| 6259211083 | parietal pericardium | outside layer of the pericardium, or tough outer layer that forms a fibrous sac that surrounds and protects the heart.
Lines the tough fibrous pericardial sac |  | 0 |
| 6260457280 | membrane on heart itself | visceral pericardium or epicardium | | 1 |
| 6259213009 | point of heart | apex | | 2 |
| 6259220784 | infection of pericardium | pericarditis | | 3 |
| 6259223394 | three layers of heart | 1. inside layer: Endocardial (if infected called endocarditis)
2. Mycocardia (if infected myocarditis)
3. Pericarditis if infected | | 4 |
| 6259231094 | walls on ventricles there are ridges of muscles called | trabeculi carni (in walls of ventricles) | | 5 |
| 6259233607 | AV valves | atrioventricular valves: tricuspid and bicuspid | | 6 |
| 6260485460 | tricuspid has how many leaflets? | three | | 7 |
| 6260485461 | bicuspid also called | mitral valve | | 8 |
| 6259238963 | what hooks onto valve leaflets | cordi tendoni which is attached to cusps of valves and other end is attached to papillary muscle | | 9 |
| 6259246211 | if you get a stab wound into heart, blood build up in pericardial space causes | puts pressure on heart, impairs filling of heart, stroke volume goes down and heart rate goes up to maintain cardiac output | | 10 |
| 6259251465 | normal cardiac output | 5000ml/minute | | 11 |
| 6259253500 | normal sinus rhythm (heart rate) | 72 beats/min | | 12 |
| 6259255985 | normal stroke volume | 70 ml/beat | | 13 |
| 6260512220 | if you limit the fill because of pressure on outside of heart, heart rate must increase by twice (144 beats/min) to maintain cardiac input so when you have fluid in space pushing on heart its called | cardiac tamponade | | 14 |
| 6259259492 | equation for cardiac output | Co=SV*HR | | 15 |
| 6259264284 | tamponade | where something is pushing on the heart (blood, fluid) causing pressure on heart | | 16 |
| 6259269145 | pathway of heart | review on lab |  | 17 |
| 6259272797 | vessels that feed heart oxygenated blood | coronary arteries which come off the ascending aorta just after the aortic valve | | 18 |
| 6259279997 | part of coronary artery that circumflexes does what? | goes around to back | | 19 |
| 6260524839 | circumflex artery | delivers oxygenated blood to the left ventricle | | 20 |
| 6259296328 | sometimes coronary arteries get occluded with hardened fat which is called | athorosclorosis
which makes lumen more and more narrow so blood volume past that area goes down | | 21 |
| 6260547266 | how to open up artery with arthoroscloris | go to cardiologist who sticks catheter/balloon in to open it up-Angioplasty | | 22 |
| 6260550672 | during angioplasty you need to make sure to | add a net so that blood chunks don't flow downstream and cause clots | | 23 |
| 6260553833 | multilumen catheters during artotoscloris | one breaks up fat, one is a net, and one is a stent ( to hold it open) | | 24 |
| 6259320599 | if I don't get enough oxygenated blood to my heart I'll get | angina pectorus-heart pain | | 25 |
| 6260572839 | if angina pectoris continues it may go to | myocardial infarction | | 26 |
| 6259328162 | myocardial infarction | cells die, dead area gets filled with scar tissue (collagen) so area becomes inert which leads to not being able to conduct action potential correctly which leads to ahrythmia | | 27 |
| 6259335910 | right and left ventricle contract what valve close? sound? | tricuspid and bicuspid or AV, Lubb | | 28 |
| 6259338045 | closing of pulmonary and aortic valves (semilunar valves) causes what sound | Dubb | | 29 |
| 6259345739 | If someone had an irregular heart beat you'd get an | EKG | | 30 |
| 6259349276 | chordi tendoni | stops AV valve from going into atrium, stops the prolapse or movement back into atrius | | 31 |
| 6260593441 | if you infarcted area where chordi tendoni attach to papillary muscle you'd | break that chordi tendoni and need an immediate valve replacement | | 32 |
| 6259357840 | if a valve is incompetent? Incompetent pulmonary valve (bw right ventricle and pulmonary trunk) | -it doesn't work
-during diastole blood would run back into heart so less blood would go to lungs. You'll experience shortness of breath and less energy | | 33 |
| 6259364495 | cardiac muscle | striated, actin and myosin which slide over each other, involuntary, branched, intercalated disk with gap junctions, one or two nuclei | | 34 |
| 6260620232 | intercalated disk | when one contracts it sends action potential through gap junction so next one contracts |  | 35 |
| 6260619052 | each individual skeletal muscle needs what to tell it to contract | an axon | | 36 |
| 6259378376 | gap junctions | allow cardiac muscle to act as a syncytium | | 37 |
| 6259394160 | electrical messages move in heart | from on cell to another including through branches | | 38 |
| 6259381035 | two syncytiums in heart | atrial and ventricular | | 39 |
| 6260628819 | branches in cardiac muscle | can be good if one section dies, but could also make message go around in a circle causing an ahrythmia | | 40 |
| 6260636098 | junction in skeletal muscle | neuromuscular junction- electrical message comes down and opens voltage gated calcium channels, tells secretary or synaptic vesicles to fuse with cell membrane and release acetylcholine into synaptic cleft. Acetylcholine comes and binds to receptor which is a ligand gated sodium channel which opens enough sodium channels to have an action potential | | 41 |
| 6259406977 | electrical pathway | SA node, atrial syncytium, AV node, Bundle of His, bundle of branches, perkinge fibers, ventricular syncytium | | 42 |
| 6259417200 | heart's energy comes from | ATP from mitochondria through aerobic respiration | | 43 |
| 6260663495 | where does impulse start? discharges what? | SA node, dischares 72 times per minute | | 44 |
| 6259421984 | this area depolarizes more rapidly than any other portion of the conduction system | SA node | | 45 |
| 6260675244 | if you infarct SA node what happens? | AV node can be a secondary pacemaker but rate goes from 72 to 35. | | 46 |
| 6259425955 | if you infarct AV node, bundle of his or bundle branches could take over | but rate keeps decreasing as you go farther down | | 47 |
| 6259433189 | when is message slowed down in electrical pathway? | after AV node because we want to have time for the atrius to contract, force the blood down into the ventricles and fully fill the ventricles | | 48 |
| 6260801599 | if the atrius and ventricles contracted together, blood would not | move | | 49 |
| 6260803546 | ventricles are much ? then atrius | stronger | | 50 |
| 6259437251 | can you live in atrial fibrillation | yes-most of ventricular filling occurs passively when ventricle is relaxing during diastole when blood vol goes up and pressure goes down which pulls blood in | | 51 |
| 6260816732 | during exercise you need | atrius to work | | 52 |
| 6260822346 | atrius contracts, gap in time, and then ventricles contract from? | apex squeezing blood up and out of heart | | 53 |
| 6259445299 | contraction begins | at apex | | 54 |
| 6260828815 | the beginning of the contraction the myocardial cell has to ? | has to do with opening on sodium fast channels | | 55 |
| 6259450735 | opening of sodium fast channels | beginning of depolarization | | 56 |
| 6259454337 | cardiac muscle needs blood calcium for contraction | true and so does vascular smooth muscle | | 57 |
| 6259454338 | hypocalcemia | low blood calcium, heart wouldn't beat with as much force, rate goes down. Basis of antihypertensive meds (calcium channel blockers) which can treat tachycardia | | 58 |
| 6259462883 | If SA node goes away what takes over | AV node | | 59 |
| 6259467056 | after contraction theres a time when myocardium is insensitive to further stimulation | called absolute refractory period | | 60 |
| 6260843760 | relative refractory period | if stimulation is enough, it may contract | | 61 |
| 6259470062 | EKG reads out as a wave on a graph. describe waves | 1. P wave: atrial depolarization
no activity
2. QRS: ventricular depolarization
no activity
3. T wave: ventricular repolarization |  | 62 |
| 6260853743 | when does atrial repolarization occur? | lost in the QRS | | 63 |
| 6260855012 | way is p wave small | doesn't take much voltage to tell atrium to contract bc the walls are very thin | | 64 |
| 6260857852 | QRS wave is so big bc? | ventricle walls are thick so needs more voltage | | 65 |
| 6259491375 | AV node to bundle of His to bundle of branches. How many branches? | one goes to left, one goes to right | | 66 |
| 6259496005 | if you had a problem with a left bundle branch block | QT interval would be longer | | 67 |
| 6259500347 | when the ventricle is contracting-isovolemic contraction | volume isn't changing during that time | | 68 |
| 6259507228 | when right ventricle contracts it needs to generate enough pressure to exceed | the pressure in the pulmonary trunk. must exceed that pressure before blood can move at all | | 69 |
| 6260874385 | what might increase pulmonary pressure? | if you had cystic fibrosis so lungs are stiff-harder for R ventricle to push blood into lungs. if you make R ventricle work harder it gets bigger which is called R ventricular hypertrophy | | 70 |
| 6259514597 | during isovolumic contraction | blood not moving. AV valves and semilunar valves are closed | | 71 |
| 6259519348 | when ventricle pressure exceeds atrial pressure what valve closes | tricuspid and bicuspid valve (AV valves) | | 72 |
| 6260887642 | most of the ventricular filling occurs before | the atrius contracts so people can walk around in chronic atrial ventribulation (problem with that is that blood can start to clot in oracles which can move and cause brain aneurysm) | | 73 |
| 6259536429 | turbulence of blood flow through a valve sounds like a | heart murmur | | 74 |
| 6259541246 | end diastolic volume | volume in ventricle at end of diastole, relaxation period when you have the most blood in that ventricle | | 75 |
| 6259545747 | end systolic volume | systole: when heart is contracting
-when its contracting the ventricle doesn't eject all the blood so there is some blood leftover which is called end systolic volume | | 76 |
| 6259553912 | end diastolic volume-end systolic volume= | stroke volume (how much is left after each beat) | | 77 |
| 6260915125 | intense cardio can increase | stroke volume, heart rate, cardiac output | | 78 |
| 6260919649 | left ventricle is causing what kind of pressures | 120/80 mmHG | | 79 |
| 6260923139 | when left ventricle retracts its generating a lot of pressure and as that pressure goes above pressure in aorta, the aortic valve | opens, and pressure will move into aorta. That pressure will stretch aorta | | 80 |
| 6260928239 | if aorta didn't stretch, our systolic pressure would be much | higher which is called systolic hypertension (like 190/80)-common for old people | | 81 |
| 6260934803 | left ventricle contracts, aortic valve opens and pressure moves into aorta and stretches it and then during diastole the aorta wants to | go back to its original diameter so it will squeeze the blood and the blood wants to go down but the valve closes so the blood is forced during diastole which causes dichroic notch | | 82 |
| 6260941620 | dichroic notch | see book for table
In aortic pressure curve-through the elasticity of the aortic wall | 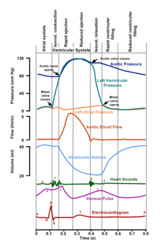 | 83 |
| 6260947953 | if you've lost elasticity of the aorta | you'll develop systolic hypertension
(190/80) | | 84 |
| 6261170376 | problem with high systolic BP is | pressure could be transmitted to circle of willis and vessels walls may weaken and form an aneurysm (barry aneurysm) which could result in hemoragic stroke | | 85 |
| 6261174673 | little hemoragic stroke | bad headache | | 86 |
| 6261176168 | burst barry aneurysm | you die | | 87 |
| 6259599517 | after load is amount of pressure | what the ventricle has to overcome before blood is ejected or moved out | | 88 |
| 6259601536 | intrinsic regulation of the heart | when cardiac muscle fibers are slightly stretched the next contraction force is going to be greater. This happens when you invert because blood rushes to core/heart which stretches right ventricle so next contraction strength is going to be greater. heart has to work harder if after load goes up | | 89 |
| 6259623697 | preload | amount of blood going back to heart | | 90 |
| 6259626119 | if preload goes up | more blood going back to heart so stroke volume and cardiac output go up | | 91 |
| 6259630883 | if you stretch the cardiac muscle a little bit the next contraction strength will be | greater or stronger | | 92 |
| 6259630884 | SA node controls | heart rate | | 93 |
| 6261196631 | ANS influences SA node, what two parts of it? | parasympathetic and sympathetic.
sympathetic will speed it up by releasing norepinephrine at the post ganglionic neuron
parasympathetic will slow it down by releasing aceytocholine | | 94 |
| 6261206642 | If I gave you an anticholinergic agent that blocks aceytochilone then heart rate? | heart rate goes up | | 95 |
| 6259640660 | what cranial nerve tells SA node to slow down | 10th or vegas | | 96 |
| 6261209690 | vegas nerve | carries parasympathetic info to SA node | | 97 |
| 6259644029 | stress response what gets released from adrenal medulla | epinephrine: gets released and heart rate goes up, prep for fight or flight | | 98 |
| 6259655365 | barro receptors in aortic body (associated with aorta)
when youre blood pressures go up, barry receptors get stimulated and thats going to send a message to the hypothalamus and parasympathetic stimulation occurs which will? (aka role of barro receptors) | decrease contraction strength of heart.
how body controls blood pressure | | 99 |
| 6261224568 | when you invert | blood runs from legs into core and stoke volume goes up so in a short period of time your heart rate will go down | | 100 |
| 6261228490 | where is most of bodies CO2 produced | mitochondria | | 101 |
| 6259633190 | two parts of ANS | 1. sympathetic: speeds up heart rate by releasing epinephrine, norepinephrine
2. parasympathetic: slows down heart rate, Aceytocholine released | | 102 |
| 6259671413 | when CO2 goes up, heart rate goes, breathing goes | heart rate goes up, breathing goes up to blow of CO2 | | 103 |
| 6259674154 | type of acidosis when CO2 goes up because you can't breathe it out | CO2 goes up and PH goes down-respitory acidosis. | | 104 |
| 6261245383 | respiratory acidosis might occur if you have period exudate (puss) in your air sacs (pneumonia) | harder to breathe | | 105 |
| 6259687607 | cardioregulatory section of brain located where? | medulla oblongata | | 106 |
| 6259692116 | chemoreceptors that are sensitive to blood oxygen are located? | carotid arteries and in the aorta. | | 107 |
| 6261248494 | peripheral chemo receptors | respond to O2 levels |  | 108 |
| 6259692117 | central chemo receptors in medulla and pons | respond to CO2 | | 109 |
| 6261251835 | when CO2 levels go up | you take deeper breathes | | 110 |
| 6261251854 | when you have COPD | -chronic bronchitis and emphysema: these people puff to try to keep airway open by creating a back pressure. people have probs getting their air out (air trapping) so people blow out through pursed lips (pink puffers and blue bloaters)
-central chemo receptors shut down, to much CO2
-if you give them O2, CO2 still continues to build=respitory acidosis | | 111 |
| 6261265818 | hypocalcemia | decreases heart contraction strength | | 112 |
| 6259730688 | increase in calcium in extracellular fluid | contraction strength goes up | | 113 |
| 6259732718 | angina | chest pain, use a vasodilator to help by putting it under tongue | | 114 |
| 6259735413 | sublingual administration of meds | very fast, put meds under tongue where there are big blood vessels | | 115 |
| 6259741548 | types of shock | 1. hypovolemic: low blood volume
2. cariogenic: something wrong with heart
3. neurogenic: something wrong with nervous system
4. hemmoragic: from bleeding | | 116 |
| 6259738336 | shock is when | body isn't circulating enough oxygenated blood | | 117 |
| 6261276826 | if you've been bleeding out | BP down, blood volume down, sympathetic stimulation takes over to try to help after norepinephrine gets released | | 118 |
| 6259746343 | if you bled out a lot what takes over | sympathetic stimulation of heart because norepinephrine is released from medulla | | 119 |
| 6259758562 | spell: tachycardia | fast heart rate | | 120 |
| 6259760985 | spell: stroke volume | The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction. | | 121 |
| 6259756755 | spell: pre potential | spontaneously developing local potential in SA node | | 122 |
| 6261286378 | SA node is discharging | 72 times per minute | | 123 |
| 6261290755 | stroke volume is so large, heart volume low. He has a big heart which is called | cardiomegaly | | 124 |
| 6261292406 | capillaries are made up of | simple squamous. | | 125 |
| 6261293894 | what normally doesn't go thru capillary wall | water and glucose do, but proteins don't unless its an inflammatory situation | | 126 |
| 6261296921 | types of capillaries | -continuous capillaries: endothelial cells fit tightly together: muscle, brain
-finistra: gaps in wall of capillary, can have diaphragms or lack diaphragms: located where we are filtering blood (i.e. kidneys) | | 127 |
| 6261303365 | what moves blood through blood vessels | heart generating a pressure difference | | 128 |
| 6261304500 | pulse pressure | difference between systolic and diastolic, normally 40 mmHG | | 129 |
| 6261307342 | low pulse pressure means | you're not moving much blood | | 130 |
| 6261308318 | if I kept doing a curl, arm muscle would | need more blood and O2, so pre capillary sphincters in that area are going to relax to let more blood into that capillary system | | 131 |
| 6259800719 | local regulation | pre-capillary sphincters system | | 132 |
| 6259803390 | anastomosis | direct connection between arteries and veins, helps with thermoregulation (i.e. fingertips get cold, not much blood in fingers because they've been bypassed to heat core to maintain 98.6) | | 133 |
| 6259810520 | different types of arteries from heart to body tissues | elastic artery: aorta
muscular
arterioles: small arteries
capillary bed | | 134 |
| 6259814017 | tunica media in a vessel contains | smooth muscle | | 135 |
| 6259819307 | distributing arteries are a type of | muscular arteries that contain a thick tunica media | | 136 |
| 6259819308 | arteries vs. vein walls | 1. arteries walls are much thicker, veins are much thinner
2. veins have one way valves | | 137 |
| 6259824964 | the aorta is really thick so how do you get O2 into wall | through vasamasorium | | 138 |
| 6259832127 | most of the blood vessels have sympathetic innervation so sympathetic stimulation to the vascular smooth muscle causes | vasoconstriction | | 139 |
| 6259834029 | vasoconstriction | A decrease in the diameter of blood vessels caused by contraction of smooth muscles in the vessel walls. | | 140 |
| 6259834030 | sympathetic nerve fibers innervate | tunica media | | 141 |
| 6259836161 | athrosclerosis | fatty plaques harden | | 142 |
| 6259838338 | arteriosclerosis | general hardening of arteries as you age | | 143 |
| 6261336713 | thickening of tunica intima and loss of elasticity in the tunica media | as you age | | 144 |
| 6261338619 | you can develop systolic hypertension and not have atherosclerosis | true | | 145 |
| 6259843243 | second branch of off aortic arch | left common carotid | | 146 |
| 6259847505 | clot in left common carotid could effect | left side of head (external) or left side of brain (internal) | | 147 |
| 6259850556 | nerve that tells diaphragm to contract | frenic nerve | | 148 |
| 6259853159 | superior frenic artery | supplies blood to diaphragm | | 149 |
| 6259856933 | arteries that send branches to stomach and liver | celiac artery | | 150 |
| 6259860478 | internal iliac arteries send blood to | organs in pelvic area: urinary bladder and rectum | | 151 |
| 6259862525 | venus sinuses in cranial vault drain blood into | internal jugular | | 152 |
| 6259867022 | one of the vessels draining blood from upper limb | cephalic vein-more lateral | | 153 |
| 6259869600 | sight that's often used for drawing blood | median cubital vein | | 154 |
| 6259871129 | longest vein in body | Great saphenous | | 155 |
| 6259876048 | liver has two blood sources | hepatic portal vein (nutrient rich such as amino acids and sugar) and hepatic artery (O2 rich, waste rich, nutrient poor). These two blood sources mix | | 156 |
| 6259886723 | how are fats absorbed? | lymphatics through lacteals | | 157 |
| 6259890322 | hepatic portal system picks up blood from | the splenic vein and superior mesentery vein | | 158 |
| 6259892486 | azygos vein | drains blood from thorax into superior vena cava | | 159 |
| 6259898367 | laminar blood flow | outer most layer of blood experiences greatest resistance to flow | | 160 |
| 6259902981 | innermost layer of blood | highest velocity bc lots less resistance | | 161 |
| 6259905995 | when you're taking a BP you use a | stethoscope - this part is called oscillation | | 162 |
| 6259908474 | sphygmomanometer | listens for korotkoff sounds, used in taking BP | | 163 |
| 6259917705 | if you decrease radius of a vessel, the resistance would go up. If you dilate, resistance goes down | so you can inhale a chemical that causes vasoconstriction (such as nicotine) | | 164 |
| 6259920495 | viscosity is | how thick blood is, thicker is harder to pump so blood pressure goes up. | | 165 |
| 6289074085 | if resistance increases, flow will | decrease | | 166 |
| 6289074813 | possuile law | if resistance increases, flow decreases | | 167 |
| 6259922898 | how to make your blood viscous | smoking because you are inhaling CO which binds to iron atom so your body thinks there's not enough oxygen so kidney release eurythropoetin which results in making more red blood cells so blood is more viscous | | 168 |
| 6279831629 | blood viscosity: if its more viscous, BP goes | up | | 169 |
| 6279834193 | if resistance increases, flow decreases | posseuille law | | 170 |
| 6289077106 | the greater the compliance of a vessel the more easily it will | stretch, most compliant are veins | | 171 |
| 6279840756 | we can store blood in | in spleen and veins | | 172 |
| 6279842702 | atherosclerosis makes the lumen of the vessel | shrinks/gets narrower, blood flow goes down | | 173 |
| 6279842703 | when lumen shrinks, flow | goes down | | 174 |
| 6279844451 | arteriosclerosis | arteries getting stiffer as you get older. Systolic BP goes up, diastolic stays the same: systolic hypertension | | 175 |
| 6279858598 | hepatic portal system starts | in capillary bed in the small intestine then goes to capillary bed in liver | | 176 |
| 6289101958 | portal system is a system that connects | two capillary systems together with no intervening pump | | 177 |
| 6279861398 | hepatic portal takes what from liver to GI tract | nutrients
drugs
allows liver to start breakdown process | | 178 |
| 6289107948 | fats absorbed though | lymphatics, not portal system | | 179 |
| 6279868524 | If I'm standing, | blood increases in legs,pressure increases in venioles, push more fluid into interstitial space | | 180 |
| 6289118063 | beth takes long plane ride she takes aspirin and drinks vodka | aspirin: stops platelets from sticking, anti platelet drug | | 181 |
| 6289883475 | if you go from lying to standing | vessels undergo vasoconstriction, BP drops which is called orthostatic hypotension | | 182 |
| 6289121203 | how does blood get back to heart | muscle contraction because veins have one way valves (lymphatic system is the same), venus return and lymph return also help, | | 183 |
| 6289219206 | lymph movement | skeletal muscle contraction, contraction of smooth muscle in the lymph vessel, just breathing | | 184 |
| 6289892837 | when CO2 levels go up | take deeper breathes, Co2 produced in mitochondria during aerobic respiration | | 185 |
| 6289896184 | when you dilate right atria what is released | (atrial niatriatic hormone) ANH which goes to kidney and tells it to not reabsorb sodium so blood volume goes down and BP goes down | | 186 |
| 6289905504 | endorphins effect | hindbrain | | 187 |
| 6289911510 | If you're BP is up, you can increase hydrostatic pressure and | cause edema | | 188 |
| 6289913908 | if you have lots of water loss | blood volume does down, BP goes down, Barro receptors stimulated and signal sent to hypothalamus and then sympathetic stimulation cause vasoconstriction and heart will beat at a greater force to bring BP up | | 189 |
| 6289918015 | kidneys and hypovalemia (when blood volume drops) | kidneys read blood volume and when it drops, renin gets released and then vasoconstriction which brings BP up and releases aldosterone so blood volume goes back up | | 190 |
| 6289923493 | pulse pressure | difference between systolic and diastolic | | 191 |
| 6289924581 | normal pulse pressure | 40 | | 192 |
| 6289925750 | narrow pulse pressure | ie 120/110 (pulse pressure of 10) you need pressure difference for things to move so blood wouldn't move effectively | | 193 |
| 6289943885 | lymphatic vessels job | drain excess interstitial fluid, filters lymph, absorption of fats | | 194 |
| 6289952696 | right lymphatic ducts drains | right thorax, right arm and right head | | 195 |
| 6290040246 | thoracic duct drains | left head, left thorax, lower extremity | | 196 |
| 6290041592 | we want to filter the lymph before its emptied into blood by | subclavian veins (thoracic vein drains into it) | | 197 |
| 6297062326 | in the lymph nodes are | macrophages | | 198 |
| 6297062327 | macrophages | differentiated from monocytes and are in a network of reticular fibers and that network is connective tissue which traps microbes like a net and macrophage comes in and phagocytes it | | 199 |
| 6297072011 | first phagocyte to scene of infection | neutrophil, | | 200 |
| 6297076972 | in your throat are lymphatic tissue called tonsils, the tonsils you can see are called | palatine, lingual tonsils. the ones you can't see are called pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids | | 201 |
| 6297082869 | what filters blood | spleen, left upper quadrant organ. | | 202 |
| 6297084587 | what takes over role of spleen | liver | | 203 |
| 6297087356 | innate immunity | body responds same way each time. example is tears/saliva | | 204 |
| 6297090820 | whats in saliva that helps with immunity | enzymes and antibodies | | 205 |
| 6297100224 | distal eurethra is colonized so by urinating you are | flushing it out-innate immunity | | 206 |
| 6297106961 | you inhale particulate matter and it gets stuck in your mucous and cilia move it back and you swallow | innate immunity | | 207 |
| 6297108625 | complement proteins are? produced by? | liver, coat (opsonesation) the bad guy and call in phagocytes and that can pull a white blood cell to area which is called chemotaxis, it can also cut holes in cell membrane so sodium goes in and water goes in so cell lyses and dies | | 208 |
| 6297233263 | interferon is produced by | cells that are infected by viruses. Tells healthy cells nearby that a virus is in the area which then interfere with making if virus | | 209 |
| 6297239962 | lyzezyme | in tears, destroys bacteria | | 210 |
| 6297242013 | after neutrophil comes | macrophages, they are bigger so it takes them longer to reach area. they also last longer | | 211 |
| 6297246399 | two things that make histamine | 1. mast cells
2. basophils
they also release heparine and leukotryinse (takes time)
histamine is ready to go | | 212 |
| 6297518834 | basophils | cells of inflammation | | 213 |
| 6297525792 | white blood cell thats anti-inflammatory | eosinophils | | 214 |
| 6297527207 | if you have a lot of allergies you're | eosinophil levels will be elevated, this is called eosinophilia (allergies or you could be infected with worms) | | 215 |
| 6297536056 | natural killer cells | part of innate immunity | | 216 |
| 6297538682 | inflammatory response: top layer of skin (stratified squamos keritinzed) then dermis (connective) and then hypodermis. Dirty splinter with dirt enters: | basophils and mast cells release histamine, makes capillaries more permeable. Now, fibrinogen goes in and turns to fibrin. then bad guy gets trapped in that area so neutrophil can come up with macrophage. fibrinogen also helps with healing
Summary: during the inflammatory response, chemical mediators get released, histamine and leukotryense. | | 217 |
| 6297578162 | adaptive immunity | Bacteria A and B.
macrophage phagocytosis it and puts some of it on its own cell membrane and present it to pre T and pre B cells: sensitizes them.
now they are sensitized so they'll be specific for bacteria A (primary immune response). now next time we get exposed to A, immune response will be quicker because of B and T memory cells and antibody response will be more robust. but, if we get exposed to bacteria B, whole process starts over again | | 218 |
| 6297796365 | specificity and memory leads to | an increased response to secondary/subsequent exposures | | 219 |
| 6297797785 | two types of immunity | cell specific/cell mediated and humoral (blood)/antibody mediated immunity | | 220 |
| 6297799740 | T cells carry out | cell mediated immunity. Go after bad guy itself.
IE T cytotoxic cell which goes after cancer cell. | | 221 |
| 6297806452 | B cells carry out | humoral immunity. produce antibodies | | 222 |
| 6297808332 | which B cell produces antibodies | plasma cell which flow in humor | | 223 |
| 6297814849 | what stimulates immunity process | an antigen. such as bacteria, viruses, worms, pollen (any foreign protein) | | 224 |
| 6297817631 | T cell types | T-4 helper cell, T-8 cytotoxic cell, T memory cells | | 225 |
| 6297820860 | B cell types | B memory cells, B plasma cells | | 226 |
| 6297823341 | virus that infects T-4 helper cell | HIV | | 227 |
| 6297824723 | helper cell | helps with sensitization of T and B cells so if you get HIV then both cell mediated and humoral immunity are impaired over time | | 228 |
| 6297828271 | where do T cells go to mature | thymus, located in mediastinum | | 229 |
| 6297832457 | we may have lymphocytes that response against self, if they are around they lead to autoimmune disorder so elimination of them is called | called negative selection | | 230 |
| 6297845801 | major histocompatibility complex, class one | allows immune system to respond to antigens inside the cells. Come and kill me | | 231 |
| 6297848247 | class 2 | found on B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells
Rally around the flag | | 232 |
| 6297862937 | T 4 helper cells possess these class 2 MHC molecules | true | | 233 |
| 6297884308 | tolerance is where the body is unresponsive to antigens. We definitely want to be tolerant to | our own antigens | | 234 |
| 6297886081 | examples of autoimmune disorders | MS, lupus, hashimotos, Multiple sclerosis | | 235 |
| 6297888619 | 5 types of antibodies | IG: G, A, M, E, D | | 236 |
| 6297897588 | what do you get through breastmilk | IGA: found in saliva, tears, breastmilk (exocrine gland secretion) | | 237 |
| 6297921166 | first of the antibodies that develop when you've been challenged is | IGM then IGG | | 238 |
| 6297924117 | antibodies themselves have a variable region | this binds to a specific antigenic determinant or antigen | | 239 |
| 6297928315 | when complement coats an organism | makes whatever it is more susceptible to phagocytosis | | 240 |
| 6297931546 | when you get exposed first to a new antigen you will have | primary immune response. Macrophages involved, T and B cells involved. This takes time (7-10 days).
Second time you're exposed you already have memory T and B cells | | 241 |
| 6297939412 | second time you're exposed to a bad guy | secondary immune response (you already have antibodies/cell memory) | | 242 |
| 6297945833 | progression | 1. antigen presented to a T lymphocyte
2. activation of T cell
3. cloning of T-8 (cytotoxic) and T memory cells
4. T-8 attacks the target
what presents the antigen is macrophages or B cells | | 243 |
| 6297977169 | one way T-8 cells attack the antigen is to | attach to the surface of the cell causing them to lyse | | 244 |
| 6297983163 | artificially acquired active immunity | vaccines | | 245 |
| 6297983164 | naturally acquired active immunity | when you've gotten sick, chickenpox | | 246 |
| 6297990602 | naturally acquired passive immunity | through placenta or breastmilk | | 247 |
| 6297993403 | artificially acquired passive immunity | from a horse or another human from blood
antibodies developed in another organism then isolated and injected into you
Passive: don't last long | | 248 |
| 6297999072 | Passive immunity | goes away at some point, don't last long | | 249 |
| 6298021068 | exaggerated response to an antigen | massive release of histamine. Called a hypersensitivity | | 250 |
| 6298030944 | thymic corpuscles found | in the thymus | | 251 |
| 6298056095 | pyer's patches are | lymph nodules found in small intestinal wall | | 252 |
| 6298057694 | germinal areas | area of lymph nodes where lymphocytes divide | | 253 |
| 6298060700 | prostaglandins | lipids produced from arachidonic acid which cause smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation
also stimulate nerve endings and causes pain (so we take NSAIDS to get rid of prostaglandins) | | 254 |
| 6279917262 | whats responsible for osmotic pressure | albumin | | 255 |
| 6279957686 | what does angiotensin produced when | gets released when blood volume goes down, causes vasoconstriction, blood pressure when down | | 256 |
| 6279938377 | epinephrine is released from | adrenal medula during stress response | | 257 |
| 6279969564 | carotid sinuses contain barro receptors which | monitor blood pressure | | 258 |





























































