| 8487101060 | Silk Roads | the most famous of the trading routes established by pastoral nomads connecting the European, Indian, and Chinese; transmitted goods and ideas among civilizations | | 0 |
| 8487101061 | Black Death | The common name for a major outbreak of plague that spread across Asia, North Africa, and Europe in the mid-fourteenth century, carrying off vast numbers of persons. | | 1 |
| 8487101062 | Indian Ocean trading network | The world's largest sea-based system of comunication and exchange before 1500 C.E., Indian Ocean commerce stretched from southern China to eastern Africa and included not only the exchange of luxury and bulk goods but also the exchange of ideas and crops. |  | 2 |
| 8487101063 | Srivijaya | A Malay kingdom that dominated the Straits of Malacca between 600 and 1075 CE. A state based on the Indonesian island of Sumatra, between the seventh and eleventh centuries C.E. It amassed wealth and power by a combination of selective adaptation of Indian technologies and concepts, and control of trade routes. |  | 3 |
| 8487101064 | Borobrodur | Buddhist temple on the island of Java that is a primary example of Indian ocean trade causing cultural diffusion. | | 4 |
| 8487101065 | Angkor Wat | This place was first a Hindu (dedicated to the god Vishnu), then subsequently a Buddhist, temple complex in Cambodia and the largest religious monument in the world. |  | 5 |
| 8487101066 | Swahili civilization | an East African civilization that emerged in the 8th century ce from a blending of Bantu, Islamic, and other Indian Ocean trade elements |  | 6 |
| 8487101067 | Great Zimbabwe | City, now in ruins (in the modern African country of Zimbabwe), whose many stone structures were built between about 1250 and 1450, when it was a trading center and the capital of a large state. | | 7 |
| 8487101068 | Sand roads | The system of roads that led across the Sahara desert in Africa. |  | 8 |
| 8487101069 | Ghana, Mali, Songhay | Capitalizing on these new saharan trades Ghana mali and Songhay monarchies were established trading gold for salt and slaves |  | 9 |
| 8487101070 | Trans-Saharan slave trade | A fairly small-scale trade that developed in the twelfth century C.E., exporting West African slaves captured in raids across the Sahara for sale mostly as household servants in Islamic North Africa; the difficulty of travel across the desert limited the scope of this trade. | | 10 |
| 8487101071 | American web | A term used to describe the network of trade that linked parts of the pre-Columbian Americas; although less intense and complete than the Afro-Eurasian trade networks, this web nonetheless provided a means of exchange for luxury goods and ideas over large areas. |  | 11 |
| 8487101072 | pochteca | Special merchant class in Aztec society, specialized in long-distance trade in luxury items | | 12 |
| 8487101073 | Sui dynasty | The short dynasty between the Han and the Tang; built the Grand Canal, strengthened the government, and introduced Buddhism to China |  | 13 |
| 8487101074 | Tang dynasty | 618-907 CE. Much like the Han using Confucianism. had the equal field system, a bureaucracy based on merit and a Confuciansim education system. Trained strong armies of almost a million troops to fight off nomadic powers from Asia. Made story cultural influence over Korea and Vietnam. |  | 14 |
| 8487101075 | Song dynasty | During this Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 AD) China saw many important inventions. There was a magnetic compass; had a navy; traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton); paper money, gun powder; landscape black and white paintings |  | 15 |
| 8487101076 | Hangzhou | Capital of later Song dynasty; located near East China Sea; permitted overseas trading; population exceeded 1 million. |  | 16 |
| 8487101077 | economic revolution | Economic development of Song; mass production for trade; equal field system | | 17 |
| 8487101078 | foot binding | Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household. | 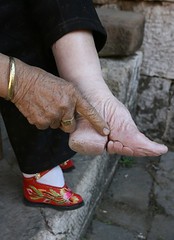 | 18 |
| 8487101079 | tribute system | Chinese method of dealing with foreign lands and people's that assumed the subordination of all non-Chinese authorities and required the payment of tribute --produce of value from their countries--to the Chinese emperor(although the Chines gifts given in return were often much more valuable). | | 19 |
| 8487101080 | Xiongnu | A confederation of nomadic peoples living beyond the northwest frontier of ancient China. Chinese rulers tried a variety of defenses and stratagems to ward off these 'barbarians,' as they called them, and dispersed them in 1st Century. (168) |  | 20 |
| 8487101081 | Khitan | Nomadic peoples of Manchuria; militarily superior to Song dynasty China but influenced by Chinese culture; forced humiliating treaties on Song China in 11th century | | 21 |
| 8487101082 | Jurchen | Founders of Qin kingdom that succeeded the Liao in northern China; annexed most of the Yellow River basin and forced Song to flee to south. | | 22 |
| 8487101083 | Silla Dynasty | Korean dynasty that resisted Tang for first time. Respected China, performed kowtow, ritual bow to Chinese emperor. Studied Buddhism/Confucianism | | 23 |
| 8487101084 | hangui | Korean written alphabet | | 24 |
| 8487101085 | chu nom | a style of writing adapted from China to Vietnam. It became the basis for the development of an independent national literature. |  | 25 |
| 8487101086 | Shotoku Taishi | Who: Prince of Japan. What: Borrowed heavily from China: writing and art (kana and ink on silk), architecture (pagoda), well-field system, etc. Also wrote the 17 point constitution. When: 573-621. Where: Japan. Why: Made changes that greatly influenced Japan and were around for centuries. | | 26 |
| 8487101087 | bushido | "the way of the warrior"; Japanese word for the Samurai life ; Samurai moral code was based on loyalty, chivalry, martial arts, and honor until the death |  | 27 |
| 8487101088 | Chinese Buddhism | China's only large-scale cultural borrowing before the 20th century. Buddhism entered China from India in the first and second centuries C.E but only became popular between 300-800 C.E through a series of cultural accommodations. At first supported by the state, Buddhism suffered persecution during the 9th century but continued to play a role in Chinese society. | | 28 |
| 8487101089 | Emperor Wendi | a Chinese general, who secured his Emperor position by killing 59 princes of the Zhou royal house, and founded the Sui Dynasty. Presented himself as a Buddhist Cakravartin King, that is, a monarch who uses military force to defend the Buddhist faith. | | 29 |
| 8487101090 | Quran | The holy book of Islam | | 30 |
| 8487101091 | umma | The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a community. | | 31 |
| 8487101092 | Pillars of Islam | The five core practices required of Muslims: a profession of faith, regular prayer, charitable giving, fasting during Ramadan, and a pilgrimage to Mecca (if physically and financially possible). | | 32 |
| 8487101093 | hijra | The Migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in A.D. 622, marking the founding of Islam |  | 33 |
| 8487101094 | sharia | Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life | | 34 |
| 8487101095 | jizya | tax paid by Christians and Jews who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion | | 35 |
| 8487101096 | ulama | Muslim religious scholars. From the ninth century onward, the primary interpreters of Islamic law and the social core of Muslim urban societies. | | 36 |
| 8487101097 | Umayyad Caliphate | (661-750 CE) The Islamic caliphate that established a capital at Damascus, conquered North Africa, the Iberian Pennisula, Southwest Asia, and Persia, and had a bureaucracy with only Arab Muslims able to be a part of it. |  | 37 |
| 8487101098 | Abbasid Caliphate | (750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Mulim could be a part of. |  | 38 |
| 8487101099 | Sufism | A branch of Islam, defined by adherents as the inner, mystical dimension of Islam; others contend that it is a perennial philosophy of existence that pre-dates religion, the expression of which flowered within Islam |  | 39 |
| 8487101100 | al-Ghazali | Brilliant Islamic theologian; struggled to fuse Greek and Qur'anic traditions; not entirely accepted by ulama | | 40 |
| 8487101101 | Sikhism | the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam | | 41 |
| 8487101102 | Ibn Battuta | (1304-1369) Morrocan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period. |  | 42 |
| 8487101103 | Timbuktu | Mali trading city that became a center of wealth and learning |  | 43 |
| 8487101104 | Mansa Musa | Ruler of Mali (r. 1312-1337). His extravagant pilgrimage through Egypt to Mecca in 1324-1325 established the empire's reputation for wealth in the Mediterranean world. |  | 44 |
| 8487101105 | al-Anadalus | Muslim kingdom in southern Spain, established in 756 | | 45 |
| 8487101106 | madrassas | Formal colleges for higher institutions in the teaching of Islam as well as in secular subjects founded throughout the Islamic world in beginning in the 11th century | | 46 |
| 8487101107 | House of Wisdom | Combination library, academy, and translation center in Baghdad established in the 800s. |  | 47 |
| 8487101108 | Ibn Sinna | He was one of the most famous doctors of all times. He read the works of Hippocrates and Galen and improved them, by adding more accurate descriptions. He also created anatomical charts using newly invented surgical tools. His text "Cannon of Medicine" (aka "Code of Laws in Medicine") was reference source for doctors for hundreds of years following his death. | | 48 |
| 8487101109 | Nubian Christianity | Christianity was introduced by traders and missionaries. Preserved Christianity for 600 years. | | 49 |
| 8487101110 | Nestorian | Theological position of Nestorius, who allegedly taught that there are two complete natures and thus two persons, human and divine, in Jesus Christ; rejected by the Council of Ephesus (431), which taught that human nature and divine nature are united in the one person of Christ. | | 50 |
| 8487101111 | Ethiopian Christianity (aka Coptic church) | Rulers of axum had adopted Christianity. Christian island in a Muslim sea protected by its moutanous geography and distance from major centers of islamic power. Also helped muhammad's followers be safe. This isolation made it develop a fascination with judaism and jerusalem. Justified their rule through a connection with Solomon as a descendent of jesus. Tried to create a new jerusalem |  | 51 |
| 8487101112 | Byzantine Empire | (330-1453) The eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived after the fall of the Western Empire at the end of the 5th century C.E. Its capital was Constantinople, named after the Emperor Constantine. |  | 52 |
| 8487101113 | Constantinople | A large and wealthy city that was the imperial capital of the Byzantine empire and later the Ottoman empire, now known as Istanbul | | 53 |
| 8487101114 | Justinian | Byzantine emperor in the 6th century A.D. who reconquered much of the territory previously ruler by Rome, initiated an ambitious building program , including Hagia Sofia, as well as a new legal code |  | 54 |
| 8487101115 | caesarpapism | a political-religious system where the secular ruler is also the head of the religious establishment (Byzantine Empire) | | 55 |
| 8487101116 | Eastern Orthodox Christianity | Eastern branch of Christianity that evolved following the division of the Roman Empire and the subsequent development of the Byzantine Empire in the east and the medieval European society in the west. The church recognized the primacy of the patriarch of Constantinople | | 56 |
| 8487101117 | icons | A painting of Christ or another holy figure, used as an aid to devotion in the Byzantine and other Eastern Churches. | | 57 |
| 8487101118 | Prince Vladimir of Kiev | converted to Orthodox Christianity, and allowed Byzantine influence in his realm | | 58 |
| 8487101119 | Kievan Rus | A monarchy established in present day Russia in the 6th and 7th centuries. It was ruled through loosely organized alliances with regional aristocrats from. The Scandinavians coined the term "Russia". It was greatly influenced by Byzantine | | 59 |
| 8487101120 | Charlemagne | King of the Franks (r. 768-814); emperor (r. 800-814). Through a series of military conquests he established the Carolingian Empire, which encompassed all of Gaul and parts of Germany and Italy. Illiterate, though started an intellectual revival. | | 60 |
| 8487101121 | Holy Roman Empire | A medieval and early modern central European Germanic empire, which often consisted of hundreds of separate Germanic and Northern Italian states. In reality it was so decentralized that it played a role in perpetuating the fragmentation of central Europe. | | 61 |
| 8487101122 | Roman Catholic church | One of three major branches of Christianity, together with the Eastern Orthodox Church, a second of the three major divisions of Christianity, arose out of the division of the Roman empire into four governmental regions. In 1054 CE Christianity was divided along that same line when the Eastern Orthodox, centered in Constantinople, and the ______ ______ ______, centered in Rome, split. | | 62 |
| 8487101123 | Western Christendom | Western Europe was on the margins of world history for most of the postclassical millennium; It was far removed from the growing world trade routes; European geography made political unity difficult; Coastlines and river systems facilitated internal exchange; | | 63 |
| 8487101124 | Cecilia Penifader | The book "A Medieval Life" by Judith Bennett is written about her. She lived from 1295-1344. Cecilia was a peasant, and her actions were exceptionally well documented in the courts of Brigstock. She amassed a substantial amount of wealth and land. Unmarried and childless, she lived as a singlewoman in Brigstock and remained close to her brothers and sisters throughout her life. | | 64 |
| 8487101125 | Crusades | Armed pilgrimages to the Holy Land by Christians determined to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule. The Crusades brought an end to western Europe's centuries of intellectual and cultural isolation. |  | 65 |
| 8487101126 | pastoralism | A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter. | | 66 |
| 8487101127 | Modun | leader of the Xiongnu Empires (r. 210-174 BCE) that transformed egalitarian fragmented societies into a more centralized and hierarchical political system with a divinely sanctioned ruler. | | 67 |
| 8487101128 | Turks | 6th-10th centuries C.E.
•Pastoral ethnic group that originated in northern Eurasia
and spread into Central Asia and the Middle East
•Had significant cultural and political interactions with China, Persia, Byzantium
•Conversion to Islam 10th-14th centuries
•Diffused Islam throughout Middle East, India, Anatolia(Turkey) | | 68 |
| 8487101129 | Almoravid Empire | Founded in the 11th century by Muslim reformers. Its members came from a Berber group living in the western Sahara in what is today Mauritania. The movement began after devout Berber Muslims made a hajj. | | 69 |
| 8487101130 | Temujin | leader of the largest Mongol clans; he unites them all(plans to conquer Asia); and receives title Genghis Khan(universal ruler) | | 70 |
| 8487101131 | the Mongol world | Eurasia, 13th-15th centuries
•50-year period of Mongol conquests across Eurasia that
created the Mongol empire
•Subjected huge populations to Mongol rule
•Military strength allowed for rapid conquest
•Mongol rule created interactions between diverse groups
•Served to diffuse technology, culture, political and economic systems |  | 71 |
| 8487101132 | Yuan Dynasty | (1279-1368 CE) The dynasty with Mongol rule in China; centralized with bureaucracy but structure is different: Mongols on top->Persian bureaucrats->Chinese bureuacrats. | | 72 |
| 8487101133 | Kublai Khan | (1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China. | | 73 |
| 8487101134 | Hulegu | Ruler of the Ilkhan khanate; grandson of Chinggis Khan; responsible for capture and destruction of Baghdad in 1257 | | 74 |
| 8487101135 | Khutulun | most famous daughter of Kaidu and the niece of Kublai Khan. Her father was most pleased by her abilities, and she accompanied him on military campaigns. Never married because no man could defeat her.
wrestler princes | | 75 |
| 8487101136 | Kipchak Khanate | Name given to Russia by the Mongols after they conquered it and incorporated it into the Mongol Empire in the mid-thirteenth century; known to Russians as the "Khanate of the Golden Horde." |  | 76 |
| 8487101137 | Paleolithic Persistence | pre-1492 life in much of the Americas(especially North America); characterized by living a simple primitive lifestyle, without entering into large settlements or the iron age | | 77 |
| 8487101138 | Igbo | Nigeria's third largest group who are mostly Christian. They are located in the southeast part of Nigeria. This group has many conflicts with the Yoruba and at one point they tried to become a independent nation. | | 78 |
| 8487101139 | Iroquois | A later native group to the eastern woodlands. They blended agriculture and hunting living in common villages constructed from the trees and bark of the forests |  | 79 |
| 8487101140 | Timur | Sometimes known as Tamerlane, this was the Central Asian leader of a Mongol tribe who attempted to re-establish the Mongol Empire in the late 1300's. His empire included Persia (Iran) and many surrounding lands. He is the great great grandfather of Babur. who later founds the Mughal Empire in India. | | 80 |
| 8487101141 | Fulbe | West Africa's largest pastoral society, whose members gradually adopted Islam and took on a religious leadership role that lead to the creation of a number of new states. | | 81 |
| 8487101142 | Ming Dynasty | Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China. |  | 82 |
| 8487101143 | European Renaissance | a "rebirth" of classical learning that is most often associated with the cultural blossoming of Italy is the period 1350-1500 and included Greek learning and growing secularism | | 83 |
| 8487101144 | Zheng He | An imperial eunuch and Muslim, entrusted by the Ming emperor Yongle with a series of state voyages that took his gigantic ships through the Indian Ocean, from Southeast Asia to Africa. |  | 84 |
| 8487101145 | Ottoman Empire | Islamic state founded by Osman in northwestern Anatolia. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire was based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople) from 1453-1922. It encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe. |  | 85 |
| 8487101146 | seizure of Constantinople | Constantinople fell to army of Ottoman sultan Mehmed II "the Conqueror" in 1453, marking end of Christian Byzantium | | 86 |
| 8487101147 | Safavid Empire | Turkish-ruled Iranian kingdom (1502-1722) established by Ismail Safavi, who declared Iran a Shi'ite state. |  | 87 |
| 8487101148 | Songhay Empire | A state located in western Africa. From the early 15th to the late 16th century, it was one of the largest Islamic empires in history. | | 88 |
| 8487101149 | Mughal Empire | Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries; a minority of Muslims ruled over a majority of Hindus. | | 89 |
| 8487101150 | Malacca | Port city in the modern Southeast Asian country of Malaysia, founded about 1400 as a trading center on the Strait of Malacca. Also spelled Melaka. |  | 90 |
| 8487101151 | Aztec Empire | 1325-1500 CE. Also known as Mexica, the Aztecs created a powerful empire in central Mexico. Forced defeated people to provide goods and labor as tax. At its best had complex myth and religious traditions and reached amazing architectural and artistic accomplishments. |  | 91 |
| 8487101152 | Inca Empire | (1450-1572 CE), Largest Empire ever built in South America; territory extended 2,500 miles from north to south and embraced almost all of modern Peru, most of Ecuador, much of Bolivia, and parts of Chile and Argentina; maintained effective control from the early 15th century until the coming of Europeans in the early 16th century. As the most powerful people of Andean America, the Inca dominated Andean society until the coming of Europeans; was an extremely diverse culture cause it spanned north and south rather then east and west. |  | 92 |









































































