Flashcards
AP World History - Period 3 Flashcards
The Post-Classical World, 500-1450
| 8718717651 | Bedouin | nomadic pastoralists of the Arabian peninsula with a culture based on herding camels and goats | 0 | |
| 8718717652 | Mecca | Arabian commercial center; dominated by the Quraysh; the home of Muhammad and the future center of Islam | 1 | |
| 8718717653 | Medina | town northeast of Mecca; asked Muhammad to resolve its intergroup differences; Muhammad's flight to Medina, the hijra, in 622 began the Muslim calendar | 2 | |
| 8718717654 | Umayyad | clan of the Quraysh that dominated Mecca; later an Islamic dynasty | 3 | |
| 8718717655 | Muhammad | (570-632); prophet of Allah; originally a merchant of the Quraysh | 4 | |
| 8718717656 | Qur'an | the word of god as revealed through Muhammad; made into the holy book of Islam | 5 | |
| 8718717657 | Umma | community of the faithful within Islam | 6 | |
| 8718717658 | Five Pillars | the obligatory religious duties for all Muslims; confession of faith, prayer, fasting during Ramadan, zakat, and hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca) | 7 | |
| 8718717659 | Caliph | the successor to Muhammad as head of the Islamic community | 8 | |
| 8718717660 | Ali | cousin and son-in-law of Muhammad; one of the orthodox caliphs; focus for the development of shi'ism | 9 | |
| 8718717661 | Abu Bakr | succeeded Muhammad as the first caliph | 10 | |
| 8718717662 | Jihad | Islamic holy war | 11 | |
| 8718717663 | Sunnis | followers of the majority interpretation within Islam; included the Umayyads | 12 | |
| 8718717664 | Shi'a | followers of Ali's interpretation of Islam | 13 | |
| 8718717665 | Mawali | non-Arab converts to Islam | 14 | |
| 8718717666 | Dhimmis | "the people of the book"-- Jews, Christians; later extended to Zoroastrians and Hindus | 15 | |
| 8718717667 | Abbasids | dynasty that succeeded the Umayyads in 750; their capital was at Baghdad | 16 | |
| 8718717668 | Hadiths | "traditions" of the prophet Muhammad; added to the Qur'an, form the essential writings of Islam | 17 | |
| 8718717669 | Wazir | chief administrative official under the Abbasids | 18 | |
| 8718717670 | Dhows | Arab sailing vessels; equipped with lateen sails; used by Arab merchants | 19 | |
| 8718717671 | Seljuk Turks | nomadic invaders from central Asia; staunch Sunnis; ruled from the 11th c. in the name of the Abbasids | 20 | |
| 8718717672 | Crusades | invasions of western Christians into Muslim lands, especially Palestine; captured Jerusalem and established Christian kingdoms enduring until 1291 | 21 | |
| 8718717673 | Ulama | Islamic religious scholars; pressed for a more conservative and restrictive theology; opposed to non-Islamic thinking | 22 | |
| 8718717674 | Sufis | Islamic mystics; spread Islam to many Afro-Asian regions | 23 | |
| 8718717675 | Mongols | central Asian nomadic peoples; captured Baghdad in 1258 and killed the last Abbasid caliph | 24 | |
| 8718717676 | Chinggis Khan | (1162-1227); Mongol ruler; defeated the Turkish Persian kingdoms | 25 | |
| 8718717677 | Mamluks | Rulers of Egypt; descended from Turkish slaves | 26 | |
| 8718717678 | Arabic numerals | Indian numerical notation brought by the Arabs to the West | 27 | |
| 8718717679 | Shrivijaya | trading empire based on the Malacca straits; its Buddhist government resisted Muslim missionaries; when it fell, southeastern Asia was opened to Islam | 28 | |
| 8718717680 | Malacca | flourishing trading city in Malaya; established a trading empire after the fall of Shrivijaya | 29 | |
| 8718717681 | Mali | state of the Malinke people centered between the Senegal and Niger rivers | 30 | |
| 8718717682 | Mansa | title of the ruler of Mali | 31 | |
| 8718717683 | Ibn Battuta | Arab traveler throughout the Muslim world | 32 | |
| 8718717684 | Sundiata | created a unified state that became the Mali empire; died in 1260 | 33 | |
| 8718717685 | Songhay | successor state to Mali; dominated middle reaches of the Niger valley; capital at Gao | 34 | |
| 8718717686 | East African trading ports | urbanized commercial centers mixing African and Arab cultures; included Mogadishu, Mombasa, Malindi, Kilwas, Pate, and Zanzibar | 35 | |
| 8718717687 | Great Zimbabwe | with massive stone buildings and walls, incorporates the greatest early buildings in sub-Saharan Africa | 36 | |
| 8718717688 | Greek Fire | Byzantine weapon consisting of mixture of chemicals that ignited when exposed to water; used to drive back the Arab fleets attacking Constantinople | 37 | |
| 8718717689 | Icons | images of religious figures venerated by Byzantine Christians | 38 | |
| 8718717690 | Iconoclasm | the breaking of images; religious controversy of the 8th c; Byzantine emperor attempted, but failed, to suppress icon veneration | 39 | |
| 8718717691 | Manzikert | Seljuk Turk victory in 1071 over Byzantium; resulted in loss of the empire's rich Anatolian territory | 40 | |
| 8718717692 | Cyril and Methodius | Byzantine missionaries sent to convert eastern Europe and Balkans; responsible for creation of Slavic written script called Cyrillic | 41 | |
| 8718717693 | Kiev | commercial city in Ukraine established by Scandinavians in 9th c; became the center for a kingdom that flourished until 12th c | 42 | |
| 8718717694 | Rurik | legendary Scandinavian, regarded as founder of Kievan Rus' in 855 | 43 | |
| 8718717695 | Vladmir I | ruler of Kiev (980-1015); converted kingdom to Orthodox Christianity | 44 | |
| 8718717696 | Russian Orthodoxy | Russian form of Christianity brought from Byzantine Empire | 45 | |
| 8718717697 | Tatars | Mongols who conquered Russian cities during the 13th c; left Russian church and aristocracy intact | 46 | |
| 8718717698 | Middle Ages | the period in western European history between the fall of Roman Empire and the 15th c | 47 | |
| 8718717699 | Gothic | an architectural style developed during the 13th and 14th c in western Europe; featured pointed arches and flying buttresses as external support on main walls | 48 | |
| 8718717700 | Vikings | seagoing Scandinavian raiders who disrupted coastal areas of Europe from the 8th to 11th c; pushed across the Atlantic to Iceland, Greenland, and North America; formed permanent territories in Normandy and Sicily | 49 | |
| 8718717701 | Manorialism | rural system of reciprocal relations between landlords and their peasant laborers during the Middle Ages; peasants exchanged labor for use of land and protection | 50 | |
| 8718717702 | Serfs | peasant agricultural laborers within the manorial system | 51 | |
| 8718717703 | Three-field system | practice of dividing land into thirds, rotating between two different crops and pasturage-- an improvement making use of manure | 52 | |
| 8718717704 | Clovis | King of the Franks; converted to Christianity circa 496 | 53 | |
| 8718717705 | Carolingians | royal house of Franks from 8th c to 10th c | 54 | |
| 8718717706 | Charles Martel | first Carolingian king of the Franks; defeated Muslims at Tours in 732 | 55 | |
| 8718717707 | Charlemagne | Carolingian monarch who established large empire in France and Germany circa 800 | 56 | |
| 8718717708 | Holy Roman Emperors | political heirs to Charlemagne's empire in northern Italy and Germany; claimed title of emperor but failed to develop centralized monarchy | 57 | |
| 8718717709 | Feudalism | personal relationship during the Middle Ages by which greater lords provided land to lesser lords in return for military service | 58 | |
| 8718717710 | Vassals | members of the military elite who received land or a benefice from a lord in return for military service and loyalty | 59 | |
| 8718717711 | William the Conqueror | invaded England from Normandy in 1066; established tight feudal system and centralized monarchy in England | 60 | |
| 8718717712 | Magna Carta | Great charter issued by King John of England in 1215; represented principle of mutual limits and obligations between rulers and feudal aristocracy, and the supremacy of law | 61 | |
| 8718717713 | Parliaments | bodies representing privileged groups; institutionalized the principle that kings ruled with the advice and consent of their subjects | 62 | |
| 8718717714 | Hundred Years War | conflict between England and France over territory (1337-1453) Established a since of Nationalism with each country. Joan of Arc united the French and promoted French patriotism. | 63 | |
| 8718717715 | Pope Urban II | organized the first Crusade in 1095; appealed to Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim control | 64 | |
| 8718717716 | Investiture | the practice of appointment of bishops; Pope Gregory attempted to stop lay investiture, leading to a conflict with the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV | 65 | |
| 8718717717 | Gregory VII | 11th c pope who attempted to free church from secular control; quarreled with Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV over practice of lay investiture of bishops | 66 | |
| 8718717718 | Thomas Aquinas | creator of one of the great syntheses of medieval learning; taught at University of Paris; author of Summas; believed that through reason it was possible to know much about natural order, moral law, and nature of God | 67 | |
| 8718717719 | Scholasticism | dominant medieval philosophical approach; so-called because of its base in the schools or universities; based on use of logic to resolve theological problems | 68 | |
| 8718717720 | Hanseatic League | an organization of north German and Scandinavian cities for the purpose of establishing a commercial alliance | 69 | |
| 8718717721 | Guilds | associations of workers in the same occupation in a single city; stressed security and mutual control; limited membership, regulated apprenticeships, guaranteed good workmanship; held a privileged place in cities | 70 | |
| 8718717722 | Black Death | bubonic plague that struck Europe in the 14th c; significantly reduced Europe's population; affected social structure; decimated populations in Asia | 71 | |
| 8718717723 | Period of the Six Dynasties | era of continuous warfare (220-589) among the many kingdoms that followed the fall of the Han | 72 | |
| 8718717724 | Jinshi | title given students who passed the most difficult examinations; became eligible for high office | 73 | |
| 8718717725 | Mahayana (Pure Land) Buddhism | emphasized salvationist aspects of Chinese Buddhism; popular among the masses in East Asia | 74 | |
| 8718717726 | Wuzong | Tang emperor (841-847); persecuted Buddhist monasteries and reduced influence of Buddhism in favor of Confucianism | 75 | |
| 8718717727 | Southern Song | smaller surviving dynasty (1127-1279); presided over one of the greatest cultural reigns in world history. Fell to the Mongols in 1276 and eventually taken over in 1279. | 76 | |
| 8718717728 | Grand Canal | great canal system begun by Yangdi; joined Yellow River region to the Yangtze basin | 77 | |
| 8718717729 | Junks | Chinese ships equipped with watertight bulkheads, stern-post rudders, compasses, and bamboo fenders; dominant force in Asian seas east of the Malayan peninsula | 78 | |
| 8718717730 | Flying money | Chinese credit instrument that provided vouchers to merchants to be redeemed at the end of a venture; reduced danger of robbery; an early form of currency | 79 | |
| 8718717731 | Footbinding | male imposed practice to mutilate women's feet in order to reduce size; produced pain and restricted movement; helped to confine women to the household; seen a beautiful to the elite. | 80 | |
| 8718717732 | Taika reforms | attempt to remake Japanese monarch into an absolutist Chinese-style emperor; included attempts to create professional bureaucracy and peasant conscript army | 81 | |
| 8718717733 | Fujiwara | mid-9th c Japanese aristocratic family; exercised exceptional influence over imperial affairs; aided in decline of imperial power | 82 | |
| 8718717734 | Bushi | regional warrior leaders in Japan; ruled small kingdoms from fortresses; administered the law, supervised public works projects, and collected revenues; built up private armies | 83 | |
| 8718717735 | Samurai | mounted troops of the bushi; loyal to local lords, not the emperor | 84 | |
| 8718717736 | Seppuku | ritual suicide in Japan; also known as hari-kiri; demonstrated courage and was a means to restore family honor | 85 | |
| 8718717737 | Gempei wars | Waged for 5 years from 1180-1185, on the island of Honshu between Taira and Minamoto families; resulted in the destruction of Taira and also resulted in the feudal age | 86 | |
| 8718717738 | Bakufu | military government established by the Minamoto following Gempei wars; centered at Kamakura; retained emperor, but real power resided in military government and samurai | 87 | |
| 8718717739 | Shoguns | military leaders of the bakufu | 88 | |
| 8718717740 | Daimyos | warlord rulers of small states following Onin war and disruption of Ashikaga shogunate; holding consolidated into unified and bounded mini-states | 89 | |
| 8718717741 | Sinification | extensive adaptation of Chinese culture in other regions | 90 | |
| 8718717742 | Yi | dynasty (1392-1910); succeeded Koryo dynasty after Mongol invasions; restored aristocratic dominance and Chinese influence | 91 | |
| 8718717743 | Trung Sisters | leaders of a rebellion in Vietnam against Chinese rule in 39 CE; demonstrates importance of women in Vietnamese society | 92 | |
| 8718717744 | Khmers and Chams | Indianized Vietnamese peoples defeated by northern government at Hanoi | 93 | |
| 8718717745 | Nguyen | southern Vietnamese dynasty with capital at Hue that challenged northern Trinh dynasty with center at Hanoi | 94 | |
| 8718717746 | Chinggis Khan | born in 1170s; elected supreme Mongol ruler (khagan) in 1206; began the Mongols rise to world power; died 1227 | 95 | |
| 8718717747 | Shamanistic religion | Mongol beliefs focused on nature spirits | 96 | |
| 8718717748 | Batu | grandson of Chinggis Khan and ruler of Golden Horde; invaded Russian in 1236 | 97 | |
| 8718717749 | Golden Horde | one of four regional subdivisions of the Mongol Empire after death of Chinggis Khan; conquered and ruled Russua during the 13th and 14th c | 98 | |
| 8718717750 | Ilkhan khanate | one of four regional subdivisions of the Mongol empire after the death of Chinggis Khan; eventually included much of Abbasid empire | 99 | |
| 8718717751 | Hulegu | grandson of Chinggis Khan and rule of Ilkhan khanate; captured and destroyed Abbasid Baghdad | 100 | |
| 8718717752 | Mamluks | Muslim slave warriors; established dynasty in Egypt; led by Baibars defeated Mongols in 1260 | 101 | |
| 8718717753 | Kubilai Khan | grandson of Chinggis Khan; conquered China; established Yuan dynasty in 1271 | 102 | |
| 8718717754 | White Lotus Society | secret religious society dedicated to overthrow of Yuan dynasty | 103 | |
| 8718717755 | Ottoman Empire | Turkish empire established in Asia Minor and eventually extending through the Middle East and the Balkans; conquered Constantinople in 1453 and ended Byzantine Empire | 104 | |
| 8718717756 | Ming Dynasty | replaced Mongal Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted large trade expeditions to southern Asia and Africa; later concentrated on internal development within China | 105 | |
| 8718717757 | Ethnocentrism | judging foreigners by the standards of one's own group; leads to problems in interpreting world history | 106 | |
| 8718717768 | Muhammad's primary historical achievement | spread of Islam | 107 | |
| 8718717769 | Silk Road Trade system |  | 108 | |
| 8718717770 | Kingdom of Mali |  | 109 | |
| 8718717771 | Inca and Rome both had | extensive road systems | 110 | |
| 8718717772 | Important continuity in social structure of states and empires 600-1450 | land holding aristocracies, patriarchies, peasant systems still in place | 111 | |
| 8718717773 | Champa Rice | tributary gift from Vietnam to China, led to population increase | 112 | |
| 8718717774 | Diasporic communities | merchant communities that introduced their own cultures into other areas | 113 | |
| 8718717775 | Trans Saharan trade | Dominated my Muslims in 13th century after rise of Islamic caliphates.. |  | 114 |
| 8718717776 | Effect of Muslim conquests | collapse of other empires, mass conversion | 115 | |
| 8718717777 | Tang Dynasty | followed Sui, established tributary states in Vietnam and Korea, influence Japan, Established strong Buddhist and Confucian presence | 116 | |
| 8718717778 | Black Death | plague that originated with Mongols, led to mass population decrease in Europe, later weakened faith in Christian church and increased the power of serfs/peasants. Led partly to fall of Feudal structures in Europe. |  | 117 |
| 8718717779 | Indian Ocean Maritime Trade |  | 118 | |
| 8718717780 | Cities that rose during this time due to increased trade | Novgorod, Constantinople, Timbuktu | 119 | |
| 8718717781 | Timbuktu | trade center of Mali, cosmopolitan city that saw the blending of many different cultures and people | 120 | |
| 8718717782 | New forms of monetization | Checks, Bills of Exchange | 121 | |
| 8718717783 | Bantu Migrations |  | 122 | |
| 8718717784 | footbinding | began during Tang/Song era, demonstrates objectification and oppression of women, abolished during Yuan and brought back during Ming |  | 123 |
| 8718717785 | Marco Polo | traveler/merchant from Europe who spend 17 years at court of Kublai Khan | 124 |
Flashcards
AP World History: Ancient World Flashcards
First set of words in the AP World History book by the Princeton Review.
| 5314692927 | Agriculture | The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain. | 0 | |
| 5314692928 | Agrarian | pertaining to land or its cultivation; Ex. agrarian reform, agrarian society | 1 | |
| 5314692929 | Bands/ Clans | extended family groups that generally lived together | 2 | |
| 5314692930 | Barbarian | without civilizing influences | 3 | |
| 5314692931 | Bureaucracy | system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials (not elected) | 4 | |
| 5314692932 | Civilization | a society in an advanced state of social development (e.g., with complex legal and political and religious organizations) | 5 | |
| 5314692933 | City-States | different sections of land owned by the same country but ruled by different rulers (e.g. Greece) | 6 | |
| 5314692934 | Classical | of or characteristic of a form or system felt to be of first significance before modern times | 7 | |
| 5314692935 | Domestication | process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans | 8 | |
| 5314692936 | Economy | system by which goods and services are produced and distributed to meet people's needs | 9 | |
| 5314692937 | Egalitarian | a person who believes in the equality of all people | 10 | |
| 5314692938 | Emperor | supreme ruler of an empire | 11 | |
| 5314692939 | Empire | many territories, countries, or peoples controlled by one government (also just any territory ruled by an emperor) | 12 | |
| 5314692940 | Feudalism | a political system and a social system where by a powerful lord would offer "protection" in return for "service" | 13 | |
| 5314692941 | Foraging | the process of scavenging for food | 14 | |
| 5314692942 | Hierarchy | a series of ordered groupings of people or things within a system | 15 | |
| 5314692943 | Hierarchical | Of, relating to, or arranged in a hierarchy | 16 | |
| 5314692944 | Hunter-Gatherer | A hunter-gatherer society is one whose primary subsistence method involves the direct procurement of edible plants and animals from the wild, foraging and hunting without significant recourse to the domestication of either plants nor animals | 17 | |
| 5314692945 | Irrigation | supplying dry land with water by means of ditches, sprinklers, etc. | 18 | |
| 5314692946 | Monarchy | a government in which power is in the hands of a single person who usually inherits their power | 19 | |
| 5314692947 | Monotheism | belief in a single God | 20 | |
| 5314692948 | Neolithic | The New Stone Age from circa 8500 to 4500 BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution(s) | 21 | |
| 5314692949 | Nomadic | (of groups of people) tending to travel and change settlements frequently | 22 | |
| 5314692950 | Pastoral | relating to shepherds or herdsmen or devoted to raising sheep or cattle (e.g. pastoral peoples) | 23 | |
| 5314692951 | Paleolithic | The Old Stone Age from circa 750,00 to 500,000 years BCE to 8,500 years BCE: The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans and the development of minor tools | 24 | |
| 5314692952 | Philosophy | the rational investigation of questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics | 25 | |
| 5314692953 | Polytheism | belief in multiple Gods | 26 | |
| 5314692954 | River Valley | the fertile land surrounding a river- the first civilizations arose near them | 27 | |
| 5314692955 | Sedentary | remaining in one place | 28 | |
| 5314692956 | Settlement | the act of colonizing or a small group of people in a sedentary position | 29 | |
| 5314692957 | Subsistence | the necessities of life, the resources of survival | 30 | |
| 5314692958 | Surplus | a quantity much larger than is needed | 31 | |
| 5314692959 | Sustenance | the act of sustaining life by food or providing a means of subsistence | 32 | |
| 5314692960 | Theocracy | government run by religious leaders | 33 | |
| 5314692961 | Traditional | consisting of or derived from tradition; customary practices | 34 | |
| 5314692962 | Urbanization | the social process whereby cities grow and societies become more urban | 35 | |
| 5314692963 | Vassals | lesser lords who pledged their service and loyalty to a greater lord -- in a military capacity | 36 | |
| 5314692964 | Alexander the Great | king of Macedon, conqueror of Greece, Egypt, and Persia; founder of Alexandria (356-323 BC) |  | 37 |
| 5314692965 | Analects of Confucius | "something that is repeated" - a collection of Confucius' famous sayings | 38 | |
| 5314692966 | Bronze Age | a period between the Stone and Iron ages, characterized by the manufacture and use of bronze tools and weapons |  | 39 |
| 5314692967 | Calendar | a system of timekeeping that defines the beginning and length and divisions of the year | 40 | |
| 5314692968 | Code of Hammurabi | the set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi dating to the 18th century BC, the earliest legal code known in its entirety |  | 41 |
| 5314692969 | Cuneiform | One of the first written languages known: A system of writing in which wedge-shaped symbols represented words or syllables. It originated in Mesopotamia and was used initially for Sumerian and Akkadian but later was adapted to represent other languages of western Asia. |  | 42 |
| 5314692970 | Democracy | a political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them | 43 | |
| 5314692971 | Eight Fold Path | Eight steps to end suffering and attain enlightenment according to Buddhist tradition. | 44 | |
| 5314692972 | Four Noble Truths | as taught by the Buddha, the four basic beliefs that form the foundation of Buddhism | 45 | |
| 5314692973 | Gothic Migrations | The Migration period, also called the Barbarian Invasions or German: Völkerwanderung (wandering of the peoples), was a period of human migration that occurred roughly between the years 300 to 700 CE in Europe, marking the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. These movements were catalyzed by profound changes within both the Roman Empire and the so-called 'barbarian frontier'. Migrating peoples during this period included the Goths, Vandals, Bulgars, Alans, Suebi, Frisians, and Franks, among other Germanic and Slavic tribes. | 46 | |
| 5314692974 | Great Wall | a fortification 1,500 miles long built across northern China in the 3rd century BC | 47 | |
| 5314692975 | Han Dynasty | imperial dynasty that ruled China (most of the time from 206 BC to AD 220) and expanded its boundaries and developed its bureaucracy |  | 48 |
| 5314692976 | Hellenism | The ideals and principles that spread from Greece through much of the ancient world. Much of its influence such as philosophy, athletics, and architecture penetrated the Middle East. |  | 49 |
| 5314692977 | The Huns | Fierce warriors from Central Asia- First invaded southeastern Europe and then launched raids on nearby kingdoms | 50 | |
| 5314692978 | Indian Ocean Trade | connected to Europe, Africa, and China.; worlds richest maritime trading network and an area of rapid Muslim expansion. |  | 51 |
| 5314692979 | Iron Age | the period following the Bronze Age; characterized by rapid spread of iron tools and weapons | 52 | |
| 5314692980 | Jewish Diaspora | A "scattering" of the Jewish people | 53 | |
| 5314692981 | Legalism | In Chinese history, Legalism was one of the main philosophic currents during the Warring States Period- A philosophy of focusing on the text of written law to the exclusion of the intent of law, elevating strict adherence to law over justice, mercy and common sense |  | 54 |
| 5314692982 | Pax Romana | A period of peace and prosperity throughout the Roman Empire, lasting from 27 B.C. to A.D. 180. |  | 55 |
| 5314692983 | Pyramids | Huge stone tombs with four triangle-shaped walls that met in a point on top |  | 56 |
| 5314692984 | Roman Republic | The period from 507 to 31 B.C.E., during which Rome was largely governed by the aristocratic Roman Senate. | 57 | |
| 5314692985 | Roman Senate | a council of wealthy and powerful Romans that advised the city's leaders | 58 | |
| 5314692986 | Shang Civilization | China's first dynasty almost 2000 BCE | 59 | |
| 5314692987 | Shi Huang Di | harsh ruler who united China for the first time and used legalism in ruling (Qin China) |  | 60 |
| 5314692988 | Siddhartha Gautama | founder of Buddhism; born a prince; left his father's wealth to find the cause of human suffering; also know as Buddha |  | 61 |
| 5314692989 | Silk Road Trade | The most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the Chinese, Indian, Persian, and Mediterranean civilizations; transmitted goods and ideas among civilization. |  | 62 |
| 5314692990 | The Torah | the most sacred text of Judaism |  | 63 |
| 5314692991 | The Vedas of Hinduism | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books from the 6th century B.C.E. |  | 64 |
| 5314692992 | Ziggurats | a temple or tomb of the ancient Assyrians, Sumerians, or Babylonians, having the form of a terraced pyramid of successively receding stories |  | 65 |
| 5314692993 | Christianity | Monotheistic religion born out of Judaism, preached by Jesus of Nazareth and later codified by his disciples. Persecuted by Romans early on; however, gained support under Constantine in the Rome. |  | 66 |
| 5314692994 | Buddhism | originally preached by Siddhartha and codified by his disciples into the sutras. Rejected Vedic rituals and the caste system. Spread throughout SE Asia and China and split into Mahayana(Buddha as a God, local gods tacked on as Bodhisativas) and Theravada(original, strict non-theistic version). |  | 67 |
| 5314692995 | Asoka | Third ruler of the Mauryan Empire in India (r. 270-232 B.C.E.). He converted to Buddhism and broadcast his precepts on inscribed stones and pillars, the earliest surviving Indian writing. |  | 68 |
| 5314692996 | Hinduism | Term for a wide variety of beliefs and ritual practices that have developed in the Indian subcontinent since antiquity. It has roots in ancient Vedic, Buddhist, and south Indian religious concepts and practices. |  | 69 |
| 5314692997 | Trans Saharan | route across the sahara desert. Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels played a huge role in the trading |  | 70 |
| 5314692998 | Monsoons | Major winds in the Indian Ocean that blew into India for half the year, and blew away from India for the other half. Helped facilitate trade in the Indian Ocean. |  | 71 |
| 5314692999 | Sumerians | people who dominated Southern Mesopotamia through the end of the 3rd Millennium BCE. Responsible for the creation of irrigation technology, cuneiform, and religious conceptions. |  | 72 |
| 5314693000 | Indo-Europeans | Groups of people who came from the area north of the Caucasus mountains, which are between the Black and Caspian seas. Herded multiple animals. Rode into battle on chariots. The Indo-European language of Sanskrit, by the Aryans, are the basis of many languages today. Often accepted and adapted aspects of technology, religions, and social order of those with whom they came in contact. |  | 73 |
| 5314693001 | Before agriculture, men and women are believed to have a greater degree of equality. But after the rise of agriculture, most human societies became ________ as a result of greater male strength. | Patriarchal |  | 74 |
| 5314693002 | caste system | a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society, there was virtually no social mobility |  | 75 |
| 5314693003 | Paleolithic | (Old Stone Age) a long period of human development before the development of agriculture |  | 76 |
| 5314693004 | Carthage | This city has existed for nearly 3,000 years, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC into the capital of the Carthaginian Empire. Controlled commerce in the Mediterranean prior to the rise of Roman Power. The expanding Roman Republic took control of many of its outposts after the two Punic Wars. |  | 77 |
| 5314693005 | Hellenization | The spread of Greek language and culture (Hellenism) throughout the Mediterranean, starting with t he conquests of Alexander the Great. Upon Alexander's death at the age of thirty-three (323 B.C.E.), his realm was divided among his leading generals. During their reigns and those of their successors, Hellenism (i.e., Greek culture) continued to flourish in major urban centers around the eastern Mediterranean (less so in rural areas). People traveling to different areas could communicate with people of other kingdoms through Greek. More than at any time in previous history, the eastern Mediterranean that emerged in Alexander's wake experienced a form of cultural unity and cosmopolitanism (a "cosmopolite" is a "citizen of the world," as opposed to a person who belongs to only one locality). The Roman Empire arose in the context of the Hellenistic world and took full advantage of its unity, promoting the use of Greek language, accepting aspects of Greek culture, and even taking over features of the Greek religion, to the point that the Greek and Roman gods came to be thought of as the same, only with different names. This complex unity achieved culturally through Hellenization and politically through the conquests of Rome is summed up by the term Greco-Roman world. | 78 | |
| 5314693006 | Daoism | Chinese religion that believes the world is always changing and is devoid of absolute morality or meaning. They accept the world as they find it, avoid futile struggles, and deviate as little as possible from 'the way' or 'path' of nature. |  | 79 |
| 5314693007 | Bureaucrat | government official | 80 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
Post Classical China- AP World History Flashcards
| 8202217996 | After the fall of the Han | -3 kingdoms for 200 years -spread of religion at times of unrest -Confucian decline, rise of Buddhism -trade decline, cities declined | 0 | |
| 8202235801 | Traditional systems of control by Chinese dynasties | -centralized bureaucracy -divine authority -civil service test -Confucian based system -legalism -census, taxes, conscriptive labor | 1 | |
| 8202277294 | Sui Dynasty | -581 to 618 -Ended civil war era and regained control | 2 | |
| 8202300690 | Yang Jian (Wendi) | -set up bureaucracy -anti-Confucian -lowered taxes -used Buddhism to unite kingdom -gave land to poor, established granaries -favored elites of the bureaucracy | 3 | |
| 8202328261 | Yangdi | -son of Wendi -established legal code -restored Confucian education and the examination system to establish a professional bureaucracy -built capital at Luoyang -began to rebuild Great Wall -construction of the Grand Canal -seen as a tyrant -assassinated by close advisors | 4 | |
| 8202364924 | Collapse of the Sui | -forced labor -failed attempt to expand into Korea -increased taxes on poor -rebellion by peasants | 5 | |
| 8202384488 | Tang Dynasty | -618 to 907 -"Golden Age" -Li Yuan led after the death of Yangdi -time of stability and prosperity | 6 | |
| 8202551391 | Tang Taizong | -built a new capital at Chang'an -Ruled using Confucian principles (in government) -Sponsored Buddhism | 7 | |
| 8202594005 | Tang Bureaucracy | -based on merit/ability -reached all levels of government -examination system | 8 | |
| 8202647743 | Equal Field System | -all land owned by government, assigned to individual families to farm based on ability to supply labor -was abolished and replaced by double tax | 9 | |
| 8202687409 | Double Tax | -levied taxes twice a based on land ownership instead of head tax -increased government revenue -helped solve momentary crisis in government revenue and stabilized the empire | 10 | |
| 8202800792 | Song Dynasty | -960 to 1279 -more control for government -vastly expanded the bureaucracy | 11 | |
| 8202843634 | Zhao Kuangyin | -(Emperor Song Taizu) -restores order during revolt -centralizes authority | 12 | |
| 8202872868 | Sui Dynasty |  | 13 | |
| 8202904410 | Tang Dynasty | 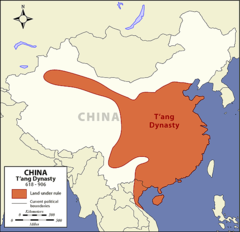 | 14 | |
| 8202911986 | Song Dynasty |  | 15 |
AP World History Period 1 Flashcards
From Hunting and Gathering to Civilizations, 2.5 million-1000 B.C.E.: Origins
Original from MrsBHatchTEACHER
| 7217585495 | hunting and gathering | Means of obtaining subsistence by humans before the mastery of sedentary agriculture; normally typical of tribal social organization |  | 0 |
| 7217585496 | civilization | Societies with reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of nonfarming elites, along with merchant and manufacturing groups | 1 | |
| 7217585497 | neolithic | The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished |  | 2 |
| 7217585498 | nomadic societies | livestock hearding societies that do not have a permanent settlement. normally found on the fringes of civilized (urban) societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian" by civilized societies |  | 3 |
| 7217585499 | culture | Combination of ideas, objects, and patterns of behavior that result from human social interaction |  | 4 |
| 7217585500 | agrarian revolution | Occurred between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; transition from hunting and gathering to sedentary agriculture |  | 5 |
| 7217585501 | pastoralism | A nomadic agricultural lifestyle based on herding domesticated animals; tended to produce independent people capable of challenging sedentary agricultural societies |  | 6 |
| 7217585502 | Catal Huyuk | Early urban culture/civiization based on sedentary agriculture; located in modern southern Turkey; larger in population than Jericho, had greater degree of social stratification |  | 7 |
| 7217585503 | Bronze Age | From 4000 to 3000 B.C.E.; increased use of plow, metalworking; development of wheeled vehicles, writing |  | 8 |
| 7217585504 | Mesopotamia | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilization that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris-Euphrates river valleys |  | 9 |
| 7217585505 | potter's wheel | A technological advance in pottery making; invented circa 6000 B.C.E.; encouraged faster and higher-quality ceramic pottery products |  | 10 |
| 7217585506 | Sumerians | People who migrated into Mesopotamia circa 4000 B.C.E.; created the first civilization within the region; organized area into city-states |  | 11 |
| 7217585507 | cuneiform | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets |  | 12 |
| 7217585508 | city-state | A form of political organization typical of Mesopotamian civilization; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king |  | 13 |
| 7217585509 | ziggurat | a massive tower building usually associated with Mesopotamian temple connections |  | 14 |
| 7217585510 | Babylonian Empire | Unified all of Mesopotamia circa 1800 B.C.E.; collapsed due to foreign invasion circa 1600 B.C.E. |  | 15 |
| 7217585511 | Hammurabi | The most important Babylonian ruler; responsible for codification of the law |  | 16 |
| 7217585512 | Pharaoh | The term used to denote the kings of ancient Egypt; the term, "great house" refers to the palace of the pharaohs |  | 17 |
| 7217585513 | pyramids | Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs |  | 18 |
| 7217585514 | hieroglyphs | Form of writing developed in ancient Egypt; more pictorial than Mesopotamian cuneiform |  | 19 |
| 7217585515 | Kush | African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nile circa 1000 B.C.E.; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries | 20 | |
| 7217585516 | monotheism | The exclusive worship of one god; introduced by Jews into Middle Eastern civilization |  | 21 |
| 7217585517 | Phoenicians | Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean |  | 22 |
| 7217585518 | Harappa and Mohenjo Daro | Major urban complexes of Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern |  | 23 |
| 7217585519 | Aryans | Indo-European nomadic, warlike, pastorialists who replaced Harappan civilization |  | 24 |
| 7217585520 | Huanghe (Yellow) River Basin | Site of the development of sedentary agriculture in China |  | 25 |
| 7217585521 | Shang | 1st Chinese dynasty (after the legendary Xia) |  | 26 |
| 7217585522 | Oracles | Shamans or priests in Chinese society who foretold the future through interpreting animal bones cracked by heat; inscriptions on bones led to Chinese writing |  | 27 |
| 7217585523 | ideographic writing | Pictograph characters grouped together to create new concepts; typical of Chinese writing | 28 | |
| 7217585524 | Big Geography | A term that draws attention to the global nature of world history. |  | 29 |
| 7217585525 | Paleolithic | The period that ended about 3,000 years after the end of the last Ice Age, it lasted until about 10,000 years ago. (Old Stone Age) The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period. |  | 30 |
| 7217585526 | Human migration during Paleolithic era | movement of humans from Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas | 31 | |
| 7217585527 | eglitarian | equality among people (no social levels) | 32 | |
| 7217585528 | tools | Humans developed a wider range of ____ specially adapted to different environments from tropics to tundra | 33 | |
| 7217585529 | Neolithic Revolution | period of change from hunter-gatherer lifesyle to agricultural lifestyles associated with domestication, farming, and settlement |  | 34 |
| 7217585530 | patriarchy | father based/male dominated society |  | 35 |
| 7217585531 | climatic change | Permanent agricultural villages emerged first in the lands of the eastern Mediterranean, possibly as a response to what? | 36 | |
| 7217585532 | weapons | Pastoralists were often the developers and disseminators of of ____ and forms of transportation that transformed warfare in agrarian civilizations | 37 | |
| 7217585533 | horses | name one mode of new transportation by the pastoralists | 38 | |
| 7217585534 | art | Elites, both political and religious, promoted ____. | 39 | |
| 7217585535 | record-keeping systems | ___ arose independently in all early civilization sand subsequently were diffused | 40 | |
| 7217585536 | Nile River | This river flooded regularly. |  | 41 |
| 7217585537 | Tigris River | This river's floods were unpredictable. |  | 42 |
| 7217585538 | Mesopotamian | Unpredictable weather patterns affected the development of the _____ civilization. | 43 | |
| 7217585539 | Egyptian | _______art demonstrated little change for nearly 1000 years. | 44 | |
| 7217585540 | Nubia and Kush | Kingdoms upriver from Egypt. | 45 | |
| 7217585541 | Standard of Ur |  | 46 | |
| 7217585542 | Harappan King or Priest Figure |  | 47 | |
| 7217585543 | Jericho | One of the earliest cities: located in modern Israel. |  | 48 |
| 7217585544 | Catal-Hyouk | One of the earliest cities: located in modern Turkey. | 49 | |
| 7217585545 | 50 |
Flashcards
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

