AP Psychology AP Review Flashcards
| 13826324605 | psychology | the study of behavior and mental processes | 0 | |
| 13826324606 | psychology's biggest question | Which is more important in determining behavior, nature or nurture? | 1 | |
| 13826324607 | psychology's three levels of analysis | biopsychosocial approach (looks at the biological, psychological, and social-cultural approaches together) | 2 | |
| 13826324608 | biological approach | genetics, close-relatives, body functions | 3 | |
| 13826324609 | evolutionary approach | species - helped with survival (ancestors) | 4 | |
| 13826324610 | psychodynamic approach | (Freud) subconscious, repressed feelings, unfulfilled wishes | 5 | |
| 13826324611 | behavioral approach | learning (classical and operant) observed | 6 | |
| 13826324612 | cognitive approach | thinking affects behavior | 7 | |
| 13826324613 | humanistic approach | becoming a better human (behavior, acceptance) | 8 | |
| 13826324614 | social-cultural approach | cultural, family, environment | 9 | |
| 13826324615 | two reasons of why experiments are important | hindsight bias + overconfidence | 10 | |
| 13826324616 | types of research methods | descriptive, correlational, and experimental | 11 | |
| 13826324617 | descriptive methods | case study survey naturalistic observation (DON'T SHOW CAUSE/EFFECT) | 12 | |
| 13826324618 | case study | studies one person in depth may not be typical of population | 13 | |
| 13826324619 | survey | studies lots of people not in depth | 14 | |
| 13826324620 | naturalistic observation | observe + write facts without interference | 15 | |
| 13826324621 | correlational method | shows relation, but not cause/effect scatterplots show research | 16 | |
| 13826324622 | correlation coefficient | + 1.0 (both increase) 0 (no correlation - 1.0 (one increases, other decreases) | 17 | |
| 13826324623 | experimental method | does show cause and effect | 18 | |
| 13826324624 | population | type of people who are going to be used in experiment | 19 | |
| 13826324625 | sample | actual people who will be used (randomness reduces bias) | 20 | |
| 13826324626 | random assignment | chance selection between experimental and control groups | 21 | |
| 13826324627 | control group | not receiving experimental treatment receives placebo | 22 | |
| 13826324628 | experimental group | receiving treatment/drug | 23 | |
| 13826324629 | independent variable | drug/procedure/treatment | 24 | |
| 13826324630 | dependent variable | outcome of using the drug/treatment | 25 | |
| 13826324631 | confounding variable | can affect dependent variable beyond experiment's control | 26 | |
| 13826324632 | scientific method | theory hypothesis operational definition revision | 27 | |
| 13826324633 | theory | general idea being tested | 28 | |
| 13826324634 | hypothesis | measurable/specific | 29 | |
| 13826324635 | operational definition | procedures that explain components | 30 | |
| 13826324636 | mode | appears the most | 31 | |
| 13826324637 | mean | average | 32 | |
| 13826324638 | median | middle | 33 | |
| 13826324639 | range | highest - lowest | 34 | |
| 13826324640 | standard deviation | how scores vary around the mean | 35 | |
| 13826324641 | central tendency | single score that represents the whole | 36 | |
| 13826324642 | bell curve | (natural curve) |  | 37 |
| 13826324643 | ethics of testing on animals | need to be treated humanly basically similar to humans | 38 | |
| 13826324644 | ethics of testing on humans | consent debriefing no unnecessary discomfort/pain confidentiality | 39 | |
| 13826324645 | sensory neurons | travel from sensory receptors to brain | 40 | |
| 13826324646 | motor neurons | travel from brain to "motor" workings | 41 | |
| 13826324647 | interneurons | (in brain and spinal cord) connecting motor and sensory neurons | 42 | |
| 13826324841 | neuron |  | 43 | |
| 13826324648 | dendrites | receive messages from other neurons | 44 | |
| 13826324649 | myelin sheath | protects the axon | 45 | |
| 13826324650 | axon | where charges travel from cell body to axon terminal | 46 | |
| 13826324651 | neurotransmitters | chemical messengers | 47 | |
| 13826324652 | reuptake | extra neurotransmitters are taken back | 48 | |
| 13826324653 | excitatory charge | "Let's do it!" | 49 | |
| 13826324654 | inhibitory charge | "Let's not do it!" | 50 | |
| 13826324655 | central nervous system | brain and spinal cord | 51 | |
| 13826324656 | peripheral nervous system | somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system | 52 | |
| 13826324657 | somatic nervous system | voluntary movements | 53 | |
| 13826324658 | autonomic nervous system | involuntary movements (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems) | 54 | |
| 13826324659 | sympathetic nervous system | arousing | 55 | |
| 13826324660 | parasympathetic nervous system | calming | 56 | |
| 13826324661 | neural networks | more connections form with greater use others fall away if not used | 57 | |
| 13826324662 | spinal cord | expressway of information bypasses brain when reflexes involved | 58 | |
| 13826324663 | endocrine system | slow uses hormones in the blood system | 59 | |
| 13826324664 | master gland | pituitary gland | 60 | |
| 13826324665 | brainstem | extension of the spinal cord responsible for automatic survival | 61 | |
| 13826324666 | reticular formation (if stimulated) | sleeping subject wakes up | 62 | |
| 13826324667 | reticular formation (if damaged) | coma | 63 | |
| 13826324668 | brainstem (if severed) | still move (without purpose) | 64 | |
| 13826324669 | thalamus | sensory switchboard (does not process smell) | 65 | |
| 13826324670 | hypothalamus | basic behaviors (hunger, thirst, sex, blood chemistry) | 66 | |
| 13826324671 | cerebellum | nonverbal memory, judge time, balance emotions, coordinate movements | 67 | |
| 13826324672 | cerebellum (if damaged) | difficulty walking and coordinating | 68 | |
| 13826324673 | amygdala | aggression, fear, and memory associated with these emotions | 69 | |
| 13826324674 | amygdala (if lesioned) | subject is mellow | 70 | |
| 13826324675 | amygdala (if stimulated) | aggressive | 71 | |
| 13826324676 | hippocampus | process new memory | 72 | |
| 13826324677 | cerebrum | two large hemispheres perceiving, thinking, and processing | 73 | |
| 13826324678 | cerebral cortex | only in higher life forms | 74 | |
| 13826324679 | association areas | integrate and interpret information | 75 | |
| 13826324680 | glial cells | provide nutrients to myelin sheath marks intelligence higher proportion of glial cells to neurons | 76 | |
| 13826324681 | frontal lobe | judgement, personality, processing (Phineas Gage accident) | 77 | |
| 13826324682 | parietal lobe | math and spatial reasoning | 78 | |
| 13826324683 | temporal lobe | audition and recognizing faces | 79 | |
| 13826324684 | occipital lobe | vision | 80 | |
| 13826324685 | corpus callosum | split in the brain to stop hyper-communication (eliminate epileptic seizures) | 81 | |
| 13826324686 | Wernicke's area | interprets auditory and hearing | 82 | |
| 13826324687 | Broca's area | speaking words | 83 | |
| 13826324688 | plasticity | ability to adapt if damaged | 84 | |
| 13826324689 | sensation | what our senses tell us | 85 | |
| 13826324690 | bottom-up processing | senses to brain | 86 | |
| 13826324691 | perception | what our brain tells us to do with that information | 87 | |
| 13826324692 | top-down processing | brain to senses | 88 | |
| 13826324693 | inattentional blindness | fail to "gorilla" because attention is elsewhere | 89 | |
| 13826324694 | cocktail party effect | even with tons of stimuli, we are able to pick out our name, etc. | 90 | |
| 13826324695 | change blindness | giving directions and person is changed and we don't notice | 91 | |
| 13826324696 | choice blindness | when defending the choice we make, we fail to notice choice was changed | 92 | |
| 13826324697 | absolute threshold | minimum stimulation needed in order to notice 50% of the time | 93 | |
| 13826324698 | signal detection theory | we notice what is more important to us (rather hear a baby crying) | 94 | |
| 13826324699 | JND (just noticeable difference) | (Weber's law) difference between different stimuli noticed in proportion | 95 | |
| 13826324700 | sensory adaptation | tired of noticing (Brain says, "Been there, done that. Next?" | 96 | |
| 13826324701 | rods | night time (peripheral) | 97 | |
| 13826324702 | cones | color and light (center) | 98 | |
| 13826324703 | parallel processing | notice color, form, depth, movement, etc. | 99 | |
| 13826324704 | Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory | 3 corresponding color receptors (RGB) | 100 | |
| 13826324705 | Hering's opponent-process theory | after image in opposite colors (RG, YB, WB) | 101 | |
| 13826324706 | trichromatic + opponent-process | Young-Helmholtz -> color stimuli Hering -> en route to cortex | 102 | |
| 13826324707 | frequency we hear most | human voice | 103 | |
| 13826324708 | Helmoltz (hearing) | we hear different pitches in different places in basilar membrane (high pitches) | 104 | |
| 13826324709 | frequency theory | impulse frequency (low pitches) | 105 | |
| 13826324710 | Helmholtz + frequency theory | middle pitches | 106 | |
| 13826324711 | Skin feels what? | warmth, cold, pressure, pain | 107 | |
| 13826324712 | gate-control theory | small fibers - pain large fibers - other senses | 108 | |
| 13826324713 | memory of pain | peaks and ends | 109 | |
| 13826324714 | smell | close to memory section (not in thalamus) | 110 | |
| 13826324715 | grouping | Gestalt make sense of pieces create a whole | 111 | |
| 13826324716 | grouping groups | proximity similarity continuity connectedness closure | 112 | |
| 13826324717 | make assumptions of placement | higher - farther smaller - farther blocking - closer, in front | 113 | |
| 13826324718 | perception = | mood + motivation | 114 | |
| 13826324719 | consciousness | awareness of ourselves and the environment | 115 | |
| 13826324720 | circadian rhythm | daily biological clock and regular cycle (sleep and awake) | 116 | |
| 13826324721 | circadian rhythm pattern | - activated by light - light sensitive retinal proteins signal brains SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) - pineal gland decreases melatonin | 117 | |
| 13826324722 | What messes with circadian rhythm? | artificial light | 118 | |
| 13826324723 | The whole sleep cycle lasts how long? | 90 minutes | 119 | |
| 13826324724 | sleep stages | relaxed stage (alpha waves) stage 1 (early sleep) (hallucinations) stage 2 (sleep spindles - bursts of activity) (sleep talk) stage 3 (transition phase) (delta waves) stage 4 (delta waves) (sleepwalk/talk + wet the bed) stage 5 (REM) (sensory-rich dreams) (paradoxical sleep) | 120 | |
| 13826324725 | purpose of sleep | 1. recuperation - repair neurons and allow unused neural connections to wither 2. making memories 3. body growth (children sleep more) | 121 | |
| 13826324726 | insomnia | can't sleep | 122 | |
| 13826324727 | narcolepsy | fall asleep anywhere at anytime | 123 | |
| 13826324728 | sleep apnea | stop breathing in sleep | 124 | |
| 13826324729 | night terrors | prevalent in children | 125 | |
| 13826324730 | sleepwalking/sleeptalking | hereditary - prevalent in children | 126 | |
| 13826324731 | dreaming (3) | 1. vivid bizarre intense sensory experiences 2. carry fear/survival issues - vestiges of ancestors' survival ideas 2. replay previous day's experiences/worries | 127 | |
| 13826324732 | purpose of dreaming (5 THEORIES) | 1. physiological function - develop/preserve neural pathways 2. Freud's wish-fulfillment (manifest/latent content) 3. activation synthesis - make sense of stimulation originating in brain 4. information processing 5. cognitive development - reflective of intelligence | 128 | |
| 13826324733 | 1. Can hypnosis bring you back in time? 2. Can hypnosis make you do things you wouldn't normally do? 3. Can it alleviate pain? 4. What state are you in during hypnosis? 5. Who is more susceptible? | 1. cannot take you back in time 2. cannot make you do things you won't do 3. can alleviate pain 4. fully conscious ((IMAGINATIVE PEOPLE MORE SUSCEPTIBLE)) | 129 | |
| 13826324734 | depressants | slows neural pathways | 130 | |
| 13826324735 | alcohol | ((depressant)) disrupts memory formation (REM) lowers inhibition expectancy effect | 131 | |
| 13826324736 | barbituates (tranquilizers) | ((depressant)) reduce anxiety | 132 | |
| 13826324737 | opiates | ((depressant)) pleasure reduce anxiety/pain | 133 | |
| 13826324738 | stimulants | hypes neural processing | 134 | |
| 13826324739 | methamphetamine | ((stimulant)) heightens energy euphoria affects dopamine | 135 | |
| 13826324740 | caffeine | ((stimulant)) | 136 | |
| 13826324741 | nicotine | ((stimulant)) CNS releases neurotransmitters calm anxiety reduce pain affects (nor)epinephrine and dopamine | 137 | |
| 13826324742 | cocaine | ((stimulant)) euphoria affects dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine | 138 | |
| 13826324743 | hallucinogen | excites neural activity | 139 | |
| 13826324744 | ecstasy | ((hallucinogen)) reuptake is blocked affects dopamine and serotonin | 140 | |
| 13826324745 | LSD | ((hallucinogen)) affects sensory/emotional "trip" (+/-) affects serotonin | 141 | |
| 13826324746 | marijuana | ((hallucinogen)) amplify sensory experience disrupts memory formation | 142 | |
| 13826324747 | learning | organism changing behavior due to experience (association of events) | 143 | |
| 13826324748 | types of learning | classical operant observational | 144 | |
| 13826324749 | famous classical psychologists | Pavlov and Watson | 145 | |
| 13826324750 | famous operant psychologist | Skinner | 146 | |
| 13826324751 | famous observational psychologists | Bandura | 147 | |
| 13826324752 | classical conditioning | outside stimulus | 148 | |
| 13826324753 | Pavlov's experiment | Step 1: US (food) -> UR (salivation) Step 2: NS (bell) -> US (food) -> UR (salivation) Later... CS (bell) -> CR (salivation) | 149 | |
| 13826324754 | Watson's experiment | white rat was given to Little Albert Step 1: US (noise) -> UR (cry) Step 2: NS (rat) -> US (noise) -> UR (cry) Later... CS (rat) -> CR (cry) | 150 | |
| 13826324755 | generalization | any small, white fluffy creature will make Albert cry now | 151 | |
| 13826324756 | discriminate | any large, white fluffy creature won't make Albert cry | 152 | |
| 13826324757 | extinction | stop "treating" with conditioned response | 153 | |
| 13826324758 | spontaneous recovery | bring stimulus back after a while | 154 | |
| 13826324759 | operant conditioning | control by organism | 155 | |
| 13826324760 | Skinner's experiment | operant chamber / Skinner box (lead to shaping) | 156 | |
| 13826324761 | shaping | get animal closer to doing what you want them to do | 157 | |
| 13826324762 | reinforcers | want to continue behavior (positive reinforcement: give money to do laundry) (negative reinforcement: do to avoid nagging) | 158 | |
| 13826324763 | punishments | want to stop behavior (positive reinforcement: smack) (negative reinforcement: take away phone) | 159 | |
| 13826324764 | fixed ratio | happens a certain number of times (Starbucks punch card) | 160 | |
| 13826324765 | variable ratio | happens an unpredictable number of times (winning the lottery) | 161 | |
| 13826324766 | organism must do these (2 times) | fixed ratio and variable ratio | 162 | |
| 13826324767 | fixed interval | happens at a certain time (mailman comes to the house at 10:00 AM) | 163 | |
| 13826324768 | variable interval | happens at any time (receive texts from friends) | 164 | |
| 13826324769 | these things happen regardless (2 times) | fixed interval and variable interval | 165 | |
| 13826324770 | Which (fixed/variable) conditions better? | variable | 166 | |
| 13826324771 | criticisms of Skinner | doesn't take into account intrinsic motivation | 167 | |
| 13826324772 | intrinsic motivation | doing something for yourself, not the reward | 168 | |
| 13826324773 | extrinsic motivation | doing something for reward | 169 | |
| 13826324774 | Skinner's legacy | use it personally, at school, and at work | 170 | |
| 13826324775 | famous observational experiment | Bandura's Bobo doll | 171 | |
| 13826324776 | famous observational psychologist | Bandura | 172 | |
| 13826324777 | mirror neurons | "feel" what is observed happens in higher order animals | 173 | |
| 13826324778 | Bobo doll experiment legacy | violent video games/movies desensitize us see good: do good see evil: do evil | 174 | |
| 13826324779 | observational learning | biological behaviors work best | 175 | |
| 13826324780 | habituation | get used to it -> stop reacting | 176 | |
| 13826324781 | examples for observational learning | lectures and reading | 177 | |
| 13826324782 | serotonin involved with memory | speeds the connection between neurons | 178 | |
| 13826324783 | LTP | ((long-term potentiation)) strengthens potential neural forming (associated with speed) | 179 | |
| 13826324784 | CREB | protein that can switch genes on/off with memory and connection of memories | 180 | |
| 13826324785 | glutamate involved with memory | neurotransmitter that enhances LTP | 181 | |
| 13826324786 | glucose involved with memory | released during strong emotions ((signaling important event to be remembered)) | 182 | |
| 13826324787 | flashbulb memory | type of memory remembered because it was an important/quick moment | 183 | |
| 13826324788 | amygdala (memory) | boosts activity of proteins in memory-forming areas to fight/flight | 184 | |
| 13826324789 | cerebellum (memory) | forms and stores implicit memories ((classical conditioning)) | 185 | |
| 13826324790 | hippocampus (memory) | active during sleep (forming memories) ((information "moves" after 48 hours)) | 186 | |
| 13826324791 | memory | learning over time contains information that can be retrieved | 187 | |
| 13826324792 | processing stages | encoding -> storage -> retrieval | 188 | |
| 13826324793 | encoding | information going in | 189 | |
| 13826324794 | storage | keeping information in | 190 | |
| 13826324795 | retrieval | taking information out | 191 | |
| 13826324796 | How long is sensory memory stored? | seconds | 192 | |
| 13826324797 | How long is short-term memory stored? | less than a minute | 193 | |
| 13826324798 | How many bits of information is stored in short-term memory? | 7 | 194 | |
| 13826324799 | How many chunks of information is stored in short-term memory? | 4 | 195 | |
| 13826324800 | How many seconds of words is stored in short-term memory? | 2 | 196 | |
| 13826324801 | short term memory goes to ______________ | working memory | 197 | |
| 13826324802 | working memory | make a connection and process information to mean something | 198 | |
| 13826324803 | working memory goes to _________________ | long-term memory | 199 | |
| 13826324804 | How much is stored in long-term memory? | LIMITLESS | 200 | |
| 13826324805 | implicit memory | naturally do | 201 | |
| 13826324806 | explicit memory | need to explain | 202 | |
| 13826324807 | automatic processing | space, time, frequency, well-learned information | 203 | |
| 13826324808 | effortful processing | processing that requires effort | 204 | |
| 13826324809 | spacing effect | spread out learning over time | 205 | |
| 13826324810 | serial position effect | primary/recency effect | 206 | |
| 13826324811 | primary effect | remember the first things in a list | 207 | |
| 13826324812 | recency effect | remember the last things in a list | 208 | |
| 13826324813 | effortful processing (4 things) | 1. recency effect 2. spacing effect 3. testing effect 4. serial position effect | 209 | |
| 13826324814 | semantic encoding (1) meaning (2) how to | make meaning out of something --- chunk, hierarchy, or connect to you | 210 | |
| 13826324815 | if we can't remember a memory... | 1. change memory to suit us 2. fill in the blanks with logical story | 211 | |
| 13826324816 | misinformation effect | not correct information | 212 | |
| 13826324817 | imagination inflation | imagine or visualize something that isn't real | 213 | |
| 13826324818 | source amnesia | what is the truth? (is it a dream, story, memory, etc.?) | 214 | |
| 13826324819 | priming | association (setting you up) | 215 | |
| 13826324820 | context | environment helps with memory | 216 | |
| 13826324821 | state-dependency | you may remember something if you go back to the state you were in (go back to high) | 217 | |
| 13826324822 | mood-congruency | emotion will bring back similar emotional memories | 218 | |
| 13826324823 | forgetting curve | forget after 5 days forget after 5 years | 219 | |
| 13826324824 | the forgetting curve was created by | Ebbinghaus | 220 | |
| 13826324825 | proactive interference | old information interferes with the new | 221 | |
| 13826324826 | retroactive interference | new information interferes with the old | 222 | |
| 13826324827 | children can't remember before age __ | 3 | 223 | |
| 13826324828 | Loftus | connected to abuse cases/childhood | 224 | |
| 13826324829 | prototypes | generalize | 225 | |
| 13826324830 | problem-solving (4) | trial + error algorithms heuristic (representative + availability) insight - "AHA!" | 226 | |
| 13826324831 | against problem-solving | fixation | 227 | |
| 13826324832 | mental set | what has worked in the past | 228 | |
| 13826324833 | functional fixedness | only way to do this is with this | 229 | |
| 13826324834 | Chomsky (nature or nurture?) | "born with language" (nature) | 230 | |
| 13826324835 | Skinner (nature or nurture?) | language is learned (nurture) | 231 | |
| 13826324836 | grammar is _________ | universal | 232 | |
| 13826324837 | phonemes | smallest sound unit | 233 | |
| 13826324838 | morphemes | smallest meaning unit | 234 |
Flashcards
AP Psychology AP Review Flashcards
| 13890753289 | psychology | the study of behavior and mental processes | 0 | |
| 13890753290 | psychology's biggest question | Which is more important in determining behavior, nature or nurture? | 1 | |
| 13890753291 | psychology's three levels of analysis | biopsychosocial approach (looks at the biological, psychological, and social-cultural approaches together) | 2 | |
| 13890753292 | biological approach | Believes us to be as a consequence of our genetics and physiology. It is the only approach in psychology that examines thoughts, feelings, and behaviors from a biological and thus physical point of view | 3 | |
| 13890753293 | evolutionary approach | The brain (and therefore the mind) evolved to solve problems encountered by our hunter-gatherer ancestors during the upper Pleistocene period over 10,000 years ago. It explains behavior in terms of the selective pressures that shape behavior. | 4 | |
| 13890753294 | psychodynamic approach | An approach to psychology emphasizing unconscious thought, the conflict between biological drives (such as the drive for sex) and society's demands, and early childhood family experiences. (Freud) | 5 | |
| 13890753295 | behavioral approach | An approach to psychology emphasizing that human behavior is determined mainly by what a person has learned, especially from rewards and punishments | 6 | |
| 13890753296 | cognitive approach | According to this approach, behavior is a result of information processing, such as perception, memory, thought, judgment, and decision making | 7 | |
| 13890753297 | humanistic approach | Centers on the view that each person is unique and individual, and has the free will to change at any time in his or her lives. Suggests that we are each responsible for our own happiness and well-being as humans. We have the innate (i.e., inborn) capacity for self-actualization, which is our unique desire to achieve our highest potential as people. (Maslow and Rogers) | 8 | |
| 13890753298 | social-cultural approach | cultural, family, environment | 9 | |
| 13890753299 | two reasons of why experiments are important | hindsight bias + overconfidence | 10 | |
| 13890753300 | types of research methods | descriptive, correlational, and experimental | 11 | |
| 13890753301 | descriptive methods | case study survey naturalistic observation (DON'T SHOW CAUSE/EFFECT) | 12 | |
| 13890753302 | case study | studies one person in depth may not be typical of population | 13 | |
| 13890753303 | survey | studies lots of people not in depth | 14 | |
| 13890753304 | naturalistic observation | observe + write facts without interference | 15 | |
| 13890753305 | correlational method | shows relation, but not cause/effect scatterplots show research | 16 | |
| 13890753306 | correlation coefficient | + 1.0 (both increase) 0 (no correlation - 1.0 (one increases, other decreases) | 17 | |
| 13890753307 | experimental method | does show cause and effect | 18 | |
| 13890753308 | population | type of people who are going to be used in experiment | 19 | |
| 13890753309 | sample | actual people who will be used (randomness reduces bias) | 20 | |
| 13890753310 | random assignment | chance selection between experimental and control groups | 21 | |
| 13890753311 | control group | not receiving experimental treatment receives placebo | 22 | |
| 13890753312 | experimental group | receiving treatment/drug | 23 | |
| 13890753313 | independent variable | drug/procedure/treatment | 24 | |
| 13890753314 | dependent variable | outcome of using the drug/treatment | 25 | |
| 13890753315 | confounding variable | can affect dependent variable beyond experiment's control | 26 | |
| 13890753316 | scientific method | theory hypothesis operational definition revision | 27 | |
| 13890753317 | theory | general idea being tested | 28 | |
| 13890753318 | hypothesis | measurable/specific | 29 | |
| 13890753319 | operational definition | procedures that explain components | 30 | |
| 13890753320 | mode | appears the most | 31 | |
| 13890753321 | mean | average | 32 | |
| 13890753322 | median | middle | 33 | |
| 13890753323 | range | highest - lowest | 34 | |
| 13890753324 | standard deviation | how scores vary around the mean | 35 | |
| 13890753325 | central tendency | single score that represents the whole | 36 | |
| 13890753326 | bell curve | (natural curve) |  | 37 |
| 13890753327 | ethics of testing on animals | need to be treated humanly basically similar to humans | 38 | |
| 13890753328 | ethics of testing on humans | consent debriefing no unnecessary discomfort/pain confidentiality | 39 | |
| 13890753329 | sensory neurons | travel from sensory receptors to brain | 40 | |
| 13890753330 | motor neurons | travel from brain to "motor" workings | 41 | |
| 13890753331 | interneurons | (in brain and spinal cord) connecting motor and sensory neurons | 42 | |
| 13890753523 | neuron |  | 43 | |
| 13890753332 | dendrites | receive messages from other neurons | 44 | |
| 13890753333 | myelin sheath | protects the axon | 45 | |
| 13890753334 | axon | where charges travel from cell body to axon terminal | 46 | |
| 13890753335 | neurotransmitters | chemical messengers | 47 | |
| 13890753336 | reuptake | extra neurotransmitters are taken back | 48 | |
| 13890753337 | excitatory charge | "Let's do it!" | 49 | |
| 13890753338 | inhibitory charge | "Let's not do it!" | 50 | |
| 13890753339 | central nervous system | brain and spinal cord | 51 | |
| 13890753340 | peripheral nervous system | somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system | 52 | |
| 13890753341 | somatic nervous system | voluntary movements | 53 | |
| 13890753342 | autonomic nervous system | involuntary movements (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems) | 54 | |
| 13890753343 | sympathetic nervous system | arousing | 55 | |
| 13890753344 | parasympathetic nervous system | calming | 56 | |
| 13890753345 | neural networks | more connections form with greater use others fall away if not used | 57 | |
| 13890753346 | spinal cord | expressway of information bypasses brain when reflexes involved | 58 | |
| 13890753347 | endocrine system | slow uses hormones in the blood system | 59 | |
| 13890753348 | master gland | pituitary gland | 60 | |
| 13890753349 | brainstem | extension of the spinal cord responsible for automatic survival | 61 | |
| 13890753350 | reticular formation (if stimulated) | sleeping subject wakes up | 62 | |
| 13890753351 | reticular formation (if damaged) | coma | 63 | |
| 13890753352 | brainstem (if severed) | still move (without purpose) | 64 | |
| 13890753353 | thalamus | sensory switchboard (does not process smell) | 65 | |
| 13890753354 | hypothalamus | basic behaviors (hunger, thirst, sex, blood chemistry) | 66 | |
| 13890753355 | cerebellum | nonverbal memory, judge time, balance emotions, coordinate movements | 67 | |
| 13890753356 | cerebellum (if damaged) | difficulty walking and coordinating | 68 | |
| 13890753357 | amygdala | aggression, fear, and memory associated with these emotions | 69 | |
| 13890753358 | amygdala (if lesioned) | subject is mellow | 70 | |
| 13890753359 | amygdala (if stimulated) | aggressive | 71 | |
| 13890753360 | hippocampus | process new memory | 72 | |
| 13890753361 | cerebrum | two large hemispheres perceiving, thinking, and processing | 73 | |
| 13890753362 | cerebral cortex | only in higher life forms | 74 | |
| 13890753363 | association areas | integrate and interpret information | 75 | |
| 13890753364 | glial cells | provide nutrients to myelin sheath marks intelligence higher proportion of glial cells to neurons | 76 | |
| 13890753365 | frontal lobe | judgement, personality, processing (Phineas Gage accident) | 77 | |
| 13890753366 | parietal lobe | math and spatial reasoning | 78 | |
| 13890753367 | temporal lobe | audition and recognizing faces | 79 | |
| 13890753368 | occipital lobe | vision | 80 | |
| 13890753369 | corpus callosum | split in the brain to stop hyper-communication (eliminate epileptic seizures) | 81 | |
| 13890753370 | Wernicke's area | interprets auditory and hearing | 82 | |
| 13890753371 | Broca's area | speaking words | 83 | |
| 13890753372 | plasticity | ability to adapt if damaged | 84 | |
| 13890753373 | sensation | what our senses tell us | 85 | |
| 13890753374 | bottom-up processing | senses to brain | 86 | |
| 13890753375 | perception | what our brain tells us to do with that information | 87 | |
| 13890753376 | top-down processing | brain to senses | 88 | |
| 13890753377 | inattentional blindness | fail to "gorilla" because attention is elsewhere | 89 | |
| 13890753378 | cocktail party effect | even with tons of stimuli, we are able to pick out our name, etc. | 90 | |
| 13890753379 | change blindness | giving directions and person is changed and we don't notice | 91 | |
| 13890753380 | choice blindness | when defending the choice we make, we fail to notice choice was changed | 92 | |
| 13890753381 | absolute threshold | minimum stimulation needed in order to notice 50% of the time | 93 | |
| 13890753382 | signal detection theory | we notice what is more important to us (rather hear a baby crying) | 94 | |
| 13890753383 | JND (just noticeable difference) | (Weber's law) difference between different stimuli noticed in proportion | 95 | |
| 13890753384 | sensory adaptation | tired of noticing (Brain says, "Been there, done that. Next?" | 96 | |
| 13890753385 | rods | night time | 97 | |
| 13890753386 | cones | color | 98 | |
| 13890753387 | parallel processing | notice color, form, depth, movement, etc. | 99 | |
| 13890753388 | Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory | 3 corresponding color receptors (RGB) | 100 | |
| 13890753389 | Hering's opponent-process theory | after image in opposite colors (RG, YB, WB) | 101 | |
| 13890753390 | trichromatic + opponent-process | Young-Helmholtz -> color stimuli Hering -> en route to cortex | 102 | |
| 13890753391 | frequency we hear most | human voice | 103 | |
| 13890753392 | Helmoltz (hearing) | we hear different pitches in different places in basilar membrane (high pitches) | 104 | |
| 13890753393 | frequency theory | impulse frequency (low pitches) | 105 | |
| 13890753394 | Helmholtz + frequency theory | middle pitches | 106 | |
| 13890753395 | Skin feels what? | warmth, cold, pressure, pain | 107 | |
| 13890753396 | gate-control theory | small fibers - pain large fibers - other senses | 108 | |
| 13890753397 | memory of pain | peaks and ends | 109 | |
| 13890753398 | smell | close to memory section (not in thalamus) | 110 | |
| 13890753399 | grouping | Gestalt make sense of pieces create a whole | 111 | |
| 13890753400 | grouping groups | proximity similarity continuity connectedness closure | 112 | |
| 13890753401 | make assumptions of placement | higher - farther smaller - farther blocking - closer, in front | 113 | |
| 13890753402 | perception = | mood + motivation | 114 | |
| 13890753403 | consciousness | awareness of ourselves and the environment | 115 | |
| 13890753404 | circadian rhythm | daily biological clock and regular cycle (sleep and awake) | 116 | |
| 13890753405 | circadian rhythm pattern | - activated by light - light sensitive retinal proteins signal brains SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) - pineal gland decreases melatonin | 117 | |
| 13890753406 | What messes with circadian rhythm? | artificial light | 118 | |
| 13890753407 | The whole sleep cycle lasts how long? | 90 minutes | 119 | |
| 13890753408 | sleep stages | relaxed stage (alpha waves) stage 1 (early sleep) (hallucinations) stage 2 (sleep spindles - bursts of activity) (sleep talk) stage 3 (transition phase) (delta waves) stage 4 (delta waves) (sleepwalk/talk + wet the bed) stage 5 (REM) (sensory-rich dreams) (paradoxical sleep) | 120 | |
| 13890753409 | purpose of sleep | 1. recuperation - repair neurons and allow unused neural connections to wither 2. making memories 3. body growth (children sleep more) | 121 | |
| 13890753410 | insomnia | can't sleep | 122 | |
| 13890753411 | narcolepsy | fall asleep anywhere at anytime | 123 | |
| 13890753412 | sleep apnea | stop breathing in sleep | 124 | |
| 13890753413 | night terrors | prevalent in children | 125 | |
| 13890753414 | sleepwalking/sleeptalking | hereditary - prevalent in children | 126 | |
| 13890753415 | dreaming (3) | 1. vivid bizarre intense sensory experiences 2. carry fear/survival issues - vestiges of ancestors' survival ideas 2. replay previous day's experiences/worries | 127 | |
| 13890753416 | purpose of dreaming (5 THEORIES) | 1. physiological function - develop/preserve neural pathways 2. Freud's wish-fulfillment (manifest/latent content) 3. activation synthesis - make sense of stimulation originating in brain 4. information processing 5. cognitive development - reflective of intelligence | 128 | |
| 13890753417 | 1. Can hypnosis bring you back in time? 2. Can hypnosis make you do things you wouldn't normally do? 3. Can it alleviate pain? 4. What state are you in during hypnosis? 5. Who is more susceptible? | 1. cannot take you back in time 2. cannot make you do things you won't do 3. can alleviate pain 4. fully conscious ((IMAGINATIVE PEOPLE MORE SUSCEPTIBLE)) | 129 | |
| 13890753418 | depressants | slows neural pathways | 130 | |
| 13890753419 | alcohol | ((depressant)) disrupts memory formation (REM) lowers inhibition expectancy effect | 131 | |
| 13890753420 | barbituates (tranquilizers) | ((depressant)) reduce anxiety | 132 | |
| 13890753421 | opiates | ((depressant)) pleasure reduce anxiety/pain | 133 | |
| 13890753422 | stimulants | hypes neural processing | 134 | |
| 13890753423 | methamphetamine | ((stimulant)) heightens energy euphoria affects dopamine | 135 | |
| 13890753424 | caffeine | ((stimulant)) | 136 | |
| 13890753425 | nicotine | ((stimulant)) CNS releases neurotransmitters calm anxiety reduce pain affects (nor)epinephrine and dopamine | 137 | |
| 13890753426 | cocaine | ((stimulant)) euphoria affects dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine | 138 | |
| 13890753427 | hallucinogen | excites neural activity | 139 | |
| 13890753428 | ecstasy | ((hallucinogen)) reuptake is blocked affects dopamine and serotonin | 140 | |
| 13890753429 | LSD | ((hallucinogen)) affects sensory/emotional "trip" (+/-) affects serotonin | 141 | |
| 13890753430 | marijuana | ((hallucinogen)) amplify sensory experience disrupts memory formation | 142 | |
| 13890753431 | learning | organism changing behavior due to experience (association of events) | 143 | |
| 13890753432 | types of learning | classical operant observational | 144 | |
| 13890753433 | famous classical psychologists | Pavlov and Watson | 145 | |
| 13890753434 | famous operant psychologist | Skinner | 146 | |
| 13890753435 | famous observational psychologists | Bandura | 147 | |
| 13890753436 | classical conditioning | outside stimulus | 148 | |
| 13890753437 | Pavlov's experiment | Step 1: US (food) -> UR (salivation) Step 2: NS (bell) -> US (food) -> UR (salivation) Later... CS (bell) -> CR (salivation) | 149 | |
| 13890753438 | Watson's experiment | white rat was given to Little Albert Step 1: US (noise) -> UR (cry) Step 2: NS (rat) -> US (noise) -> UR (cry) Later... CS (rat) -> CR (cry) | 150 | |
| 13890753439 | generalization | any small, white fluffy creature will make Albert cry now | 151 | |
| 13890753440 | discriminate | any large, white fluffy creature won't make Albert cry | 152 | |
| 13890753441 | extinction | stop "treating" with conditioned response | 153 | |
| 13890753442 | spontaneous recovery | bring stimulus back after a while | 154 | |
| 13890753443 | operant conditioning | control by organism | 155 | |
| 13890753444 | Skinner's experiment | operant chamber / Skinner box (lead to shaping) | 156 | |
| 13890753445 | shaping | get animal closer to doing what you want them to do | 157 | |
| 13890753446 | reinforcers | want to continue behavior (positive reinforcement: give money to do laundry) (negative reinforcement: do to avoid nagging) | 158 | |
| 13890753447 | punishments | want to stop behavior (positive reinforcement: smack) (negative reinforcement: take away phone) | 159 | |
| 13890753448 | fixed ratio | happens a certain number of times (Starbucks punch card) | 160 | |
| 13890753449 | variable ratio | happens an unpredictable number of times (winning the lottery) | 161 | |
| 13890753450 | organism must do these (2 times) | fixed ratio and variable ratio | 162 | |
| 13890753451 | fixed interval | happens at a certain time (mailman comes to the house at 10:00 AM) | 163 | |
| 13890753452 | variable interval | happens at any time (receive texts from friends) | 164 | |
| 13890753453 | these things happen regardless (2 times) | fixed interval and variable interval | 165 | |
| 13890753454 | Which (fixed/variable) conditions better? | variable | 166 | |
| 13890753455 | criticisms of Skinner | doesn't take into account intrinsic motivation | 167 | |
| 13890753456 | intrinsic motivation | doing something for yourself, not the reward | 168 | |
| 13890753457 | extrinsic motivation | doing something for reward | 169 | |
| 13890753458 | Skinner's legacy | use it personally, at school, and at work | 170 | |
| 13890753459 | famous observational experiment | Bandura's Bobo doll | 171 | |
| 13890753460 | famous observational psychologist | Bandura | 172 | |
| 13890753461 | mirror neurons | "feel" what is observed happens in higher order animals | 173 | |
| 13890753462 | Bobo doll experiment legacy | violent video games/movies desensitize us see good: do good see evil: do evil | 174 | |
| 13890753463 | observational learning | biological behaviors work best | 175 | |
| 13890753464 | habituation | get used to it -> stop reacting | 176 | |
| 13890753465 | examples for observational learning | lectures and reading | 177 | |
| 13890753466 | serotonin involved with memory | speeds the connection between neurons | 178 | |
| 13890753467 | LTP | ((long-term potentiation)) strengthens potential neural forming (associated with speed) | 179 | |
| 13890753468 | CREB | protein that can switch genes on/off with memory and connection of memories | 180 | |
| 13890753469 | glutamate involved with memory | neurotransmitter that enhances LTP | 181 | |
| 13890753470 | glucose involved with memory | released during strong emotions ((signaling important event to be remembered)) | 182 | |
| 13890753471 | flashbulb memory | type of memory remembered because it was an important/quick moment | 183 | |
| 13890753472 | amygdala (memory) | boosts activity of proteins in memory-forming areas to fight/flight | 184 | |
| 13890753473 | cerebellum (memory) | forms and stores implicit memories ((classical conditioning)) | 185 | |
| 13890753474 | hippocampus (memory) | active during sleep (forming memories) ((information "moves" after 48 hours)) | 186 | |
| 13890753475 | memory | learning over time contains information that can be retrieved | 187 | |
| 13890753476 | processing stages | encoding -> storage -> retrieval | 188 | |
| 13890753477 | encoding | information going in | 189 | |
| 13890753478 | storage | keeping information in | 190 | |
| 13890753479 | retrieval | taking information out | 191 | |
| 13890753480 | How long is sensory memory stored? | seconds | 192 | |
| 13890753481 | How long is short-term memory stored? | less than a minute | 193 | |
| 13890753482 | How many bits of information is stored in short-term memory? | 7 | 194 | |
| 13890753483 | How many chunks of information is stored in short-term memory? | 4 | 195 | |
| 13890753484 | How many seconds of words is stored in short-term memory? | 2 | 196 | |
| 13890753485 | short term memory goes to ______________ | working memory | 197 | |
| 13890753486 | working memory | make a connection and process information to mean something | 198 | |
| 13890753487 | working memory goes to _________________ | long-term memory | 199 | |
| 13890753488 | How much is stored in long-term memory? | LIMITLESS | 200 | |
| 13890753489 | implicit memory | naturally do | 201 | |
| 13890753490 | explicit memory | need to explain | 202 | |
| 13890753491 | automatic processing | space, time, frequency, well-learned information | 203 | |
| 13890753492 | effortful processing | processing that requires effort | 204 | |
| 13890753493 | spacing effect | spread out learning over time | 205 | |
| 13890753494 | serial position effect | primary/recency effect | 206 | |
| 13890753495 | primary effect | remember the first things in a list | 207 | |
| 13890753496 | recency effect | remember the last things in a list | 208 | |
| 13890753497 | effortful processing (4 things) | 1. recency effect 2. spacing effect 3. testing effect 4. serial position effect | 209 | |
| 13890753498 | semantic encoding (1) meaning (2) how to | make meaning out of something --- chunk, hierarchy, or connect to you | 210 | |
| 13890753499 | if we can't remember a memory... | 1. change memory to suit us 2. fill in the blanks with logical story | 211 | |
| 13890753500 | misinformation effect | not correct information | 212 | |
| 13890753501 | imagination inflation | imagine or visualize something that isn't real | 213 | |
| 13890753502 | source amnesia | what is the truth? (is it a dream, story, memory, etc.?) | 214 | |
| 13890753503 | priming | association (setting you up) | 215 | |
| 13890753504 | context | environment helps with memory | 216 | |
| 13890753505 | state-dependency | you may remember something if you go back to the state you were in (go back to high) | 217 | |
| 13890753506 | mood-congruency | emotion will bring back similar emotional memories | 218 | |
| 13890753507 | forgetting curve | forget after 5 days forget after 5 years | 219 | |
| 13890753508 | the forgetting curve was created by | Ebbinghaus | 220 | |
| 13890753509 | proactive interference | old information interferes with the new | 221 | |
| 13890753510 | retroactive interference | new information interferes with the old | 222 | |
| 13890753511 | children can't remember before age __ | 3 | 223 | |
| 13890753512 | Loftus | connected to abuse cases/childhood | 224 | |
| 13890753513 | prototypes | generalize | 225 | |
| 13890753514 | problem-solving (4) | trial + error algorithms heuristic (representative + availability) insight - "AHA!" | 226 | |
| 13890753515 | against problem-solving | fixation | 227 | |
| 13890753516 | mental set | what has worked in the past | 228 | |
| 13890753517 | functional fixedness | only way to do this is with this | 229 | |
| 13890753518 | Chomsky (nature or nurture?) | "born with language" (nature) | 230 | |
| 13890753519 | Skinner (nature or nurture?) | language is learned (nurture) | 231 | |
| 13890753520 | grammar is _________ | universal | 232 | |
| 13890753521 | phonemes | smallest sound unit | 233 | |
| 13890753522 | morphemes | smallest meaning unit | 234 |
Flashcards
AP Lit Tone Words Flashcards
all the tone words that you will ever need and more
| 13513739435 | aloof | not emotionally involved, at a distance |  | 0 |
| 13513739436 | apathetic | uncaring |  | 1 |
| 13513739437 | ambivalent | having mixed feelings, could go either way |  | 2 |
| 13513739438 | audacious | recklessly bold or contemptuous; |  | 3 |
| 13513739439 | Bellicose | inclined or eager to fight |  | 4 |
| 13513739440 | callous | uncaring, or feeling no emotion |  | 5 |
| 13513739441 | condescending | with an air of superiority, talking down to |  | 6 |
| 13513739442 | contemptuous | lacking respect, derisive |  | 7 |
| 13513739443 | caustic | harshly sarcastic |  | 8 |
| 13513739444 | cautionary | prudent forethought |  | 9 |
| 13513739445 | Choleric | easily angered |  | 10 |
| 13513739446 | churlish | boorish, rude |  | 11 |
| 13513739447 | cynical | distrustful (like Lucas:) |  | 12 |
| 13513739448 | demoralized | discouraged; depressed |  | 13 |
| 13513739449 | diffident | reserved, unassertive |  | 14 |
| 13513739450 | disdainful | scorn, despise |  | 15 |
| 13513739451 | didactic | intending to instruct |  | 16 |
| 13513739452 | derisive | insulting and condescending |  | 17 |
| 13513739453 | earnest | heartfelt and serious |  | 18 |
| 13513739454 | effusive | overflowing and demonstrative |  | 19 |
| 13513739455 | enervating | to deprive of force or strength; destroy the vigor of; weaken |  | 20 |
| 13513739456 | elegiac | sorrowful lamentation |  | 21 |
| 13513739457 | empathetic | sensitivity, relating to another's emotions |  | 22 |
| 13513739458 | erudite | scholarly, learned, bookish, pedantic |  | 23 |
| 13513739459 | facetious | sarcastic |  | 24 |
| 13513739460 | fatuous | foolish or insane; silly or pointless |  | 25 |
| 13513739461 | forthright | direct and outspoken; straightforward and honest |  | 26 |
| 13513739462 | flippant | frivolously disrespectful, shallow, or lacking in seriousness |  | 27 |
| 13513739463 | frivolous | carefree and unconcerned |  | 28 |
| 13513739464 | gauche | lacking social grace, sensitivity, or acuteness; awkward; crude; tactless |  | 29 |
| 13513739465 | hubristic | excessively prideful, arrogant, or self-confident |  | 30 |
| 13513739466 | incredulous | skeptical and unbelieving |  | 31 |
| 13513739467 | incensed | full of rage |  | 32 |
| 13513739468 | indignant | righteously angry |  | 33 |
| 13513739469 | intimate | personal and emotional |  | 34 |
| 13513739470 | jejune | immature or childish |  | 35 |
| 13513739471 | jovial | hearty conviviality and good cheer |  | 36 |
| 13513739473 | laudatory | praiseful |  | 37 |
| 13513739474 | laissez-faire | laid back, unwilling to get involved |  | 38 |
| 13513739475 | lugubrious | mournful, dismal, or gloomy |  | 39 |
| 13513739476 | morose | ill-humored, very down |  | 40 |
| 13513739477 | malicious | vicious, wanton, or mischievous |  | 41 |
| 13513739478 | mordant | caustic or sarcastic in a mean way |  | 42 |
| 13513739479 | Nihilistic | totally rejecting of established laws or institutions; rejecting all religious and moral principles in the belief that life is meaningless |  | 43 |
| 13513739480 | obsequious | overly obedient, dutiful, brown-nosing, fawning |  | 44 |
| 13513739481 | omnipotent | all mighty or infinite in power; all-knowing |  | 45 |
| 13513739482 | patronizing | talking down to, conveying experience to one who has none |  | 46 |
| 13513739483 | pompous | stuck up, considering self better than everyone else |  | 47 |
| 13513739484 | poignant | producing keen or strong emotion; totally touching |  | 48 |
| 13513739485 | provocative | inciting, stimulating, irritating |  | 49 |
| 13513739486 | quizzical | questioning, ridiculing, or chaffing |  | 50 |
| 13513739487 | reticent | reluctant or restrained |  | 51 |
| 13513739488 | reverent | deeply respectful; showing great esteem |  | 52 |
| 13513739489 | reflective | meditative or deliberative |  | 53 |
| 13513739490 | resigned | passive, accepting as inevitable |  | 54 |
| 13513739491 | ribald | abusive, or irreverent; vulgar or indecent |  | 55 |
| 13513739492 | sardonic | scornful derision, mocking, cynical |  | 56 |
| 13513739493 | seductive | enticing; beguiling; captivating; alluring |  | 57 |
| 13513739494 | sentimental | emotional attachment |  | 58 |
| 13513739495 | supercilious | haughty, disdainful or contemptuous |  | 59 |
| 13513739496 | unctuous | smug, oily (verbally that is) or excessively pious |  | 60 |
| 13513739497 | vehement | with great energy or exertion, with great emphasis and passion |  | 61 |
| 13513739498 | volatile | tending or threatening to break out into open violence |  | 62 |
AP EXAM Flashcards
| 13921577224 | environmental determinism | Human behaviors are a direct result of the surrounding environment. | 0 | |
| 13921577225 | Possibilist | humans are not a product of their environment but possess the skills necessary to modify their environment to fit human needs | 1 | |
| 13921577226 | GIS (geographic information system) | Layers geographic information into a new map, showing specific data (can be used for data of watersheds, population, density, highways, and agricultural data) | 2 | |
| 13921577227 | Remote sensing | Studying an object or location without making direct contact with it | 3 | |
| 13921577228 | equal area projection | Maps that try to distribute distortion equally throughout the map, these maps distort shape | 4 | |
| 13921577229 | Conformal maps | maps that distort area but keep shapes intact |  | 5 |
| 13921577230 | Cylindrical maps | Maps that show true direction but lose distance (e.g., a Mercator map). |  | 6 |
| 13921577231 | Planar maps | Maps that show true direction and examine the Earth from one point, usually from a pole or a polar direction (e.g., any azimuthal map). |  | 7 |
| 13921577232 | Conic maps | Maps that put a cone over the earth and keep distance intact but lose directional qualities |  | 8 |
| 13921577233 | Oval maps | Maps that combine the cylindrical and conic projections (e.g., Molleweide Projection) |  | 9 |
| 13921577234 | Thematic maps | Maps that determine geographic phenomenon (area class maps, area symbol maps, cartograms, choropleth maps, digital images, dot maps, flow line maps, isoline maps, point symbol maps, proportional symbol maps) |  | 10 |
| 13921577235 | Isoline maps | Outlines and connects points of identical value (weather map) |  | 11 |
| 13921577236 | Flow line maps | Maps that are good for determining movement, such as migration trends. |  | 12 |
| 13921577237 | Choropleth maps | Maps that put data into spatial format. Useful for determining demographic data, by assigning colors or patterns to areas |  | 13 |
| 13921593566 | toponym | place name | 14 | |
| 13921595812 | geography | the study of the earth's physical and cultural features | 15 | |
| 13921609369 | GPS (global positioning system) | uses longitude and latitude to determine exact location (found in cars and cellphones) | 16 | |
| 13921622235 | satellite imagery | Images of the earth taken from orbiting satellites. important for GIS and remote sensing | 17 | |
| 13921630273 | scale | the relationship of the size of the map to the amount of area it represents on the planet | 18 | |
| 13921639093 | human geography | The study of human characteristics on the landscape, including population, agriculture, urbanization, and culture. | 19 | |
| 13921719218 | cartograms | Maps that assign space by the size of some datum. (ex- population) | 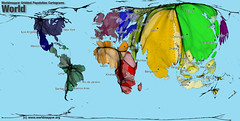 | 20 |
| 13921733483 | dot map | A map that uses dots to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences (ex- density) |  | 21 |
| 13921741784 | built landscape | produced by the physical material culture, sum of tangible human creations on the landscape | 22 | |
| 13921752298 | sequent occupance | the idea that each civilization leaves an influence on the cultural landscape of a place, affecting the civilizations that come after them | 23 | |
| 13921768160 | Physical Geography | the study of physical features of the earth's surface | 24 | |
| 13921780659 | region | a concept used to link different places together based on any parameter the geographer chooses | 25 | |
| 13921787151 | formal regions | regions where anything and everything inside has the same characteristic or phenomena (ex- democratic party) | 26 | |
| 13921792775 | functional regions | regions that can be defined around a certain point or node, experience distance decay (ex- wifi spots, pizza delivery) | 27 | |
| 13921811811 | Distance Decay | the lessening of a phenomenon as the distance from the hearth increases | 28 | |
| 13921815128 | friction of distance | people will feel resistance to going some place far away because of energy and money | 29 | |
| 13921832276 | perceptual/vernacular region | a region that exists primarily in the individual's idea of a place or feelings on the place (ex- midwest, south) | 30 | |
| 13921841488 | relative location | the location of a place in relation to another place | 31 | |
| 13921847479 | absolute location | location based on longitude and latitude | 32 | |
| 13921851566 | site | the internal characteristics of a place based on its physical features | 33 | |
| 13921853817 | situation | the relationship that a particular location has with the locations around it | 34 | |
| 13921863007 | mental map | A map which represents the perceptions and knowledge a person has of an area | 35 | |
| 13921866322 | latitudes | parallel lines that run east/west on the surface of the earth (highest degree is 90) | 36 | |
| 13921876426 | equator | 0 degrees latitude (divides northern and southern hemispheres) | 37 | |
| 13921883046 | Longitude | parallel lines that run north/south on earth's surface | 38 | |
| 13921888343 | prime meridian | 0 degrees longitude (divides eastern and western hemispheres) | 39 | |
| 13921898678 | time zone | a geographic region within which the same standard time is used (15 degrees longitude apart, 24 zones) | 40 | |
| 13921916262 | international date line | an imaginary boundary between one day and the next (180 degrees longitude) | 41 | |
| 13921934706 | Human Environment Interaction | how people modify or alter the environment to fit their needs | 42 | |
| 13921941769 | five toos | too hot, too cold, too wet, too dry, too hilly | 43 | |
| 13921943763 | spatial interaction | how well an area is connected to the world determines its importance | 44 | |
| 13921953816 | time-space compression | increasing interconnectedness that human civilization enjoys despite physical distance being fixed (ex- social media, facetime) | 45 | |
| 13921967387 | hearth | the place where something begins | 46 | |
| 13921976573 | relocation diffusion | spreading when people move (ex- language) | 47 | |
| 13921979833 | expansion diffusion | spreading of an idea through a central node through hierarchical, contagious, or stimulus diffusion | 48 | |
| 13921994813 | Hierarchical Diffusion | spreading through the elite leaders (ex- celebrities, political leaders) | 49 | |
| 13922009010 | Contagious Diffusion | The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population (ex- viral videos, diseases) | 50 | |
| 13922021084 | stimulus diffusion | the spread of a particular concept that is then used in another product, but is adapted (ex- pasta) | 51 | |
| 13922037331 | density | how often an object occurs within a given area | 52 | |
| 13922053842 | Physiological Density | The number of people per unit of area of arable land | 53 | |
| 13922060311 | Arithmetic Density | The total number of people divided by the total land area. | 54 | |
| 13922062882 | Concentration | density of a particular phenomenon over an area (clustered or dispersed) | 55 | |
| 13922072523 | Clustered/Agglomerated | objects are close together | 56 | |
| 13922077787 | Dispersed/Scattered | objects are spread out | 57 | |
| 13922082153 | linear | a pattern where items are laid out in a singular line | 58 | |
| 13922090361 | centralized | a pattern where items are clustered together | 59 | |
| 13922093236 | random distribution | lack of pattern on a landscape | 60 | |
| 13922097866 | ecological fallacy | assumption that the relationships at one scale also exist at other scales (ex- group level also exists at individual level) | 61 | |
| 13922134619 | rank-size rule | cities relative population sizes relate to their rank within a country | 62 | |
| 13922150971 | Demography | study of population characteristics | 63 | |
| 13922154742 | birth rate | number of births per 1,000 people in the population | 64 | |
| 13922157935 | death rate | number of deaths per 1,000 people in the population | 65 | |
| 13922162725 | population explosion | crisis where population growth occurs in countries that are ill-prepared to handle the growing number of people | 66 | |
| 13922177214 | ecumene | habitable land | 67 | |
| 13922182285 | underpopulation | a sharp drop or decrease in a region's population | 68 | |
| 13922188856 | Overpopulation | too many people in one place for the resources available | 69 | |
| 13922191622 | carrying capacity | Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support | 70 | |
| 13922196682 | environmental degradation | harming of the environment (when humans place a strain on the environmental resources) | 71 | |
| 13922214625 | Thomas Malthus | concluded that population was growing at a faster rate than productivity in the 1700s (population will outrun food) | 72 | |
| 13922267599 | linear growth | growth that occurs evenly across each unit of time | 73 | |
| 13922270005 | exponential growth | growth as a percentage of the total population | 74 | |
| 13922275680 | Neo-Malthusians | people who believed thomas malthus and are critical of the demographic transition model | 75 | |
| 13922287603 | Demographic Transition Model | indicator of what will happen to a society's population based on birth rate, death rate, and total population | 76 | |
| 13922306116 | demographic transition model stage 1 | High death rates, high birth rates, low growth, hunting and gathering societies, no one is in this stage today | 77 | |
| 13922331148 | demographic transition model stage 2 | high birth rate, low death rate, sharp increase in growth, agricultural societies, sub-saharan africa | 78 | |
| 13922358486 | demographic transition model stage 3 | low death rates, decreasing birth rates, moderate growth, industrial societies, central and south america | 79 | |
| 13922392484 | demographic transition model stage 4 | birth rates and death rates almost equal, stable growth, tertiary societies, europe and usa | 80 | |
| 13922419174 | demographic transition model stage 5 | Very low birth rates, low death rates, population decrease, japan | 81 | |
| 13922442360 | s curve | starts in stage 2 of DTM when total population begins to increase, stabilizes in stage 4, creates s shaped curve | 82 | |
| 13922455163 | zero population growth | a phenomenon in stage 4 of DTM when birth rate equals death rate | 83 | |
| 13922463528 | sex ratio | The number of males per 100 females in the population. | 84 | |
| 13922466121 | Age Distribution | individual brackets that demonstrate age groupings in population pyramids | 85 | |
| 13922477982 | population projection | estimate of future population size, age, and sex composition | 86 | |
| 13922480591 | dependency ratio | ratio that states people aged 0-14 and over 65 depend on the workforce for support | 87 | |
| 13922496499 | demographic momentum | a continued population increase as a result of a large segment of the population being young (stage 2 of DTM) | 88 | |
| 13922507380 | negative growth | when the natural increase rate falls below 2, the country begins to lose population (stage 5 of DTM) | 89 | |
| 13922517055 | demographic equation | Determines the population growth rate for the world by subtracting global deaths from global births. | 90 | |
| 13922527073 | infant mortality rate | number of babies that die before 1 year | 91 | |
| 13922531269 | doubling time | The number of years needed to double a population | 92 | |
| 13922542609 | Sustainability | saving of resources for future generations so they can live at the same or higher standard of life as us | 93 | |
| 13922554247 | j curve | a growth curve that depicts exponential growth | 94 | |
| 13922561079 | net migration | the number of immigrants minus the number of emigrants | 95 | |
| 13922565109 | place utility | when communities offer incentives for people to move to their areas | 96 | |
| 13922575099 | internal migration | movement within a country | 97 | |
| 13922577023 | Ravenstein's Laws of Migration | ten statements related to migration made in 1885 | 98 | |
| 13922585476 | human capital model | people seek to improve their incomes over the course of their lives; people weigh costs against the benefits if migrating. (developed by larry sjaastad in 1962) | 99 | |
| 13922607140 | life course theory | people make major decisions early on in life that may dictate migration prefernces in the future. (deveolped in 1960s) | 100 | |
| 13922630849 | Intercontinental Migration | movement across international borders | 101 | |
| 13922637290 | Acculturation | The adoption of cultural traits by one group under the influence of another (ex- language, adopts new country's ways) | 102 | |
| 13922930508 | Chain Migration | migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there | 103 | |
| 13922934848 | Interregional Migration | migration within a country (region to region) | 104 | |
| 13922940328 | International Migration | movement from one country to another. | 105 | |
| 13922943436 | Intraregional Migration | movement within one region | 106 | |
| 13922947174 | cyclic migration | seasonal migration, often associated with agricultural seasons | 107 | |
| 13922957427 | transhumance | The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures. | 108 | |
| 13922959898 | intervening obstacle | An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration. | 109 | |
| 13922964045 | intervening opportunity | causes a migrant to stop and stay at a location along their journey because they like it more (economic or environmental) | 110 | |
| 13922979003 | transmigration | removal of people from one place and their relocation somewhere else within a country | 111 | |
| 13922990400 | material culture | anything that can physically seen on the landscape | 112 | |
| 13922997371 | built environment | tangible impact of human beings on the landscape | 113 | |
| 13923001030 | nonmaterial culture | anything on the landscape that comprises culture that cannot be physically touched (ex- language and religion) | 114 | |
| 13923013363 | folk culture | the practice of a particular custom of a relatively small group of people that increases the group's uniqueness | 115 | |
| 13923016861 | folklore | the traditional beliefs, customs, and stories of a community, passed through the generations by word of mouth. | 116 | |
| 13923023264 | popular culture | cultural patterns that are widespread among a society's population | 117 | |
| 13923027324 | cultural landscape | Cultural attributes of an area often used to describe a place (ex- buildings, theaters, places of worship) | 118 | |
| 13923040849 | natural landscape | The physical landscape or environment that has not been affected by human activities. | 119 | |
| 13923047094 | adaptive strategy | the way humans adapt to physical and cultural landscape they are living in | 120 | |
| 13923053508 | hooligans | sports fans that incite violence at soccer games | 121 | |
| 13923062149 | indigenous architecture | architecture that is not built by a professional craftsperson or artist | 122 | |
| 13923076756 | Anglo-American landscape | styles of housing or infrastructure based on british and early american influences | 123 | |
| 13923093638 | traditional architecture | the style of building that was characteristic when that area was established | 124 | |
| 13923107740 | lingua franca | a language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different. | 125 | |
| 13923113584 | dialect | a form of language spoken by people in a particular region or group (different in speed, sound, syntax, and vocab) | 126 | |
| 13923122007 | syntax | the grammatical arrangement of words in sentences | 127 | |
| 13923125145 | isogloss | boundary that separates dialects | 128 | |
| 13923133980 | pidgin language | a simplified language that forms from the fusion of two languages | 129 | |
| 13923143277 | trade language | language that is used between people who don't share a native language to conduct business | 130 | |
| 13923159275 | Creole language | A stable language resulting from the blend of two or more languages | 131 | |
| 13923174099 | official language | Language in which all government business occurs in a country. | 132 | |
| 13923176991 | linguistic diversity | learning of more languages (on an individual, societal, or global scale) | 133 | |
| 13923195345 | language families | large groups of languages having similar roots (ex- indo-european) | 134 | |
| 13923213348 | language subfamilies | smaller groups of languages within a language family (ex- west germanic) | 135 | |
| 13923224311 | language groups | languages descended from a common ancestral language (ex- romance languages) | 136 | |
| 13923249462 | faith | belief in something based on spirituality rather than physical proof | 137 | |
| 13923255797 | Fundamentalism | strict adherence to a set of beliefs, literal interpretation | 138 | |
| 13923269871 | ethnic religion | a religion that is particular to an ethnic group and is passed down at birth | 139 | |
| 13923282579 | universalizing religion | religion that attempts to appeal to all people in the world | 140 | |
| 13923292299 | secularist | someone who believes religion and society should be separate | 141 | |
| 13923295643 | jainism | religion based on non materialism and transcending the cycles of life and death, don't believe in a god | 142 | |
| 13923310302 | Christianity | worlds largest religion, focused on the life of jesus (roman catholic, protestant, orthodox) | 143 | |
| 13923321252 | denominations | Branches of a religion that differ on specific practices or principles of the religion | 144 | |
| 13923326648 | mormonism | universalizing religion centered in Utah; Book of Mormon and Old and New Testaments | 145 | |
| 13923333458 | islam | second largest religion, monotheistic, shares common heritage with jewish and christian religions | 146 | |
| 13923342493 | hajj | muslim pilgrimage to Mecca | 147 | |
| 13923350081 | mecca | holiest city in the islamic religion | 148 | |
| 13923354486 | shiites | smaller branch of islam, 10-15% (in azerbaijan, bahrain, iran, iraq) | 149 | |
| 13923366865 | sunnis | bigger branch of islam, 85 to 90% (in middle east, nothern africa, southeast asia) | 150 | |
| 13923389421 | theocracy | A government controlled by religious leaders (iran and saudi arabia) | 151 | |
| 13923395187 | shariah law | islamic law that does not recognize separation between church and state | 152 | |
| 13923403046 | judaism | one of the oldest religions, ethnic and monotheistic | 153 | |
| 13923413612 | Zoroastrianism | one of oldest religions, belief that zarathustra is the father of religion (india and iran) | 154 | |
| 13923429591 | Hindusim | polytheistic, oldest religion, mainly in india | 155 | |
| 13923436772 | vedas | holy books of hinduism | 156 | |
| 13923444759 | syncretic religion | blends two or more religious belief systems into a new system | 157 | |
| 13923454492 | sikhism | monotheistic, rejects caste system, believes all people are created equal, punjab region of india | 158 | |
| 13923466082 | Baha'i | universalizing, similar to sikhism, africa and asia | 159 | |
| 13923478114 | animism | the belief that all things possess a soul | 160 | |
| 13923483735 | Confucianism | focuses on relationships within the world and is associated with feng shui, china | 161 | |
| 13923497881 | taoism | philosophy based on the release of personal desires, emphasizes mysticism, china | 162 | |
| 13923508458 | shintoism | japan, poly and monotheistic, believe that nature is divine and emphasize ancestors | 163 | |
| 13923523123 | interfaith boundaries | boundaries between the major religions | 164 | |
| 13923526171 | enclave | an area within or surrounded by a larger area whose inhabitants are culturally or ethnically distinct | 165 | |
| 13923544488 | exclave | a group of people who are physically separated from their religious hearth | 166 | |
| 13923549794 | Assimilation | dying out of the old culture as it becomes replaced with the culture where a person currently resides (3 generations) | 167 | |
| 13936283477 | Political Geography | Studies geographical influences on political systems and power relationships | 168 | |
| 13936283478 | Geopolitics | The study of the interplay between political relations and the territories in which they occur | 169 | |
| 13936283479 | Core country | A country that is well developed with a strong economic base (ex - USA) | 170 | |
| 13936283480 | Periphery country | A less developed, economically poor country (ex - Ghana) | 171 | |
| 13936283481 | State | An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government with control over its internal and foreign affairs. | 172 | |
| 13936283482 | Sovereignity | Political authority for a state to govern itself | 173 | |
| 13936283483 | Microstate/Ministate | A country that is small in population and area (ex - Monaco) | 174 | |
| 13936283484 | City state | Small sovereign state that is made up of a town or city and the surrounding area | 175 | |
| 13936283485 | Nation | a group of people united by bonds of race, language, custom, tradition, and sometimes religion (ex - the French, Koreans, Mexicans) | 176 | |
| 13936283486 | Stateless nation | A nation of people without a state that it considers home (ex - Kurds, basques, Palestinians) | 177 | |
| 13936283487 | Nation state | A state in which the cultural borders of a nation correspond with the state borders of a country (ex - Japan, Iceland, Denmark) | 178 | |
| 13936283488 | Political boundary | a boundary that divides the territory of one country from that of another | 179 | |
| 13936283489 | Frontier | A zone of territory where no state has governing authority | 180 | |
| 13936283490 | Geometric boundary | A boundary created using geometric patterns (lines, arcs) | 181 | |
| 13936283491 | physical boundary | Boundary based on the geographical features of earths surface (mountains, water) | 182 | |
| 13936283492 | ethnographic/cultural boundary | Boundary based on ethnographic and cultural considerations (like language and religion) | 183 | |
| 13936283493 | Boundary evolution | the technical wording of a treaty that legally defines where a boundary should be located | 184 | |
| 13936283494 | Delimination | The process in which cartographers put the boundaries on the map. | 185 | |
| 13936283495 | Demarcation | the process of physically representing a boundary on the landscape | 186 | |
| 13936283496 | Border landscape | Zonal area on both sides of the boundary | 187 | |
| 13936283497 | antecedent boundary | a boundary line established before the area in question is well populated | 188 | |
| 13936283498 | Subsequent boundary | boundary that develops along with the development of the cultural landscape | 189 | |
| 13936283499 | superimposed boundary | a political boundary that ignores the existing cultural organization on the landscape | 190 | |
| 13936283500 | Irredentism | A political movement by an ethnic group or other closely aligned group that aims to reoccupy an area that the group lost | 191 | |
| 13936283501 | relic boundary | Boundary that is no longer used but still can be seen on the landscape (ex - Great Wall of China) | 192 | |
| 13936283502 | Reunification | The rejoining of 2 formerly divided nations (ex - east and west Germany) | 193 | |
| 13936283503 | Ethnic conflict | disagreements that usually result in military action of violence of one ethnic group against another (ex - balkans with Bosnian Muslims, Serbs, Croats) | 194 | |
| 13936283504 | Religious conflict | Conflicts that involve violence between members of different religious groups (ex - Muslims and Hindus in South Asia) | 195 | |
| 13936283505 | Balkanization | Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities (ex - Yugoslavia) | 196 | |
| 13936283506 | Annexation | Legally adding land area to an already existing state (ex - USA purchasing Alaska from Russia) | 197 | |
| 13936283507 | Definitional boundary dispute | a dispute that arises from legal language of the treaty's definition of the boundary | 198 | |
| 13936283508 | Locational Boundary Dispute | Disputes that arise when the definition of the border is not questioned but the intention of the border is (ex - a river shifts its course, changing the landscape). | 199 | |
| 13936283509 | Operational Boundary Dispute | Dispute when two neighboring countries disagree on major issues involving the border | 200 | |
| 13936283510 | Allocational Boundary Dispute | Dispute over the actual use of a boundary (ex - use of a resource that cross the boundary) | 201 |
APES AP Review Flashcards
| 13865249338 | Asthenosphere | The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move | 0 | |
| 13865250802 | Lithosphere | A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. | 1 | |
| 13865254511 | gully erosion | erosion that occurs when a rill channel widens and deepens | 2 | |
| 13865256229 | rill | a small stream | 3 | |
| 13865259423 | soil horizon | The layer of soil that differs in color and texture from the layers above or below it. |  | 4 |
| 13865264205 | Subduction | The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary. | 5 | |
| 13865269873 | thermal inversion | A situation in which a relatively warm layer of air at mid-altitude covers a layer of cold, dense air below. | 6 | |
| 13865273601 | Upwelling | The movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface | 7 | |
| 13865275213 | zone of aeration | upper soil layers that hold both air and water | 8 | |
| 13865277991 | zone of illuviation | the layer of soil (the "B" layer) that imports the ions and colloids from the zone of eluviation | 9 | |
| 13865280560 | zone of saturation | The lower zone where water accumilates between small rock particles. | 10 | |
| 13865288524 | age of the earth | 4.6 billion years | 11 | |
| 13865295194 | rain shadow | a region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing precipitation on the windward side | 12 | |
| 13865296489 | ENSO | El Niño Southern Oscillation, see-sawing of air pressure over the S. Pacific | 13 | |
| 13865304002 | Desertification | Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting. | 14 | |
| 13865306833 | climax community | A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time | 15 | |
| 13865310684 | ecosystem diversity | variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere | 16 | |
| 13865352105 | Evapotranspiration | The combined amount of evaporation and transpiration | 17 | |
| 13865376848 | survivorship curve | Graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species. | 18 | |
| 13865391870 | debt-for-nature swap | When agencies such as the World Bank make a deal with third world countries that they will cancel their debt if the country will set aside a certain amount of their natural resources. | 19 | |
| 13865406102 | Rule of 70 | Doubling time (in years) = 70/(percentage growth rate). | 20 | |
| 13865434240 | alley cropping | Planting of crops in strips with rows of trees or shrubs on each side. | 21 | |
| 13865436871 | by-catch | any other species of fish, mammals, or birds that are caught that are not the target organism. | 22 | |
| 13865438383 | arable land | land suitable for growing crops | 23 | |
| 13865438384 | drift-net fishing | the use of fishing nets of great length and depth | 24 | |
| 13865439693 | Feedlot | a plot of land on which livestock are fattened for market | 25 | |
| 13865441317 | Micronutrients | vitamins and minerals | 26 | |
| 13865446331 | minimum-tillage farming | use of special tillers that break up and loosen the subsurface soil without turning over the topsoil | 27 | |
| 13865450619 | no-till farming | farming that excludes the usage of tillage to avoid the negative effects of tillage such as loss of organic matter, soil erosion, etc, leaves roots holding soil | 28 | |
| 13865452145 | second-growth forest | a stand of trees resulting from secondary ecological succession | 29 | |
| 13865453442 | tar sands | sand or sandstone naturally impregnated with petroleum | 30 | |
| 13865454821 | Xeriscaping | a method of landscaping that uses plants that are well adapted to the local area and are drought resistant. | 31 | |
| 13865470042 | lake zones | littoral, limnetic, profundal, benthic |  | 32 |
| 13865478977 | ocean zones | 1. intertidal--high and low tides, 2. benthic--ocean floor, 3. pelagic--ocean water (divided into neritic and oceanic provinces) |  | 33 |
| 13865482010 | CAFO | Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation | 34 | |
| 13865488563 | FIRFA | Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act | 35 | |
| 13865515851 | Dredging | Type of surface mining in which chain buckets and draglines scrape up sand, gravel, and other surface deposits covered with water. It is also used to remove sediment from streams and harbors to maintain shipping channels. | 36 | |
| 13865532266 | anthracite coal | A type of coal, noted for being hard and clean burning. | 37 | |
| 13865533553 | bituminous coal | The most common form of coal; produces a high amount of heat and is used extensively by electric power plants. | 38 | |
| 13865533554 | lignite coal | -Lowest rank of coal, brownish black, visible plant material, crumbly, organic rock. | 39 | |
| 13865535335 | Peat | partially decayed plant matter found in bogs | 40 | |
| 13865536802 | Petrochemicals | Compounds that are made from oil | 41 | |
| 13865538040 | Synfuels | Synthetic gaseous and liquid fuels produced from solid coal or sources other than natural gas or crude oil. | 42 | |
| 13865546982 | ANWR | Arctic National Wildlife Refuge | 43 | |
| 13865553627 | nuclear fission reactor | reactors that release energy steadily due to the fission of a suitable isotope, such as uranium-235 |  | 44 |
| 13865562078 | passive solar heating | the use of sunlight to heat buildings directly |  | 45 |
| 13865575160 | CERCLA | Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act | 46 | |
| 13865575161 | effluent | liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea. | 47 | |
| 13865576291 | Leachate | polluted liquid produced by water passing through buried wastes in a landfill | 48 | |
| 13865583494 | Phytoremediation | A method employed to clean up a hazardous waste site that uses plants to absorb and accumulate toxic materials | 49 | |
| 13865588957 | urban heat island | Local heat buildup in an area of high population density | 50 | |
| 13865594102 | indoor air pollutants | radon, cigarette smoke, carbon monoxides, nitrogen dioxide (gas stoves), formaldehyde (carpeting, furniture), household pesticides, cleaning solvents, ozone (photocopiers), abestos + organic pests in ventilation | 51 | |
| 13865598277 | outdoor air pollutants | CO2, NO2, tropospheric ozones, particulate matter, lead, sulfur dioxides. | 52 | |
| 13865600420 | carcinogen examples | • Ionizing radiation (UV) • Chemicals (tobacco!!, occupational exposure) • Viruses (hep b,c, HPV, H. Pylori) • Other physical agents | 53 | |
| 13865602222 | mutagen examples | Radiation (UV, X-ray, gamma) Arsenic, Bromine Pesticides, Tobacco Infection agents | 54 | |
| 13865604205 | teratogen examples | FAS- small head, nervous system problems Nicotine-cleft lip, growth retardation, possible miscarriage Cocaine-spontaneous abortion, detachment of placenta Thalidomide-born without limbs | 55 | |
| 13865606536 | Turbidity | A measure of how clear water is. | 56 | |
| 13865615352 | NIMBY | Not In My Backyard attitude. People don't want things like landfills to be put where they live. | 57 | |
| 13865629685 | Lacey Act | prohibits interstate transport of wild animals dead or alive without federal permit. | 58 |
AP psych defense mechanisms Flashcards
| 13157765582 | projection | blame is attached to others/environment for unacceptable desires, thoughts, or mistakes -deny mistakes, helps self-image | 0 | |
| 13157817799 | regression | return to an earlier, more comfortable level of functioning that is less demanding -return to less stressed time, accepted with comfort | 1 | |
| 13157839354 | reaction formation | causes people to act exactly opposite to the way they feel -feelings to be acted out in a more acceptable way | 2 | |
| 13157867926 | identification | attempt to manage anxiety by imitading behavior of someone feared/respected -helps avoid self-devaluation | 3 | |
| 13157881956 | denial | ignore unacceptable realities by refusing to acknowledge them -can isolate a person from traumatic events | 4 | |
| 13157902146 | repression | unconciously having threatning thoughts/feelings that are kept from being concious -protects from traumatic events until able to cope | 5 | |
| 13157933219 | displacement | transfer/discharge of emotional reactions from one person/object to another person/object -feelings can be expressed to less dangerous things/people | 6 | |
| 13157954163 | rationalization | justification of behaviors by faulty logic/motives that are socially acceptable but didn't actually inspire the behavior -helps cope with the inability to meet goals/standards | 7 | |
| 13157976879 | sublimation | displacement of energy associated with more primitive sexual/agressive drives into socially acceptable activities -protects from acting in irrational/impulsive ways | 8 |
Flashcards
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

