his memoirs | i would doubtless be capable of governing other empires just as the sun was capable of lighting up other worlds if they were exposed to its rays | 33 | |
| 8868698293 | Ruler emphasized the use of spectacle and public display to convey the impression of the exalted role of the monarch | louis xiv | 34 | |
| 8868698294 | 13.1, the flame or tongue of fire in the sky was viewed by the aztecs as a sign of | death | 35 | |
| 8868698295 | 13.2, the portrayal of moctezuma and cortes seared on european style chairs suggest me that the 2 men met | as equals | 36 | |
| 8868698296 | 13.3 protrays aztec | as victims | 37 | |
| 8868698297 | 13.4, the native americas depicted in the larger box on the left hand side represent | the tlaxcala | 38 | |
| 8868698298 | Notably absent in the depictions of the encounters between aztec and the spanish in visual sources | firearms | 39 |
Ap world history Flashcards
| 7238026537 | Hominids | Primates of a family | 0 | |
| 7238026909 | Homosapiens | Humans to think | 1 | |
| 7238026910 | Lucy | 3.2 mil year old female remains | 2 | |
| 7238027117 | Migration | Move one region to another | 3 | |
| 7238027466 | Paleolithic society | Human group of hunter gathers | 4 | |
| 7238027467 | Neolithic era | Development farmin and domestication | 5 | |
| 7238028266 | Specialization of labor | A certain job in a assembly line | 6 | |
| 7238031674 | Venus figurines | Statues of humans in stone | 7 |
AP World History chapter 3, 4 Flashcards
| 7396326962 | Terra Cotta Warriors |  | 0 | |
| 7396330818 | Trung Trac and Trung Nhi |  | 1 | |
| 7396332850 | Chinese painting depicting Buddha, Laozi, and Confucius |  | 2 | |
| 7396827587 | Who is who in the Chinese painting depicting Buddha, Laozi, and Confucius | Buddha is the baby, Laozi is crouched over on the left, and Confucius is the tall old man on the right | 3 | |
| 7396395617 | Vedas | the earliest known texts consisting of hymns poems and prayers that were the beginning of Hinduism, written in Sanskrit (the language of the elite) | 4 | |
| 7396479122 | Brahmins | priests who performed rituals often for a fee who were responsible for compiling the Vedas | 5 | |
| 7396482238 | Upanishads | second body of sacred texts by anonymous writers that came after many people became dissatisfied with the heavy fees of the Brahmins | 6 | |
| 7396504766 | Atman | the idea of the individual soul | 7 | |
| 7396511479 | Brahman | the world soul is the Brahman, atman made up the Brahman | 8 | |
| 7396517011 | Samsara | rebirth or reincarnation | 9 | |
| 7396520102 | Karma | your actions will be reflected in what you will come back as in reincarnation | 10 | |
| 7396526703 | Law of Manu | the idea that there was a divinely ordained social order or gender system, women were never to be independent and were always subordinate to men | 11 | |
| 7396539051 | Buddhism | founder is the Enlightened one, Buddha, he was original not seen as God like | 12 | |
| 7396541123 | Daoism | founder is Laozi, education was not important, encouraged withdrawal into nature | 13 | |
| 7396543602 | Legalism | harsh punishments, high rewards, Qin Shihuangdi | 14 | |
| 7396552903 | Confucius | analex became the body of thought, after Confucius died, emphasis on education for moral betterment, heaven was male, earth was female, high importance on family life, and strict patriarch | 15 | |
| 7396557152 | Hinduism | believed in samsara and karma, developed the caste system, believes in atman and brahman and the law of Manu, Vedas and Upanishads were the texts | 16 | |
| 7396561255 | Zoroastrianism | believed in Angra manu and Ayuha mazda, believed in savior and judgement day | 17 | |
| 7396564411 | Judaism | God was Yahweh, relationship was contractional, blessed if did good, punished if bad, strict loyalty | 18 | |
| 7396568204 | Greek rationalism | asking questions to make a point or prove something, Socrates critical of Athens and supported Sparta, got him killed | 19 | |
| 7396580893 | founder is the Enlightened One | Buddhism | 20 | |
| 7396588848 | The founder was not original not seen as God like | Buddhism | 21 | |
| 7396591522 | founder is Laozi | Daoism | 22 | |
| 7396601806 | education was not important | daoism | 23 | |
| 7396606138 | encouraged withdrawal into nature | Daoism | 24 | |
| 7396666318 | Harsh punishments, high rewards | Legalism | 25 | |
| 7396670876 | Used by Qin Shihuangdi | Legalism | 26 | |
| 7396677362 | The Analex became the body of thought, after the founder died | Confucius | 27 | |
| 7396686028 | emphasis on education for moral betterment | Confucius | 28 | |
| 7396690079 | heaven was male, earth was female | Confucius | 29 | |
| 7396693883 | high importance on family life | Confucius | 30 | |
| 7396696598 | a strict patriarch | Confucius | 31 | |
| 7396700279 | Believed in Samsara and karma | Hinduism | 32 | |
| 7396703632 | developed the caste system | Hinduism | 33 | |
| 7396712027 | believes in Atman and Brahman and the Law of Manu | Hinduism | 34 | |
| 7396717529 | Vedas and Upanishads were the texts for it | Hinduism | 35 | |
| 7396722966 | believed in Angra Manu and Ayuha Mazda | Zoroastrianism | 36 | |
| 7396730886 | believed in a savior and judgement day | Zoroastrianism | 37 | |
| 7396733509 | God was Yahweh | Judaism | 38 | |
| 7396740970 | relationship was contractional | Judaism | 39 | |
| 7396746587 | blessed if did good, punished if bad | Judaism | 40 | |
| 7396750879 | required strict loyalty | Judaism | 41 | |
| 7396754977 | asking questions to make a point | Greek rationalism | 42 | |
| 7396768411 | Socrates was critical of Athens and supported Sparta, this got him killed | Greek rationalism | 43 |
Flashcards
AP World History: Common World History Vocabulary Flashcards
| 10313139752 | Absolutism | The acceptance of or belief in absolute principles in political, philosophical, ethical, or theological matters. Unlimited power. Modern-day ex. Saudi Arab |  | 0 |
| 10313139753 | Agriculture | Cultivation of land and breeding of animals and plants to provide food, fiber, medicinal plants and other products to sustain and enhance life. Farming. Modern-day ex. Everywhere in the world. |  | 1 |
| 10313139754 | Aristocracy | Highest class in certain societies, especially those holding hereditary titles or offices. Kings/Queens, Government officials. Modern-day ex. Hindu caste system Brahmins |  | 2 |
| 10313140261 | BCE | Before Common Era. Before Christ/Jesus. Modern-day ex. None |  | 3 |
| 10313140262 | CE | Common Era. After Christ/Jesus was born. Modern-day ex. None |  | 4 |
| 10313140263 | Bias | Disproportionate weight in favor of or against one thing, person, or group compared with another, usually in a way considered to be unfair. A particular preference or point of view that is personal, rather than scientific. Modern-day ex. Politics |  | 5 |
| 10313140941 | Bureaucracy | A system of government in which most of the important decisions are made by state officials rather than by elected representatives. Non-elected officials. Modern-day ex. Department of Labor United States of American and U.S. Department of Homeland Security. |  | 6 |
| 10313140942 | Capitalism | An economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state. Trade. Modern-day ex. China |  | 7 |
| 10313140943 | Chiefdom | A form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. The political/class structure used in Misissippian societies. Modern-day ex. None |  | 8 |
| 10313141748 | City-State | A city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state. A city that governs itself and surrounding areas. Modern-day ex. Monaco, Monaco |  | 9 |
| 10313141749 | Civilization | The stage of human social development and organization that is considered most advanced. Organized society. Modern-day ex. United States |  | 10 |
| 10313141750 | Classical Era | the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th or 6th century AD centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome. 500 BC-AD 600 Greek. Modern-day ex. None |  | 11 |
| 10313141751 | Codify | The process of collecting and restating the law of a jurisdiction in certain areas, usually by subject, forming a legal code. Arrange and set down in writing. Modern-day ex. Code of laws. |  | 12 |
| 10313142515 | Colonization | The action or process of settling among and establishing control over the indigenous people of an area. Imperialism. Modern-day ex. None |  | 13 |
| 10313142516 | Commercial | Relating to, or characteristic of commerce. engaged in commerce. prepared, done, or acting with sole or chief emphasis on profit, or success. Buying/Selling goods. Modern-day ex. Imports/Exports |  | 14 |
| 10313143150 | Contemporary Era | (1950-present) post World War II, scrutinized moral and political dilemmas that society offers. Era were living in. Modern-day ex. Era were in. |  | 15 |
| 10313143151 | Contextualization | Historical thinking skill that involves the ability to connect historical events and processes to specific circumstances of time and place as well as broader regional, national, or global processes. Elaborating. Modern-day ex. None |  | 16 |
| 10313143655 | Corroboration | Evidence that confirms or supports a statement, theory, or finding. Confirmation. Modern-day ex. Evidence |  | 17 |
| 10313143656 | Demography | The study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which illustrate the changing structure of human populations. Study of human population. Modern-day ex. How many people are born/die each day. |  | 18 |
| 10313143657 | Dynasty | A line of hereditary rulers of a country. Ruling family. Modern-day ex. Qing (Ch'ing) Dynasty. |  | 19 |
| 10313144298 | Early Modern Era | Early modern European history is usually seen to span from the start of the 15th century, through the Age of Enlightenment in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century. 1500-1800. Modern-day ex. None |  | 20 |
| 10313144299 | Empire | A group of states or territories controlled by one ruler. A country with many territories around the world. Modern-day ex. United States. |  | 21 |
| 10313144300 | Ethnocentrism | Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group. Believe that your better than the rest. Modern-day ex. Politics in the United State |  | 22 |
| 10313144673 | Epidemic | A widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time. In a certain area (NOT WORLD WIDE). Modern-day ex. Diseases in certain parts of the world. |  | 23 |
| 10313144674 | Forager | People who support themselves by hunting wild animals and gathering wild edible plants and insects. Wander in search of food/water. Modern-day ex. People living in Alaska |  | 24 |
| 10313144675 | Globalization | The process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale. Growth to a global or worldwide scale. Modern-day ex. McDonald's |  | 25 |
| 10313145142 | Hierarchy | A system or organization in which people or groups are ranked one above the other according to status or authority. A group organized by rank. Modern-day ex. Caste system. |  | 26 |
| 10313145143 | Imperialism | A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force. Expand territory for resources. Modern-day ex. Afghanistan, Iraq and Iran. |  | 27 |
| 10313145902 | Indentured Servant | A person under contract to work for another person for a definite period of time, usually without pay but in exchange for free passage to a new country. Work for free for passage way to America. Modern-day ex. None |  | 28 |
| 10313146481 | Interregional | Relating to or occurring between different regions. Occur regionally not locally. Modern-day ex. Trading |  | 29 |
| 10313146482 | Kingdom | A country, state, or territory ruled by a king or queen. Territory controlled by a King or Queen. Modern-day ex. Swaziland, Saudi Arabia, and Brunei. |  | 30 |
| 10313146483 | Merchant | A person who buys and sells commodities for profit. Trades for profit. Modern-day ex. Pawn shops |  | 31 |
| 10313146484 | Modern Era | 1600 - Present Day. Renaissance to present. Modern-day ex. 21st Century |  | 32 |
| 10313147235 | Monotheism | The doctrine or belief that there is only one God. Belief in one God. Modern-day ex. Christianity |  | 33 |
| 10313147236 | Nation | A large aggregate of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular country or territory. Large amount of people living together because of a common cause. Modern-day ex. United States |  | 34 |
| 10313147237 | Neolithic | Relating to or denoting the later part of the Stone Age, when ground or polished stone weapons and implements prevailed. Stone Age. Modern-day ex. None |  | 35 |
| 10313147238 | Nobility | The quality of being noble in character, mind, birth, or rank. High/Upper Class. Modern-day ex. England |  | 36 |
| 10313147239 | Nomad | A member of a people having no permanent abode, and who travel from place to place to find fresh pasture for their livestock. Hunters. Modern-day ex. People who live in Alaska |  | 37 |
| 10313148084 | Pandemic | Disease prevalent over a whole country or the world. Whole world effected. Modern-day ex. HIV/AIDS |  | 38 |
| 10313148085 | Papacy | The office or authority of the Pope. Pope is leader. Modern-day ex. Pope Francis |  | 39 |
| 10313148086 | Pastoral | Farms used for or related to the keeping or grazing of sheep or cattle. Ranch. Modern-day ex. Ranch's in the US |  | 40 |
| 10313149092 | Patiarchal | Relating to or characteristic of a system of society or government controlled by men. Men have primary power. Modern-day ex. Iran |  | 41 |
| 10313149093 | Periodization | Process or study of categorizing the past into discrete, quantified named blocks of time in order to facilitate the study and analysis of history. Creating subjects based on similarity. Modern-day ex. Periodic table |  | 42 |
| 10313149094 | Polytheism | The belief in or worship of more than one god. More than one God. Modern-day ex. Buddhism |  | 43 |
| 10313150098 | Post-Classical Era | Crusades, Beginning of Renaissance. 600-1450. Modern-day ex. None |  | 44 |
| 10313150099 | Post-Modern Era | Broad movement that developed in the mid- to late-20th century across philosophy, the arts, architecture, and criticism and that marked a departure from modernism. 20th Century movement in the 21st century arts. Modern-day ex. 2000-2018 |  | 45 |
| 10313150100 | Prehistoric | Relating to or denoting the period before written records. Before written records. Modern-day ex. Dinosaur fossils |  | 46 |
| 10313150633 | Revolution | A forcible overthrow of a government or social order in favor of a new system. Overthrowing the government. Modern-day ex. American Revolution |  | 47 |
| 10313150634 | Rural | In, relating to, or characteristic of the countryside rather than the town. Farmland/Far away from the city. Modern-day ex. Some places in Asia. |  | 48 |
| 10313150635 | Scribe | A person who copies out documents, especially one employed to do this before printing was invented. Writes down information. Modern-day ex. Journalist |  | 49 |
| 10313151561 | Sedentary Agriculture | Practiced in one place by a settled farmer in which fields are not rotated. Not rotating crops. Modern-day ex. Wheat-sheep farming in Australia |  | 50 |
| 10313151562 | Serf | An agricultural laborer bound under the feudal system to work on his lord's estate. Work on the land in return for protection. Modern-day ex. None |  | 51 |
| 10313151563 | Slave | A person who is the legal property of another and is forced to obey them. People treated like property forced to work for their owner. Modern-day ex. None |  | 52 |
| 10313151564 | Socialism | A political and economic theory of social organization that advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the community as a whole. Political and economic organizations are run by the government. Modern-day ex. India |  | 53 |
| 10313152755 | State (not the US states) | A nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government. Land under control of an organized society. Modern-day ex. Germany |  | 54 |
| 10313152756 | Stateless society | a society that is not governed by a state, or, especially in common American English, has no government. No set of laws. Modern-day ex. Kwakiutl |  | 55 |
| 10313152757 | Syncretism | The amalgamation or attempted amalgamation of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought. Modern-day ex. Gnosticism | 56 | |
| 10313152758 | Synthesis | The combination of ideas to form a theory or system. Combined ideas. Modern-day ex. Synthesis | 57 | |
| 10313153301 | Steppes | A large area of flat unforested grassland in southeastern Europe or Siberia. Plains area. Modern-day ex. Steppes | 58 | |
| 10313160881 | Urban | In, relating to, or characteristic of a city or town. Towns or cities. Modern-day ex. Davidson | 59 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

