| 5991289982 | Purpose of Mitosis | -Growth
-Repair
-Replacement
-Create 2 identical cells | | 0 |
| 5991289983 | Parts of the Cell Cycle | Interphase- G1, S, G2, and G0
Mitosis (M)- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Cytokinesis |  | 1 |
| 5991289984 | What happens in each part of the Cell Cycle | Interphase:
G1- Cell doing it's thing, first gap, cell grows, DNA in the form of chromatin
S- DNA is replicated
G2- Prep for cell division, and more growing occurs
G0- Non-dividing state
Mitosis (M): Cell Division
Prophase- Chromatin condenses into distinct chromosomes, nuclear membrane is gone, spindle fibers form as well as centrioles
Metaphase- Spindles are attached at the centromere, chromosomes line up in the middle (equator)
Anaphase- Chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindles and move towards opposite poles
Telophase- Cell starts to split by a wall or cleavage furrow, nuclear membrane reappears
Cytokinesis: Splitting of the Cytoplasm | | 2 |
| 5991289985 | Steps of Mitosis and what happens in each | Early Prophase- Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
Late Prophase- Distinct chromosomes, nuclear membrane gone, spindle fibers, and centrioles
Metaphase- Spindles are attached at the centromere, chromosomes line up in the middle (equator)
Anaphase- Chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindles and move towards opposite poles
Telophase- Cell starts to split by a wall or cleavage furrow, nuclear membrane reappears |  | 3 |
| 5991289986 | Longest phase of Mitosis | Prophase |  | 4 |
| 5991289987 | Shortest Phase of Mitosis | Anaphase |  | 5 |
| 5991289988 | Structure of the Mitotic Spindles:
Role of the Centrosomes | A sub-cellular region containing material that functions throughout the cell cycle yo organize the cells microtubules
Another name is the microtubule-organizing center | | 6 |
| 5991289990 | Structure of the Mitotic Spindles:
Role of the Microtubules | Rope like components, they are used to position the chromosomes at a specific spot in the cell.
They are also used to increase or decrease the tension on each side of the chromosome |  | 7 |
| 5991289991 | Structure, Function, and Location of Kinetochores | Structure- Structure made up of proteins
Function- Where microtubules attach to the centromeres of the chromatids
Location- Assembled on specific sections of DNA at the centromere |  | 8 |
| 5991289993 | Chromosome | Packed DNA in structures |  | 9 |
| 5991289994 | Sister Chromatids | Two identical copies of a chromosome that are connected by a centromere |  | 10 |
| 5991289995 | Daughter Chromosomes | A chromosome that results from the separation of the sister chromatids during cell division |  | 11 |
| 5991289996 | Difference in Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cells | Plant: During Telophase, a cell plate separates the cytoplasm and 2 cells
Animal: During Telophase, the cell membrane begins to pinch together (cleavage furrow), and separates the one cell to create 2 cells | | 12 |
| 5991289997 | Ploidy Numbers | A measure of the number of chromosomes in a cell | | 13 |
| 5991289998 | Chromosome numbers | Before Mitosis: 46 (2n)
During Mitosis: 46 (2n)
After Mitosis: 46 (2n) | | 14 |
| 5991289999 | Difference in Bacteria Replication and Eukaryotes | Bacteria Replication-
-occurs inside the cytoplasm
-replication is very rapid
Eukaryotes replication-
-occurs inside the nucleus
-replication is slow | | 15 |
| 5991290000 | Cell Cycle Control System and Checkpoints | Cell Cycle Control System-
What they are: the system that controls the cell cycle and is driven by specific signaling molecules present in the cytoplasm
Checkpoints-
What they are: a control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle | | 16 |
| 5991290001 | Cyclins | Group of proteins that control the development of cells through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinase. | | 17 |
| 5991290002 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinases | Group of proteins that regulate the cell cycle. Involved in transcription, mRNA processing, and the differentiation of the nerve cells. | | 18 |
| 5991290003 | Example of the molecular control of the cell cycle at the G2 checkpoint (including MPF) | G2 checkpoint: maturation-promoting factor (MPF)- which triggers the cells passage into the (m) phase past the G2 checkpoint, cyclin-dependent kinases
Goes from G2 to Mitosis | | 19 |
| 5991290004 | External Signals: Growth Factors | A protein released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide | | 20 |
| 5991290007 | Role of the Cell Cycle in Cancer | The cell cycle is the production of making more cells and cancer is uncontrolled cell growth | | 21 |
| 5991290008 | Role of genes and Mutations in the cell cycle in cancer | Mutations are caused by extrinsic factors and those increase risk of cancer | | 22 |
| 5991290009 | Three extrinsic factors that can cause cancer and how | 1- Chemicals (smoking)
2- Radiation
3- Viruses
4- Bacteria
Why there can be a lag time between exposure and cancer- Because this is the period between exposure and onset of disease | | 23 |
| 5991290010 | Relationship between time and the survival rates | quicker the cancer is found in time in an earlier stage, the longer survival rate one would have | | 24 |
| 5991290011 | Benign Tumor | A tumor that can't spread by invasion or metastasis to other areas | | 25 |
| 5991290012 | Malignant Tumor | A tumor that can spread by invasion or metastasis to other areas of the cell | | 26 |
| 5991290013 | Metastasis | The ability of cancer cells to penetrate into blood vessels, circulate the blood stream, and then invade normal tissue elsewhere |  | 27 |
| 5991290014 | Apoptosis | Programmed cell death, cell suicide | | 28 |
| 5991290017 | Biopsy | The removal of a piece of tissue for microscopic examination | | 29 |
| 5991290018 | Carcinoma | An uncontrolled growth of cells that remains in original location | | 30 |
| 5991290019 | Oncogene | Damaged genes that help develop cancer | | 31 |
| 5991290020 | Carcinogen | Any substance that has the potential to cause cancer in living tissues | | 32 |
| 5991290022 | drawn examples of the stages of Mitosis | |  | 33 |
| 5991290023 | Cell in Interphase | | 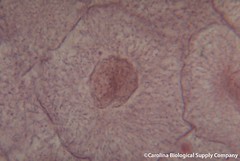 | 34 |
| 5991290024 | Cell in Prophase | |  | 35 |
| 5991290025 | Cell in Metaphase | | 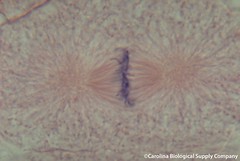 | 36 |
| 5991290026 | Cell in Anaphase | | 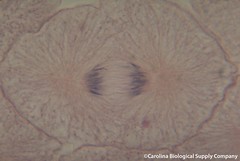 | 37 |
| 5991290027 | Cell in Telophase | | 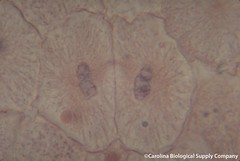 | 38 |
| 5991290028 | Gametes | A reproductive cell- sperm or egg | | 39 |
| 5991290029 | Somatic Cells | All other body cells besides reproductive | | 40 |
| 5991290030 | Karyotype | Visual expression of chromosomes that have paired up, or the chromosome complement of a cell or a whole organism | | 41 |
| 5991290031 | Homologous Chromosomes | A chromosome with the same gene sequence as another, each derived from one parent | | 42 |
| 5991290032 | Homologs | same thing as a homologous chromosome, A chromosome with the same gene sequence as another, each derived from one parent | | 43 |
| 5991290033 | Autosomes | chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes | | 44 |
| 5991290034 | Sex Chromosomes | Determine the sex of a person,
XY= male XX=female | | 45 |
| 5991290035 | Diploid | (2n), 2 of the halves, full set of genetic information | | 46 |
| 5991290036 | Haploid | (1n), half of the genetic information | | 47 |
| 5991290037 | Fertilization | merging of 2 haploid cells | | 48 |
| 5991290038 | Zygote | early stage development of an organism | | 49 |
| 5991290039 | Gene | The set of information that controls a trait;a segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. | | 50 |
| 5991290041 | Variation | The differences that occur in individuals within a species | | 51 |
| 5991290043 | Asexual Reproduction | Advantages- can reproduce twice as many, does not require fertilization, can quickly occur, don't need mate
Disadvantages- reproduction is based on amount of food, very little variation | | 52 |
| 5991290044 | Sexual Reproduction | Advantages- more genetic variation, children are different from parents, able to produce more offspring because of mate
Disadvantages- slower reproduction rate, less reliable, takes time and energy to find mate | | 53 |
| 5991290046 | Recombination | New allele combinations produced by crossing over, source that results in the variation in population gene pools | | 54 |
| 5991290047 | Recombinant Chromosomes | When genetic material combine in which half is from the mother and half is from the father and makes a new chromosome | | 55 |
| 5991290048 | Synapsis | Occurs in Prophase of Meiosis 1, the homlogs pair up to form bivalents | | 56 |
| 5991290049 | Chiasma | Regions where non-sister chromatids become entangled and the chromosomes exchange segments, place of crossing over | | 57 |
| 5991290050 | Tetrad | A group of 4 closely associated chromatids of a homologous pair formed by synapsis, copied chromosomes | | 58 |
| 5991290051 | "n" | half of the genetic information, haploid | | 59 |
| 5991290052 | Meiosis | Purpose- Sex cell division
Product- 4 gametes used in fertilization
Location of Occurrence- within the testes and the ovaries | | 60 |
| 5991290053 | Number of human Chromosome pairs | 23 pairs | | 61 |
| 5991290054 | Number of human Chromosomes | 46 individual | | 62 |
| 5991290055 | Number of human chromosomes in cells of meiosis | At Beginning- (2n) or 46
At End-(n) or 23 | | 63 |
| 5991290056 | Relationship between genetic diversity and Meiosis | Ways that Meiosis increases Genetic Diversity- because of crossing over and the fact that individual genes come from 2 different places and combine together | | 64 |
| 5991290057 | Crossing Over | When- Prophase of Meiosis 1
Where- at the Chiasma site
How- non-sister Chromatids become entangled and the chromosomes exchange segments | | 65 |
| 5991290058 | Genetic Recombination | When- During Meiosis 1
Where-Anaphase
How- New allele combinations produced by crossing over, source that results in the variation in population gene pools | | 66 |
| 5991290059 | Ploidy number during meiosis | Before-(2n) or 46
After-(n) or 23 | | 67 |
| 5991290060 | The Stages of Meiosis and what happens in each | Meiosis 1:
Prophase- Chromatin condenses into distinct chromosomes, nucleus disappears, spindle fibers form as well as centrioles, chromosomes are a tetrad
Metaphase- Spindles are attached at the centromere, chromosomes line up in the middle (equator)
Anaphase- Chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindles and move towards opposite poles
Telophase- Cell starts to split by a cleavage furrow, nuclear membrane reappears
Cytokinesis: Splitting of the Cytoplasm
Meiosis 2:
-same steps as Meiosis 1 except for at the end instead of producing 2 haploid cells, either creates 4 sperm by spermatogenesis or 1 egg and 3 polar bodies by oogenesis | | 68 |
| 5991290061 | Purpose of Meiosis 1 | To create 2 haploid cells each with 2 sister chromatids per chromosome | | 69 |
| 5991290062 | Purpose of Meiosis 2 | To create 4 haploid cells with each chromosome consisting of a single chromatid | | 70 |
| 5991290063 | Significant events of Prophase in Meiosis 1 | Where crossing over occurs and in result ensures that each sex cell is unique, chromosomes are tetrad | | 71 |
| 5991290064 | The difference between Metaphase of Meiosis 1 and Mitosis | In Meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes line up in the middle whereas in mitosis individual chromosomes line up in the middls | | 72 |
| 5991303061 | anaphase | Stage of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite spindle poles. | | 73 |
| 5991303062 | asexual reproduction | Reproductive mode by which offspring arise from a single parent only. | | 74 |
| 5991303063 | cell cycle | A series of events from the time a cell forms until its cytoplasm divides. | | 75 |
| 5991303064 | cell plate | After nuclear division in a plant cell, a disk-shaped structure that forms a cross-wall between the two new nuclei. | | 76 |
| 5991303065 | cleavage furrow | In a dividing animal cell, the indentation where cytoplasmic division will occur. | | 77 |
| 5991303066 | cytokinesis | Cytoplasmic division. | | 78 |
| 5991303067 | growth factor | Molecule that stimulates mitosis and differentiation. | | 79 |
| 5991303068 | homologous chromosomes | Chromosomes with the same length, shape, and set of genes. | | 80 |
| 5991303069 | interphase | In a eukaryotic cell cycle, the interval between mitotic divisions when a cell enlarges, roughly doubles the number of its cytoplasmic components, and replicates its DNA. | | 81 |
| 5991303070 | metaphase | Stage of mitosis at which the cell's chromosomes are aligned midway between poles of the spindle. | | 82 |
| 5991303071 | metastasis | The process in which cancer cells spread from one part of the body to another. | | 83 |
| 5991303072 | mitosis | Nuclear division mechanism that maintains the chromosome number. Basis of body growth and tissue repair in multicelled eukaryotes; also asexual reproduction in some plants, animals, fungi, and protists. | | 84 |
| 5991303073 | neoplasm | An accumulation of abnormally dividing cells. | | 85 |
| 5991303074 | oncogene | Gene that helps transform a normal cell into a tumor cell. | | 86 |
| 5991303075 | prophase | Stage of mitosis during which chromosomes condense and become attached to a newly forming spindle. | | 87 |
| 5991303076 | proto-oncogene | Gene that, by mutation, can become an oncogene. | | 88 |
| 5991303077 | spindle | Dynamically assembled and disassembled network of microtubules that moves chromosomes during nuclear division. | | 89 |
| 5991303078 | telomere | Noncoding, repetitive DNA sequence at the end of chromosomes; protects the coding sequences from degradation. | | 90 |
| 5991303079 | telophase | Stage of mitosis during which chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles and decondense, and new nuclei form. | | 91 |
| 5991303080 | tumor | A neoplasm that forms a lump. | | 92 |
| 5991303082 | crossing over | Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange corresponding segments during prophase I of meiosis. | | 93 |
| 5991303083 | egg | Mature female gamete, or ovum. | | 94 |
| 5991303084 | fertilization | Fusion of two gametes to form a zygote. | | 95 |
| 5991303085 | gamete | Mature, haploid reproductive cell; e.g., an egg or a sperm. | | 96 |
| 5991303086 | gametophyte | A haploid, multicelled body in which gametes form during the life cycle of land plants and some algae. | | 97 |
| 5991303087 | germ cell | Immature reproductive cell that gives rise to haploid gametes when it divides. | | 98 |
| 5991303088 | haploid | Having one of each type of chromosome characteristic of the species. | | 99 |
| 5991303089 | meiosis | Nuclear division process that halves the chromosome number. Basis of sexual reproduction. | | 100 |
| 5991303090 | sexual reproduction | Reproductive mode by which offspring arise from two parents and inherit genes from both. | | 101 |
| 5991303091 | somatic | Relating to the body. | | 102 |
| 5991303092 | sperm | Mature male gamete. | | 103 |
| 5991303093 | sporophyte | Diploid, spore-producing stage of a plant life cycle. | | 104 |
| 5991303094 | zygote | Diploid cell formed by fusion of two gametes; the first cell of a new individual. | | 105 |




















































































































































