| 8234525231 | analogous | partially similar or parallel | | 0 |
| 8234525232 | duty | tax on imported goods | | 1 |
| 8234525233 | emulate | to imitate or surpass someone | | 2 |
| 8234525234 | piety | religious devotion | | 3 |
| 8234525235 | stagnate | showing no activity; dull or sluggish | | 4 |
| 8234525236 | steppe | a level, grassy, unforested plain, especially in southeastern europe or siberia | | 5 |
| 8234525237 | primogeniture | the right of succession belonging to the first born, especially the feudal rule by which the whole estate passes to the eldest son | | 6 |
| 8234525238 | divine right of kings | the god given right to rule | | 7 |
| 8234525239 | Why is money better than the barter system? | Constant prices and more stable economy | | 8 |
| 8234525240 | Nobles in Feudal Europe | Granted some power in exchange for military service and loyalty to the king | | 9 |
| 8234525241 | Feudal Hierarchy - Japan | Shogun
Daimyo
Samurai
Peasants | | 10 |
| 8234525242 | What was the appeal of the Crusades? | Empire and wealth | | 11 |
| 8234525243 | What did the Crusades lead to? | Interaction between Muslims and West European Christians (culture mixing)
Western Europe rediscovered aspects of the ancient past which was being preserved by Byzantine and Islamic Empires | | 12 |
| 8234525244 | Stuff that caused 600 BCE trade routes | -expansion of Empires
-changes in transportation (caravaans, ships)
-technology, navigation, mapmaking, tools
-geographic features
-diffusion | | 13 |
| 8234525245 | Tang Dynasty | Imperial dynasty of China from 618 to 907; noted for its openness to foreign cultural influences. "China's Golden Age" | | 14 |
| 8234525246 | Song Dynasty | Imperial dynasty of China from 960 to 1279; noted for art and literature and philosophical acheivements | | 15 |
| 8234525247 | Abbasid Dynasty | The "golden age" of the Muslim Empire; capital in Baghdad; trading and learning; replaced Umayyads, and were replaced by the Mongols | | 16 |
| 8234525248 | Sunni | ruler should be elected from the people. agree with umayyads | | 17 |
| 8234525249 | Shi'a | rule by bloodline. (mohammed's son in law, ali) disagreed with umayyads | | 18 |
| 8234525250 | Umayyad Dynasty | Capital in Damascus; expanded empire to greatest size; spread Islam and Arabic. Conquered by the Abbasids | | 19 |
| 8234525252 | Byzantine Empire | Society that developed in the eastern Roman Empire after the fall of the western Roman Empire | | 20 |
| 8234525253 | Mansa Musa | Mali ruler who created a large kingdom with capital at Timbuktu and adopted Islam. Known for his extravagant pilgrimage to Mecca | | 21 |
| 8234525254 | Samurai | Class of warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble in return for land. | | 22 |
| 8234525255 | What did the followers of Islam believe? | Muslims believed that Allah (God) transmitted his words to the faithful through Muhammad | | 23 |
| 8234525259 | Five Pillars of Islam | Confession of faith; prayer five times a day; charity to the needy; fasting during the holy month of Ramadan; pilgrimage to Mecca at least once during one's lifetime (hajj) | | 24 |
| 8234525260 | Split of Islam | The split occurred over a disagreement over who should succeed Muhammad as the leader of the faith | | 25 |
| 8234525263 | Abu Bakr | When Muhammed died in 632, Abu Bakr became Caliph | | 26 |
| 8234525264 | Caliph | The head of state, military commander, chief judge, and religious leader | | 27 |
| 8234525265 | Caliphate | Theocratic Islamic Empire ruled by Abu Bakr | | 28 |
| 8234525266 | Which dynasty enlarged the Islamic Empire? | The Umayyed Dynasty | | 29 |
| 8234525267 | Effects of the Umayyed Dynasty | Arabic became the official language; gold and silver coins became the standard monetary unit; conquered subjects were "encouraged" to convert | | 30 |
| 8234525268 | Where did the Umayyed Dynasty spread Islam to? | North Africa and Spain | | 31 |
| 8234525269 | Which dynasty was the Umayyed Dynasty replaced by? | Abbasid Dynasty around 750 in all areas except Spain | | 32 |
| 8234525270 | What trade item did merchants introduce to the Islamic Empire? | Credit; freed them of the burden-and danger- of carrying coins; they also developed a system of itemized receipts and bills | | 33 |
| 8234525271 | The Vikings | Merchants and fishermen and developed some of the earliest commercial fisheries in northern Europe | | 34 |
| 8234525272 | What was an effect of Viking fisheries and raids? | Led to settlements as diverse as new found land in Canada around 1000 CE, inland Russia, and northern France | | 35 |
| 8234525273 | William (Viking) | French viking who conquered Anglo-Saxon England in 1066 | | 36 |
| 8234525274 | Advancements during the Tang and Song dynasties in China | Art, architecture, science, philosophy, porcelain, silk weaving, construction of transportation systems | | 37 |
| 8234525275 | Main reason for stability during the Tang and Song dynasties | The bureaucratic system that was based on merit through the use of the civil service examinations | | 38 |
| 8234525276 | Civil Service exam during the Tang and Song dynasties | The Tang and Song rulers continued to modify the exam, but kept it focused on Confucian principles, which created a large core of educated, talented, and loyal government workers | | 39 |
| 8234525277 | Business Practices in Tang and Song China | Introduction of paper money and letters of credit, which led to increased trade and cultural diffusion | | 40 |
| 8234525278 | Effect of moveable-type printing | Resulted in an increase of literacy in bureaucrats from the lower classes; printed books also spread agricultural and technological knowledge | | 41 |
| 8234525279 | Militaristic Technology in Song China | Gun powder, the magnetic compass, water-tight bulk heads, and sternpost rutters | | 42 |
| 8234525280 | Incan Advancements | they were able to record census data and keep an accounting of their harvests on quipu, a set of knotted strings | | 43 |
| 8234525281 | How was the eastern coast of Africa linked to India and Southeast Asia? | Through the shipping lanes of the indian ocean trade | | 44 |
| 8234525282 | Who dominated the Indian Ocean Trade? | The Persians and the Arabs | | 45 |
| 8234525283 | Persian and Arabic Trade Routes | Connected ports in western India to ports in the Persian Gulf, which in turn were connected to ports in eastern Africa | | 46 |
| 8234525284 | Cultural Diffusion of Sailors | Cultures started to intermix as many sailors took foreign wives home and created bilingual and bicultural families | | 47 |
| 8234525285 | Who populated the east coast of Africa (Swahili Coast)? | Bantu speaking peoples who settled into lives of farmers, merchants, and fisherman | | 48 |
| 8234525286 | Swahili Trade | Trade with the Muslims began in the early 10th century as Swahili traders brought gold, slaves, ivory, and other exotic products to the coast. | | 49 |
| 8234525287 | How were stories transmitted in African culture? | Oral literature and story telling | | 50 |
| 8234525288 | The Hanseatic League | A collection of city-states in the Baltic and North Sea regions of Europe that banded together in 1241 to establish common trade practices, fight off pirates and foreign governments, and establish a trade monopoly from that region to the rest of the world | | 51 |
| 8234525289 | Result of the Hanseatic League (2) | -It resulted in a substantial "middle class" in northern Europe
-It set a precedent for large, European trade operations that affected the Dutch and English | | 52 |
| 8234525290 | Effects of Population Growth (2) | -Led to huge movements of people such as Germanic tribes into Southern Europe
-More crowded conditions in the manor (estate) or small towns | | 53 |
| 8234525291 | Religious Pilgrimages | -Rome and Constantinople attracted thousands to their cathedrals
-The Islamic duty to travel to Mecca | | 54 |
| 8234525292 | Buddhist Missionaries Effect on Japan | In 522, Buddhist missionaries went to Japan and brought Chinese cultures | | 55 |
| 8234525293 | Effect of the mix of Shinto and Buddhism in Japan | Most Japanese adopted Buddhism while also hanging onto their Shinto beliefs; they followed both religions simultaneously | | 56 |
| 8234525294 | Taika Reforms | Prince Shotoku borrowed the bureaucratic and legal reforms from China, which were modeled on the successes of the Tang Dynasty | | 57 |
| 8234525295 | New Japanese Capital (8th Century) | Modeled after the Tang capital; largely rejected Confucianism, as well as the idea of the civil service exam | | 58 |
| 8234525296 | how did Japan hold the status of education? | Education wasn't nearly as important as birth; noble classes were hereditary, not earned | | 59 |
| 8234525297 | How did China's dynastic leaders expand? | By trade and force | | 60 |
| 8234525298 | How did China influence Korea? | Korea had its own independent and powerful dynasty | | 61 |
| 8234525299 | How did Korea maintain the appearance of cordial relations with China? | Korea became a vassal-state of the Tang | | 62 |
| 8234525300 | Vassal State | Smaller nations that pay tribute to a bigger state to avoid conquest and occupation | | 63 |
| 8234525301 | Effect of Korean gift-giving and exchanges to China | Resulted in Korean schools and the imperial court being organized like those of the Chinese | | 64 |
| 8234525302 | Effect of the power of the royal houses and nobility in Korea | Prevented the development of a true bureaucracy based merit | | 65 |
| 8234525303 | Chinese influence on Korean religion | The tribute relationship was also responsible for the spread of both Confucianism and Chan Buddhism to Korea | | 66 |
| 8234525304 | How did Vietnam feel about a tribute relationship with China> | The Viet people of southeast Asia were much less willing to accept even the appearance of a tribute relationship with China, and resisted the Tang armies | | 67 |
| 8234525305 | What was the effect of the eventually established tribute relationship in Vietnam? (3) | Confucian education was accepted, an active trade relationship existed between Vietnam and China, the Vietnamese maintained local traditions and continued to actively revolt against Tang authorities | | 68 |
| 8234525306 | Islamic influence in India | After defeating the disorganized Hindus, the Islamic invaders moved to Delhi under their leader the Sultan; Resulted in the kingdom known as the Delhi Sultanate | | 69 |
| 8234525307 | Sultans effect on Hindu beliefs in India | While many Hindus held on to their religious beliefs, individual sultans were offended by Hinduism's polytheistic ways and did their best to convert them | | 70 |
| 8234525308 | What caused Hindus in northern India to convert to Islam? | Non-Muslims under the sultans in India had to pay a tax | | 71 |
| 8234525309 | Progress caused by sultans in India | Colleges were founded and irrigation systems were improved | | 72 |
| 8234525310 | Islamic Empire's effect on African Kingdoms | When the Islamic Empire spread across North Africa in the 7th and 8th centuries, African Kingdoms began trading with a larger Mediterranean economy | | 73 |
| 8234525311 | Effect of African search for salt | When they encountered Islamic traders along the salt road, they traded for more than salt, and created an explosion of trade | | 74 |
| 8234525312 | Major Resource in Ghana and Mali!!!!! | GOLD | | 75 |
| 8234525313 | Effect of traders bringing Islam to West Africa | -Ghana fought against the muslims in a Holy War, and even though they won, the empire declined
-By the time Mali came to power, the region had converted to Islam | | 76 |
| 8234525316 | Bantu Migration and Disease | Malaria was common in West Africa, where Bantu speakers may have immunity due to exposure, but the people they met when they migrated had no such immunity, thus spreading the disease | | 77 |
| 8234525317 | Where did the Black Death originate? | China, but spread rapidly through Europe in the mid-14th century | | 78 |
| 8234525318 | Spread of the Bubonic Plague | Asian silk roads increased the interaction between Europe and Asia | | 79 |
| 8234525319 | What conditions lead to the rapid spread of the plague? | Crowded conditions and lack of adequate sanitation and medical knowledge | | 80 |
| 8234525320 | Impact of the plague on feudal society | Quickened the decline of feudal society because many manors weren't able to function:
-Wage raise for peasants
-Shift toward a commercial economy, more individual freedoms, and development of new industries | | 81 |
| 8234525321 | Spreading agriculture in Africa | -Bantu speakers brought the cultivation of yams and oil palms as well as grains such as millet ans sorghum
-Indonesian seafarers traveling across the Indian Ocean introduced bananas to sub-saharan Africa | | 82 |
| 8234525332 | Middle Ages | The period after the fall of Rome and before the Renaissance | | 83 |
| 8234525333 | Eastern Roman Empire during the Middle Ages | Still centered in Constantinople, became the highly centralized Byzantine Empire | | 84 |
| 8234525334 | Europe structure during the Byzantine Empire | Much of Europe was fragmented in small feudal kingdoms with few cultural and intellectual developement | | 85 |
| 8234525335 | Why was the Byzantine Empire significantly different? | -Emperors ruled by absolute authority, especially over the economy
-Used coined money | | 86 |
| 8234525336 | What is the period of Justinian (r. 527-565) known for? (3) | -The Justinian's Code
-The flourishing of the arts and sciences: construction of buildings and churches, especially the Hagia Sophia
-An ambitious plan to reconquer the losed provinces of the western half of the Roman Empire | | 87 |
| 8234525338 | The Great Schism (1054) | The separation of the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church (1054 CE) | | 88 |
| 8234525339 | The Pope of Western Europe | Roman Catholic emperors of the West regarded the Pope as the leader of the see of Rome
-Basing his claims on his succession from St Peter, the Pope asserted his direct jurisdiction over the entire church- east, as well as west | | 89 |
| 8234525340 | How did the Byzantines view their church? | In the context of the imperial system; their sources of law were ecumenical councils and the emperor, whom God had placed over all things, spiritual and temporal | | 90 |
| 8234525341 | How did Byzantine Emperors disagree? | They disagreed over the sacrament of communication, whether priests should be allowed to marry, and the use of local languages in church | | 91 |
| 8234525342 | Overall Effect of the Great Schism | The church of Constantinople (AKA Eastern Orthodoxy) influenced the East, and Roman Catholicism continued to influence the West | | 92 |
| 8234525344 | High Middle Ages | 1000 to 1300 CE | | 93 |
| 8234525345 | Late Middle Ages | 1300 to 1450 CE | | 94 |
| 8234525346 | Impact of Orthodoxy on Russia | In the 9th Century, the Slavic peoples of Southeastern Europe were converted to Christianity by St. Cyril | | 95 |
| 8234525347 | St. Cyril | An orthodox Christian who used the Greek alphabet to create a slavic alphabet known as Cyrillic Alphabet | | 96 |
| 8234525348 | Why did Prince Vladimir choose Eastern Orthodoxy? | It had no restrictions about what he could or could not eat, among other things | | 97 |
| 8234525349 | Mongol Expansion | Spanned from the pacific ocean to Eastern Europ | | 98 |
| 8234525350 | Death of Genghis Khan | His followers split off into groups, known as hordes | | 99 |
| 8234525351 | The Mongols | Destroyed cities and were ruthless warriors on the path to expansion | | 100 |
| 8234525353 | Kush Empire in Southern Egypt | Kush developed around 750 BCE; after the Kush decline around 200 CE, Axum rose to powere | | 101 |
| 8234525354 | Axum Empire in Southern Egypt | Modern day Ethiopia; In the 4th century, Axum converted to Christianity; In the 7th century, many converted to Islam due to trade | | 102 |
| 8234525355 | The Aztecs | Arrived in Central Mexico in the mid 1200's and built their capital at Tenochtitlan (modern-day Mexico City) | | 103 |
| 8234525356 | Aztec Religious System | Tied to the military: Military obtained victims for human sacrifice | | 104 |
| 8234525357 | The Inca | Controlled their vast territory using a professional army, and established bureaucracy (manned by nobility)/ a unified language, and a complex system of roads and tunnels | | 105 |
| 8234525358 | Incan Religion | Polytheistic, but the sun God was most important
-Practiced human sacrifice
-had a strong moral quality | | 106 |
| 8234525359 | Concept of Private Property in Incan Society | The ruler was viewed as having descended from the sun and owning everything on earth, therefore there was no concept of private property because the ruler owns everything | | 107 |
| 8234525360 | What was surprising about the Mongols? | Their empire was one of territory, infrastructure, and conquest, but not one of "culture" | | 108 |
| 8234525361 | Mongols Effect on Religion | -stifled cultural growth rather than contributing to it
-yet, their superior infrastructure allowed for the exchange and spreading of ideas | | 109 |
| 8234525362 | Kublai Khan in China | Dismissed Confucian scholars, forbade marriage between Mongols and Chinese, and wouldn't allow the Chinese to learn the Mongol language | | 110 |
| 8234525363 | Mongol Decline | By 1450, as the Mongol Empire was well into its decline, the world would never again be disconnected | | 111 |
| 8234525364 | Charles Martel (686-741) | A Frankish leader, stopped the muslim advance into Spain, so the Islamic Empire never flourished in Europe beyond Spain | | 112 |
| 8234525367 | The Sufis | Islamic Mystics; Were effective missionaries by stressing a personal relationship with Allah | | 113 |
| 8234525368 | Decline of the Abbasids | -A new Shia dynasty in northern Iran and constant threats from the Seljuk Turks, a nomadic Sunni group
-In 1258, the Mongols overran the Islamic Empire and destroyed Baghdad | | 114 |
| 8234525369 | Ottoman Turks | After the fall of the Abbasids, the Ottoman Turks would reunite Egypt, Syria, and Arabia in a new Islamic state, which would last until 1918 | | 115 |
| 8234525370 | The Vikings: Raids from the North | Beginning around 800 CE, the vikings used their multi-oared boats to raid well beyond their borders | | 116 |
| 8234525371 | The Crusades | The Christians felt threatened by the expansion of the Muslims, especially as Islam moved into areas that Christians identified with historically | | 117 |
| 8234525372 | Result of the Crusades | Through the year 1204, a total of four crusades failed to produce results and the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church separated even further. | | 118 |
| 8234525373 | Global Interaction through Conquest (The Crusades) | -Besides religion, the Crusades were also initiated through the lure of empire and wealth
-Religion, when combined with conquest and feelings of superiority, can be very bloody | | 119 |
| 8234525374 | Crusades impact on World History | -They led to the interaction between cultures that might not otherwise interact
-Western Europe rediscovered aspects of the ancient past which was being preserved by the Byzantine and Islamic Empires | | 120 |
| 8234525376 | European Feudalism | 1. Top: Kings
2. Nobles
3. Vassals(knights)
4. Peasants | | 121 |
| 8234525377 | Nobles | In exchange for military services and loyalty to the king were granted power over sections of the kingdom | | 122 |
| 8234525378 | Vassals | The nobles divided their land into smaller sections under the control of lesser lords (vassals) | | 123 |
| 8234525379 | The Manor | Economic part of feudalism; the estates granted to vassals were called fiefs, later known as manors | | 124 |
| 8234525380 | Peasant exchange withe Lords | The peasants worked the land on behalf of the lord in exchange for a place to live and protection | | 125 |
| 8234525381 | Three-Field System | Rotation of three fields: One for fall harvest, one for spring harvest, and one left fallow to replenish nutrients | | 126 |
| 8234525383 | Emergence of a Middle Class | As many of the peasants became skilled in trades other than farming, and Western Europe began trading with the rest of the world, some of these skilled crafts people began to earn extra income | | 127 |
| 8234525384 | Gothic Cathedrals | Pointed arches, thinner walls, larger windows, tall: soaring into the heavens | | 128 |
| 8234525385 | Women and Islam | In Arabia, women traditionally did not have property rights, or inheritance rights; rather, women were essentially viewed as property themselves | | 129 |
| 8234525386 | Chinese Women under the Tang and Song Dynasties | Highly patriarchal, Chinese men considered women inferior, and like European men of the middle ages, the considered a woman's beauty and feminity as virtues worth protection | | 130 |
| 8234525387 | Changes in the Role of Women | Restrictions on women's freedoms depended on which caste or class they belonged | | 131 |
| 8234525388 | Women in African Societies | Women commanded a bride-price rather than having to give a dowry and were considered a valuable source of wealth | | 132 |
| 8234525389 | Dar-Al-Islam | Formed through conquest, a predominantly muslim region of land that stretched from the Iberian Peninsula to China | | 133 |
| 8234525390 | New Crops of Dar-Al-Islam | New crops in dar-al-Islam consisted of sugarcane, rice, wheat, oranges, lemons, etc. | | 134 |
| 8234525391 | Sui Dynasty | a short-lived imperial dynasty of China of pivotal significance. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties and reinstalled the rule of ethnic Han Chinese in the entirety of China proper | | 135 |
| 8234525392 | The Grand Canal | longest artificial river in the world | | 136 |
| 8234525393 | The Tang Dynasty | an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period | | 137 |
| 8234525394 | Tang Taizong | second emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China | | 138 |
| 8234525399 | Swahili | A mix of the bantu and arabic languages, spoken on the east coast of Africa | | 139 |
| 8234525401 | Indian Ocean Trade | it remained closely tied to environmental conditions, namely the monsoon winds that merchants had to consider while scheduling their departures. This meant that the port cities along the rim of the Indian Ocean at any given time had large numbers of non-citizens waiting for changes in the monsoon winds | | 140 |
| 8234525402 | Hanseatic League | An association of trading cities stretching from novgorod to london and embracing all the significant commercial centers of poland, northern germany, and Scandinavia | | 141 |
| 8234525403 | Buddhism | a religion and dharma that encompasses a variety of traditions, beliefs and spiritual practices largely based on original teachings attributed to the Buddha and resulting interpreted philosophies | | 142 |
| 8234525404 | Daoism | a religious or philosophical tradition of Chinese origin which emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao. | | 143 |
| 8234525405 | Pilgrimage to India | In Hindu religion and spirituality, the pilgrimage has great significance. Members of the faith participate in the following types of pilgrimage. The pilgrimage to each sacred site has its own religious significance. These sites include the Ganges River and Mt. Kailas | | 144 |
| 8234525406 | Hostility Towards Buddhism | The principle of non-violence is central to Buddhist teachings, but in Sri Lanka some Buddhist monks are being accused of stirring up hostility towards other faiths and ethnic minorities. Their hard line is causing increasing concern. ... The peaceful precepts for which Buddhism is widely known barely figure in his words | | 145 |
| 8234525407 | Persecution of Buddhists | The Great Anti-Buddhist Persecution initiated by Tang Emperor Wuzong reached its height in the year 845 AD. Among its purposes were to appropriate war funds and to cleanse China of foreign influences | | 146 |
| 8234525408 | Neo Confucianism | a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, and originated with Han Yu and Li Ao in the Tang Dynasty, and became prominent during the Song and Ming dynasties | | 147 |
| 8234525409 | Confucianism and Buddhism | two differing principles/religious of the East Asian peoples that can be practiced at once, the former emphasizes respect and filial piety and the latter seeks nirvana | | 148 |
| 8234525410 | Zhu Xi | courtesy name is Yuanhui, or Zhonghui, self-titled Huian. He was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and writer of the Song dynasty | | 149 |
| 8234525411 | What did the Viet people adopt from the Chinese? Reject? | The Viet people adopted Confucianism and revolted against Tang authorities | | 150 |
| 8234525412 | Nara Japan | a city on S Honshu, in central Japan: chief Buddhist center of ancient Japan; first capital of Japan a.d. 710-84. 2. a period of Japanese history, a.d. 710-784, characterized by the adoption of Chinese culture and forms of government | | 151 |
| 8234525413 | Shintoism | the ethnic religion of Japan that focuses on ritual practices to be carried out diligently in order to establish a connection between present-day Japan and its ancient past, a blend of Buddhism and indigenous Japanese religions | | 152 |
| 8234525414 | Fujiwara family | descending from the Nakatomi clan and through them Ame-no-Koyane-no-Mikoto, was a powerful family of regents in Japan. They dominated the Japanese politics of Heian period (794-1185) through the monopoly of regent positions, sesshō and kampaku | | 153 |
| 8234525415 | Cultural similarities with China and Vietnam | Both are strongly loyal and Confucian | | 154 |
| 8234525416 | Tale of Genji | a classic work of Japanese literature written by the noblewoman and lady-in-waiting Murasaki Shikibu in the early years of the 11th century in "concertina" or "orihon" style made of several sheets of paper pasted together and folded alternately in one direction | | 155 |
| 8234525417 | Axum | an ancient kingdom located in present-day Eritrea and the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Ruled by the Aksumites, it existed from approximately 100 AD to 940 AD | | 156 |
| 8234525421 | Devotional Cults | originated in the Hindu religion. They were identified with certain local spirits or deities. They emphasized the salvation elements of Hinduism and tried to localize practices associating structures or local deities with Hinduism. They meditated, venerated, and made food sacrifices in attempts to achieve a mystical union with their god | | 157 |
| 8234525422 | Shankara | an early 8th century Indian philosopher and theologian who consolidated the doctrine of Advaita Vedanta. He is credited with unifying and establishing the main currents of thought in Hinduism | | 158 |
| 8234525423 | Ramanuja | a Hindu theologian, philosopher, and one of the most important exponents of the Sri Vaishnavism tradition within Hinduism. He was born in a Tamil Brāhmin family in the village of Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu | | 159 |
| 8234525425 | Appeal of Islam | completion of Abrahamic faiths ,personal benefits, Arabian power=social benefits | | 160 |
| 8234525426 | Conversion of Islam | Through war and conquest, Islamic emperors created dar-Al-Islam, a predominantly muslim region of land stretching from the Iberian Peninsula all the way to China | | 161 |
| 8234525427 | Sufis | mystical Islamic belief and practice in which Muslims seek to find the truth of divine love and knowledge through direct personal experience of God | | 162 |
| 8234525428 | Bhakti Movement | the spiritual devotional trend that emerged in old-fashioned Hinduism and later reformed in Sikhism. It started in the eighth-century south India (now parts of Tamil Nadu and Kerala), and spread northwards | | 163 |
| 8234525429 | Funan | the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianised state—or, rather a loose network of states (Mandala)—located in mainland Southeast Asia centered on the Mekong Delta that existed from the first to sixth century CE | | 164 |
| 8234525430 | Srivijaya | dominant thalassocratic Malay city-state based on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 8th to the 12th century | | 165 |
| 8234525431 | Angkor | the capital city of the Khmer Empire, which also recognized as Yasodharapura and flourished from approximately the 9th to 15th centuries. Angkor was a megacity supporting at least 0.1% of the global population during 1010-1220 | | 166 |
| 8234525432 | Ghana | African kingdom that was located in the same place that Mali was, 200 years before | | 167 |
| 8234525433 | Gold Trade | Mali had an abundance of gold and used this new found length to trade for other natural resources such as salt and other spices | | 168 |
| 8234525435 | Ibn Battuta | One of the greatest Moroccan trader of all time, logged more than 117000 km throughout all of his journies | | 169 |
| 8234525436 | Islam in West Africa | spread primarily through trade, conversion of elites and syncretism | | 170 |
| 8234525437 | Maya | a Mesoamerican civilization developed by the Maya peoples, and noted for its hieroglyphic script—the only known fully developed writing system of the pre-Columbian Americas—as well as for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system | | 171 |
| 8234525438 | Teotihuacan | a vast Mexican archaeological complex northeast of Mexico City. | | 172 |
| 8234525439 | Mayan Society and Religion | the Maya would often combine aspects of warfare and religion. Typically, this was in the form of taking prisoners for sacrifice | | 173 |
| 8234525440 | The Umayyad Dynasty | the first great Muslim dynasty to rule the empire of the Caliphate (661-750 ce) | | 174 |
| 8234525443 | Islam | Major world religion having its origins in 610 C.E. in the Arabian peninsula; meaning literally submission; based on prophecy of Muhammad. | | 175 |
| 8234525444 | India, and Greece: Persian, Indian, and Greek influences on Islam | persian traditions deeply influenced Islamic political and cultural leaders. Persian influence is most noticeable in literary works from the Abbasid dynasty. While Arabic served as the language of religion, theology, philosophy, and law, Persian was the principal language of literature, poetry, history, and political reflection. | | 176 |
| 8234525445 | Sultanate of Delhi | The Delhi Sultanate was a Muslim sultanate based mostly in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years. | | 177 |
| 8234525446 | The Chola Kingdom | The Chola dynasty was one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of southern India. | | 178 |
| 8234525447 | Early Byzantine Empire | During the late 10th and early 11th centuries, under the rule of the Macedonian dynasty founded by Michael III's successor, Basil, the Byzantine Empire enjoyed a golden age | | 179 |
| 8234525448 | Constantinople | capital of the byzantine empire | | 180 |
| 8234525449 | Caesaropapism | a political theory in which the head of state, notably the emperor ("Caesar", by extension a "superior" king), is also the supreme head of the church (papa, pope or analogous religious leader) | | 181 |
| 8234525450 | Justinian and Theodora | Emperor of the Byzantine empire and his wife | | 182 |
| 8234525451 | Justinian's Code | the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Eastern Roman Emperor | | 183 |
| 8234525452 | Muslim Conquests | The muslims of the Arabian peninsula fought many wars of conquest with other countries to create the Dar-al-Islam, a predominantly islamic region of land stretching from the Iberian peninsula to China | | 184 |
| 8234525453 | The Aztec Empire | The Aztec Empire, or the Triple Alliance, began as an alliance of three Nahua "altepetl" city-states: Mexico-Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan | | 185 |
| 8234525454 | Iroquois | A group of tribes speaking related languages in the eastern Great Lakes region of upper New York. | | 186 |
| 8234525455 | Cahokia | Mississippian settlement near present-day East St. Louis, home to as many as 25,000 Native Americans | | 187 |
| 8234525456 | Mound Builders | Used earth for religious, ceremonial, burial purposes; great lakes, ohio river valley | | 188 |
| 8234525457 | Maori | New Zealand indigenous culture established around 800 CE | | 189 |
| 8234525458 | Jizya | a per capita yearly tax historically levied by Islamic states on certain non-Muslim subjects—dhimmis—permanently residing in Muslim lands under Islamic law. | | 190 |
| 8234525459 | Umayyad Decline | had to adapt to new life, not governed well, no same privileges, conquest slowed causing economic tension, and criticizing of the court | | 191 |
| 8234525460 | Abu al-Abbas | Muhammad's uncle from whom the Abbasid Dynasty takes its name | | 192 |
| 8234525461 | Abbasid Administration | The Islamic Golden Age was inaugurated by the middle of the 8th century by the ascension of the Abbasid Caliphate and the transfer of the capital from Damascus to Baghdad | | 193 |
| 8234525462 | Harun al-Rashid | 5th abbasid caliph | | 194 |
| 8234525463 | Abbasid decline: reasons | Difficulty of moving armies across the great distances of the empire, retention of regional identities by the population, and difficulty of compelling local administrators to obey (no city collapse) | | 195 |
| 8234525464 | The Franks | a collection of Germanic peoples that originated in the lands between the Lower and Middle Rhine in the 3rd century AD and eventually formed a large empire dominating much of western and central Europe during the Middle Ages | | 196 |
| 8234525465 | Charles Martel | frankish statesman and military leader who as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death | | 197 |
| 8234525466 | Charlemagne | king of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor | | 198 |
| 8234525467 | Louis the Pious | the King of the Franks and co-Emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781 | | 199 |
| 8234525468 | Vikings | raided and traded from their Northern European homelands across wide areas of northern, central, eastern and western Europe, during the late 8th to late 11th centuries | | 200 |
| 8234525469 | Chinggis Khan | the Great Khan and founder of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death. | | 201 |
| 8234525470 | Mongol Arms | relied on superior tactics and speed, and was like one massive well-disciplined cavalry which moved rapidly, adapted quickly to changing situations and followed complex battle strategies | | 202 |
| 8234525471 | Mongol conquests: China and Persia | Began in the North in 1209 and overall lasted only a little over a century. (China), Mongol rule here was a disaster on a grand scale, as towns and villages were massacred, heavy taxes were collected, peasants were pushed off their land, and agricultural land was reduced to waste. (Persia) | | 203 |
| 8234525472 | Kubilai Khan | Grandson of Genghis Khan, ruled the empire from China | | 204 |
| 8234525473 | Golden Horde | Group of Mongols overran Russia between 1237 and 1241; Further overran Poland, Hungary, and eastern Germany, 1241-1242; Maintained hegemony in Russia until the mid-fifteenth century | | 205 |
| 8234525474 | Mongols and Trade | Mongols supplemented their economy by trade and raiding. They never developed a merchant class. On a regular basis the Mongols traded animals, fur, and hides for grain, tea, silk, cloth, and manufactured items with Chinese and Russian trading companies | | 206 |
| 8234525475 | Tamerlane and his conquests | founder of the Timurid Empire in Persia and Central Asia he became the first ruler in the Timurid dynasty | | 207 |
| 8234525477 | Urban II | declared the start of the crusades | | 208 |
| 8234525478 | Saladin | the first sultan of Egypt and Syria and the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty | | 209 |
| 8234525481 | Population Growth | equipped with the abundance of food during this time period, many countries' population more than doubled | | 210 |
| 8234525482 | The Three Estates | The First Estate (clergy); the Second Estate (nobility); and the Third Estate (commoners). The king was considered part of no estate | | 211 |
| 8234525484 | troubadours | a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages | | 212 |
| 8234525485 | Eleanor of Aquitaine | Queen of France and England, she was one of the most powerful women in Europe in the Middle Ages | | 213 |
| 8234525486 | guilds | Association of merchants or artisans who cooperated to protect their economic interests | | 214 |
| 8234525487 | urban women | worked as domestic servants, laundresses, and seamstresses | | 215 |
| 8234525488 | cathedral schools | schools run by secular clergy | | 216 |
| 8234525489 | Scholasticism | A medieval philosophical and theological system that tried to reconcile faith and reason | | 217 |
| 8234525490 | St. Thomas Aquinas | developed five proofs for the existence of God | | 218 |
| 8234525491 | sacraments | Sacred rituals of the Roman Catholic Church | | 219 |
| 8234525492 | Dominicans | monastic group that emphasized preaching | | 220 |
| 8234525493 | Franciscans | founded by St. Francis; order stressed vows of poverty and gentleness to all creatures | | 221 |
| 8234525494 | heresy | the crime of holding a belief that goes against established doctrine | | 222 |
| 8234525495 | Question: The observations seen in the excerpt are best seen as evidence for which of the following in Youn China? | Policies of religious toleration | | 223 |
| 8234525496 | Question: Which of the following conclusions about the period 600-1450 CE is most directly supported by the passage? | The empires of the steppe nomads united trade links across Eurasia | | 224 |
| 8234525497 | Question: Compared to the observations expressed in the excerpt, Mongol administrations of its Russian domains in the period 600-1950 CE differed that is-- | Relied heavily on tribute from Russian principles, Mongols in China had Chinese Bureaucracy | | 225 |
| 8234525498 | Question: What is the impact of improvement of saddles in spreading Islam to sub Saharan Africa? | Contributed to increased transaharan trade | | 226 |
| 8234525499 | Question: Information on camel saddles is an example of-- | People adopted technology based on their needs | | 227 |
| 8234525500 | SAQ#1:
SOURCE: Anonymous collection of stories about VIKRAMA in South Asia between 11th and 13th centuries
Wives should follow their husbands and shall purify 3 families -- their mother's, father's and marital household's. Otherwise they are as usless as a banyan tree in a cemetery.
SATI-- women burned themselves in the funeral pyre if their husbands died
"Women are completely useless without their husbands
Metaphors imply that men are essential to the survival of women-- they are dependent on their husbands
QUESTION:
One type of evidence: women were not considered equals of men in 12th century south asia
2 examples of how women in SE or SW asia enjoyed greater gender equaluty than women in S. ASIAN between 600 and 1450. | In southwest asia (arabia), the status of women in society was changing. They enjoyed rights not accorded to women in many other lands. They could legally inherit property,
Divorce husbands on their own initiative, engage in business ventures. In southeast asia (Vietnam) women dominated local and regional marketa for centuries and participated actively in business ventures closed to women in areas like China. | | 228 |
| 8234525501 | SAQ #2:
QUESTION: identify and explain 3 ways in which improved transportation technology led to cultural diffusion during the period of 600CE to 1450 CE. Use specific examples from one or more civilizations.
EXAMPLES:
Religions:
Islam
Christianity
Judaism
Hinduism
buddhism | buddhism
Hinduism and buddhism both spread on the silk road. Indian ocean trade roites led to urbanized ciries
Islam specifically-- umayyad and abbasid empires mintained roads, led to increase of muslim missionaries on trade routes
subsaharan -- built religious centers along the trade routes
Jewish Diaspora: moved to places that did not have jews , did not convert, but influenced with culture
Technology/Goods
Printing- printing of books
Gunpowder
Paper
Compass from china, used by arabs | | 229 |
| 8234525502 | SAQ #3: Identify and explain 3 ways in which rulers legitimized or consolatized their power during 600-1450. Use specific examples | -Incan Empires and worship of ruler who acted like an intermediary between man and God
-Prince Vladimir of kiev and choosing a religion for Russia
-Mali, Mansa Musa and pilgrimages to Mecca(using wealth)
-Charlemagne(holy Roman emperor)
-Mongols (Kublai Khan in China) legitimized through terrorizing
-Vikings
-Dar-Al-Islam (Islamic conquest); Islamic Empire- Delhi Sultanate
-Chinese Empires (Tang and Song) | | 230 |
| 8234525503 | a. Analyze the role geography played in the development of imperial city of Constantinople
b. One specific example of influence Byzantine Empire had on another civilization | a. Trade routes/ports straight connects the mediterranian to the black sea, Constantinople, etc.
b. Russian religion- Eastern orthodoxy (power and wealth) Prince Vladimir and kiev shopping for religions | | 231 |
| 8234807777 | consolidate | to combine into a whole; to strengthen | | 232 |
| 8237280777 | Abbasid Empire (geography) | |  | 233 |
| 8237281726 | Umayyad Empire (geography) | |  | 234 |
| 8237316026 | Mayan (geography) | |  | 235 |
| 8237316982 | Aztec (geography) | |  | 236 |
| 8237322509 | Incan (geography) | |  | 237 |
| 8237324052 | Tang Dynasty (geography) | | 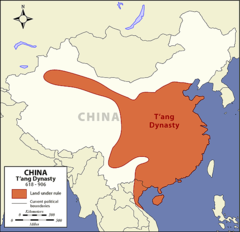 | 238 |
| 8237329167 | Song Dynasty (geography) | |  | 239 |
| 8237332021 | Byzantine Empire (geography) | |  | 240 |
| 8237334555 | Mongols (geography) | |  | 241 |
| 8237337611 | Islam (geography) | |  | 242 |
| 8237605294 | Hanseatic League (geography) | |  | 243 |





















