AP World History Periodization Review Flashcards
| 7274070218 | Period 1 Dates | Foundations to 600 BCE | 0 | |
| 7274070219 | Period 2 Dates | 600 BCE to 600 CE | 1 | |
| 7274070220 | Period 3 Dates | 600 CE to 1450 CE | 2 | |
| 7274070221 | Period 4 Dates | 1450 CE to 1750 CE | 3 | |
| 7274078036 | Which Period do I belong in: First Civilizations | Period 1: Foundations - to 600 BCE | 4 | |
| 7274090653 | Which Period do I belong in: Rise of Greece, Rome & China | Period 2: Classical Civs - 600 BCE - 600CE | 5 | |
| 7274111383 | Which Period do I belong in: Islam emerges | Period 3: Post-Classical Era 600CE - 1450CE | 6 | |
| 7274111384 | Which Period do I belong in: Discovery of the Americas | Period 4: Early Modern Period 1450 CE - 1750CE | 7 | |
| 7274131986 | Which Historical Title matches the following dates: (Prehistory) to 600 BCE | FOUNDATIONS | 8 | |
| 7274153437 | Which Historical Title matches the following dates: 600 BCE to 600 CE | CLASSICAL ERA | 9 | |
| 7274154586 | Which Historical Title matches the following dates: 600 CE to 1450 CE | POST-CLASSICAL ERA | 10 | |
| 7274156243 | Which Historical Title matches the following dates: 1450 CE to 1750 CE | EARLY MODERN ERA | 11 | |
| 7274202607 | If no large civilizations exist I must be in... | Period 1: Foundations - to 600 BCE | 12 | |
| 7274216243 | If the most of the Classical Empires have fallen i must be in | Period 3: Post-Classical Era - 600 CE to 1450 CE | 13 | |
| 7274225358 | If the trans-Atlantic Slave trade has begun I must be in | Period 4: Early Modern Era - 1450 Ce to 1750 CE | 14 | |
| 7274236188 | FOUNDATIONS - prehistory to 600 CE - MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS | Human Migration out of Africa Neolithic Revolution River Valley Civilizations Beginning of religion (Animism, Judaism & Hinduism), writing, farming, civilization, trade No Major Empires | 15 | |
| 7274281591 | CLASSICAL ERA - 600 CE to 600 BCE - Major Characteristics | Beginning of major modern religions (Buddhism, Confucianism, Daoism, Christianity) - ALL begin to spread out of their origins Rise of Empires: Persian, Greek, Roman, China, & India Islam does not exist yet! | 16 | |
| 7274307118 | POST-CLASSICAL ERA - 600 CE to 1450 CE - MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS | Most Classical empires fall/replaced New Empires: Islamic Caliphates, Mongols(rise and fall), Imperial China, Byzantine Empire, Aztecs & Incas Large Regional Trade Routes emerge Islam emerges AMERICA NOT DISCOVERED YET! | 17 | |
| 7274325392 | EARLY MODERN ERA - 1450 CE to 1750 - Major Characteristics | America discovered & integrated into the world Rise of European Maritime Empires & New type of Economy: Mercantilism Rise of Monarchies New Empires: Ottoman, Mughal, Russian, Manchu, Spanish, French, Portuguese, British, Dutch Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade, Renaissance, Reformation, Scientific Revolution | 18 | |
| 7363950289 | Discovery of the Americas occurred in | Period 4 | 19 | |
| 7363952600 | Emergence of Islam occurred in | Period 3 | 20 | |
| 7363954977 | Rise and Fall of the Mongols occurred in | Period 3 | 21 | |
| 7363957947 | Beginning of Agriculture occurred in | Period 1 | 22 | |
| 7363961214 | Rise and Fall of Greece and Rome occurred in | Period 2 | 23 | |
| 7363967181 | Hinduism & Judaism were founded in | Period 1 | 24 | |
| 7363971085 | Buddhism, Confucianism, Christianity and Daoism were founded in | Period 2 | 25 | |
| 7364001716 | Emergence of written language occurred in | Period 1 | 26 | |
| 7364005272 | Renaissance, Reformation, and Scientific Revolution occurred in | Period 4 | 27 | |
| 7364018263 | The shift from regional trade networks to global trade networks occurred between | Periods 3 and 4 | 28 |
Flashcards
AP World Periodizations and Geographic Regions Flashcards
| 4860089985 | Pre-History to 600 BCE | Technological & Environmental Transformations | 0 | |
| 4860089986 | 600 BCE to 600 CE | Organization & Reorganization of Human Societies | 1 | |
| 4860089987 | 600 CE to 1450 CE | Regional & Interregional Interactions | 2 | |
| 4860089988 | 1450 CE to 1750 CE | Global Interactions | 3 | |
| 4860089989 | 1750 CE to 1900 CE | Industrialization & Global Integration | 4 | |
| 4860089990 | 1900 CE to Present Day | Accelerating Global Change & Realignments | 5 | |
| 4860089991 | North America |  | 6 | |
| 4860089992 | South America |  | 7 | |
| 4860089993 | Europe |  | 8 | |
| 4860089994 | East Asia |  | 9 | |
| 4860089995 | Southeast Asia |  | 10 | |
| 4860089996 | South Asia |  | 11 | |
| 4860089997 | Central Asia |  | 12 | |
| 4860089998 | Middle East |  | 13 | |
| 4860089999 | North Africa | 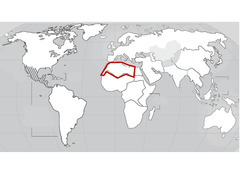 | 14 | |
| 4860090000 | East Africa |  | 15 | |
| 4860090001 | West Africa |  | 16 | |
| 4860090002 | Central Africa |  | 17 | |
| 4860090003 | South Africa |  | 18 | |
| 4860090004 | Oceania |  | 19 | |
| 4860090005 | Latin America |  | 20 |
AP World History Chapter Two Flashcards
| 7171109026 | civilization | Societies distinguished by reliance on sedentary agriculture, ability to produce food surpluses, and existence of nonfarming elites, as well as merchant and manufacturing groups. | 0 | |
| 7171109027 | Mesopotamia | Literally "between the rivers"; the civilizations that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates river valleys. | 1 | |
| 7171109028 | Sumerians | People who migrated into Mesopotamia c. 4000 B.C.E.; created first civilization within region; organized area into city-states. | 2 | |
| 7171109029 | Cuneiform | A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets. | 3 | |
| 7171109030 | ziggurats | Massive towers usually associated with Mesopotamian temple complexes. | 4 | |
| 7171109031 | city-state | A form of political organizations typical of Mesopotamian civilizations; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king. | 5 | |
| 7171109032 | Babylonians | Unified all of Mesopotamia c. 1800 B.C.E.; empire collapsed due to foreign invasion c. 1600 B.C.E. | 6 | |
| 7171109033 | Hammurabi | The most important ruler of the Babylonian empire; responsible for codification of law. | 7 | |
| 7171109034 | pharaoh | Title of kings of ancient Egypt. | 8 | |
| 7171109035 | pyramids | Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs. | 9 | |
| 7171109036 | Kush | An African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nike c. 1000 B.C.E.; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries. | 10 | |
| 7171109037 | Indus River | River sources in Himalayas to mouth in Arabian Sea; location of Harappan civilization. | 11 | |
| 7171109038 | Harappa | Along with the Mohenjodaro, major urban complex of the Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern. | 12 | |
| 7171109039 | Aryans | Indo-European nomadic pastoralists who replaced Harappan civilization; militarized society. | 13 | |
| 7171109040 | Vedas | Aryan hymns originally transmitted orally but written down in sacred books from the 6th century B.C.E. | 14 | |
| 7171109041 | Mahabharata | Indian epic of war, princely honor, love, and social duty; written down in the last centuries of B.C.E.; previously handed down in oral form. | 15 | |
| 7171109042 | Ramayana | One of the great epic tales from classical India; traces adventures of King Rama and his wife, Sita; written 4th to 2nd centuries B.C.E. | 16 | |
| 7171109043 | Upanishads | Later books of the Vedas; contained sophisticated and sublime philosophical ideas; utilized by Brahmans to restore religious authority. | 17 | |
| 7171109044 | Yellow River | Also known as the Huanghe; site of development of sedentary agriculture in China. | 18 | |
| 7171109045 | ideographs | Pictographic characters grouped together to create new concepts; typical of Chinese writing. | 19 | |
| 7171109046 | Shang | First Chinese dynasty for which archeological evidence exists; capital located in Ordos bulge of the Huanghe; flourished 1600 to 1046 B.C.E. | 20 | |
| 7171109047 | Olmecs | People of a cultural tradition that arose at San Lorenzo and La Venta in Mexico c. 1200 B.C.E.; featured irrigated agriculture, urbanism, elaborate religion, beginnings of calendrical and writing systems. | 21 | |
| 7171109048 | Chavín de Huantar | Chavin culture appeared in the highlands of the Andes between 1800 and 1200 B.C.E.; typified by ceremonial centers with large stone buildings; greatest ceremonial center was Chavín de Huantar; characterized by artistic motifs. | 22 | |
| 7171109049 | Phoenicians | Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean. | 23 | |
| 7171109050 | monotheism | The exclusive worship of a single god; introduced by the Jews into Western civilization. | 24 |
AP World History midterm: multiple choice questions Flashcards
| 5655825848 | (ch12) Confucianism... | combined with buddhism to create a cultural bridge between china and korea | 0 | |
| 5655825849 | (ch12) which was not an achievement of the tang dynasty? | the solution to the problem of nomadic peoples along china's border | 1 | |
| 5656089988 | (ch12) the position of chinese women... | was defined by confucianism because it reinforced patriarchal values | 2 | |
| 5656089989 | (ch12) Japanese feudalism... | saw the beginnings of a centralized Japan | 3 | |
| 5656089990 | (ch12) Compared to the Viets, the Chinese were more... | urbanized | 4 | |
| 5656089991 | (ch12) Compared to the Korean attitudes toward the Chinese, the Japanese... | were similar in their desire to become part of the Chinese trading system | 5 | |
| 5656089992 | (ch12) The position of the Chinese scholar-gentry... | weakened efforts to curb nomadic invasions | 6 | |
| 5656089993 | (ch12) Buddhism became more popular among China's neighbors than China itself because... | Buddhism did not originate in China, but in India | 7 | |
| 5656089994 | (ch13) In contrast to Japanese feudalism, Western European feudalism... | created a reciprocal relationship between lord and vassal | 8 | |
| 5656156074 | (ch13) The period of greatest population decline in Europe during the Middle Ages was... | the fourteenth century because of the bubonic plague/Black Death | 9 | |
| 5656156075 | (ch13) During the middle ages, the concept of limited government was seen most clearly in... | England because of the Magna Carta which limited the power of the monarchy | 10 | |
| 5656156076 | (ch13) Which statement describes Europe between the ninth to fifteenth centuries? | The expansion of the Eastern world into Western Europe | 11 | |
| 5656156077 | (ch13) Trade during the medieval period... | placed Europe within the Muslim commercial network | 12 | |
| 5656156078 | (ch13) The fifteenth century was characterized by... | the strengthening of nation-states in England and France | 13 | |
| 5656156079 | (ch13) Medieval Europe... | developed new banking institutions from multicultural contacts | 14 | |
| 5656171178 | (ch13) Early medieval Europe's strongest state was... | the Holy Roman Empire | 15 | |
| 5657401539 | (ch10) During the classical period, Africa... | saw new technology used in trans-Saharan travel | 16 | |
| 5657409371 | (ch10) The declining years of Han China and the Roman Empire saw all of the following: | poor harvests, epidemic disease, and unequal land distribution | 17 | |
| 5657414097 | (ch10) Attempts to save the Roman Empire from ruin included | the establishment of a new capital in the eastern empire (Constantinople) | 18 | |
| 5657419884 | (ch10) The eastern portion of the Roman Empire... | was a centre of trade and architecture | 19 | |
| 5657423503 | (ch10) The decline of Gupta India... | saw the increased power of local princes | 20 | |
| 5657429717 | (ch10) Silk Road(s) trade... | established links between Han China and Rome | 21 | |
| 5657433126 | (ch10) Indian Ocean trade... | saw mariners utilize the geographic forces of the Indian Ocean | 22 | |
| 5657437120 | (ch10) The decline of Han China... | witnessed Daoism rather than Confucianism, gaining popularity | 23 | |
| 5657445108 | (ch11) With regard to the doctrines of Islam in the period c. 600 CE to c. 1450... | they were embraced by members of the lower Hindu castes in India because of their emphasis on equality | 24 | |
| 5657452748 | (ch11) The area in which Islam showed the most profound change during the seventh to the fifteenth centuries was in | The role of women | 25 | |
| 5657455835 | (ch11) One of the weaknesses of the early Muslim empires was... | failure to resolve questions of succession | 26 | |
| 5657459575 | (ch11) The Abbasid Dynasty... | proved the high point of Muslim cultural achievement | 27 | |
| 5657465477 | (ch11) Which of the following qualifies as a primary source on the teachings of Muhammad? | the Hadith | 28 | |
| 5657467493 | (ch11) Muhammad... | built on the religious traditions of the Arabian peninsula | 29 | |
| 5657471278 | (ch11) The Five Pillars... | provided unity within Islam | 30 | |
| 5657474769 | (ch11) As a new faith, Islam gained strength | within portions of the former Roman Empire | 31 | |
| 5657533494 | (ch9) Both Hinduism and Buddhism didn't... | support the caste system, revere women, become increasingly popular in India | 32 | |
| 5657542212 | (ch9) Christianity... | taught the forgiveness of sins through faith in Jesus | 33 | |
| 5657545496 | (ch9) Confucianism and early Buddhism... | did not believe their founders were gods | 34 | |
| 5657547859 | (ch9) Daoism and Confucianism... | based their teachings on Chinese traditions | 35 | |
| 5657550916 | (ch9) The Silk Roads were especially instrumental in the spread of... | Buddhism | 36 | |
| 5657552536 | (ch9) During the period of the late Roman Empire, Christianity... | experienced a change in its official status (Edict of Milan) | 37 | |
| 5657555403 | (ch9) Hinduism... | addressed the consequences of one's behavior | 38 | |
| 5657558181 | (ch9) Buddhism... | changed over time to teach that common people could reach Nirvana (Bodhisattvas) | 39 | |
| 5666572518 | (ch5) Interactions between Muslims and Europeans during the 7th century are most commonly found in the... | Indian Ocean | 40 | |
| 5666586382 | (ch5) An Advanced Placement World History region that can be classified as a cultural region is... | Latin America | 41 | |
| 5666589714 | (ch5) The study of oceans in world history... | coordinates with an emphasis on societies as well as civilizations | 42 | |
| 5666596921 | (ch5) An example of diffusion rather than independent invention is the... | origin of the Greek alphabet | 43 | |
| 5666598547 | (ch5) Periodization in the Advanced Placement World History course... | assists students in comparing societies and trends within periods | 44 | |
| 5666610628 | (ch6) Early agriculture in the Americas... | began later than in the Eastern Hemisphere | 45 | |
| 5666615809 | (ch6) The Agricultural Revolution... | saw the use of agricultural methods that encouraged migration | 46 | |
| 5666622687 | (ch6) During the Agricultural Revolution, women... | observed and studied the agricultural environment | 47 | |
| 5666625988 | (ch6) The Neolithic Age... | saw the beginnings of urbanization | 48 | |
| 5666629306 | (ch6) Early urban dwellers... | saw the need for a government | 49 | |
| 5666638912 | (ch7) The Egyptian civilization was similar to the Sumerian civilization in... | its system of social stratification | 50 | |
| 5666644329 | (ch7) The earliest civilizations in both the Eastern and Western hemispheres were similar in... | their practice of polytheism | 51 | |
| 5666648794 | (ch7) The Indus valley civilization... | relied heavily on communal planning | 52 | |
| 5666655985 | (ch7) The early civilization with the least-developed technology was... | Mesoamerican | 53 | |
| 5666659816 | (ch7) The roots of classical India included... | Vedic traditional literature | 54 | |
| 5666663156 | (ch7) Shang China... | contributed to the development of central government in China | 55 | |
| 5666671838 | (ch7) Early societies of South America... | were challenged by geographic limitations | 56 | |
| 5666682633 | (ch7) Results of cultural diffusion among early civilizations included... | the legend of Quetzalcoatl | 57 |
Set 3 AP World History Flashcards
| 7842051627 | Bushido | traditional code of the Japanese samurai which stressed courage and loyalty and self-discipline and simple living | 0 | |
| 7842061101 | Abdicate | give up, such as power, as of monarchs and emperors, or duties and obligations | 1 | |
| 7842077483 | Demographics | statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it | 2 | |
| 7842082352 | Diplomacy | management and handling situations between nations through negotiations | 3 | |
| 7842099165 | Samurai | a member of a powerful military caste in feudal Japan, especially a member of the class of military retainers of the daimyos | 4 | |
| 7842120813 | Assimilation | the process of taking in and fully understanding information or ideas | 5 | |
| 7842128368 | Doctrine | a belief or set of beliefs held and taught by a church, political party, or other group | 6 | |
| 7842136617 | Daimyo | One of the great lords ,in feudal Japan, who were vassals of the shogun | 7 | |
| 7842142556 | Autonomous | Self-serving and independent of outside authority | 8 | |
| 7842160390 | Infrastructure | The basic physical and organizational structures and facilities needed for the operation of a society or enterprise | 9 | |
| 7842173188 | Shintoism | Religion of early Japanese culture; devotees worshipped numberous gods and spirits associated with the natural world; offers of food and prayers made to gods and nature spirits | 10 | |
| 7842185827 | Coerce | persuade someone through to do something force or threats | 11 | |
| 7842196203 | Mercantile | relating to trade or commerce | 12 | |
| 7842202866 | Shogun | a hereditary military dictator of Japan | 13 | |
| 7842212082 | Commerce | buying and selling goods through different countries or parts of the same country | 14 | |
| 7842214897 | Tariff | a tax or duty to be paid on a particular class of imports or exports | 15 |
AP World History Period 5 Flashcards
| 8947885634 | Enlightenment | A movement in the 18th century that advocated the use of reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions | 0 | |
| 9115991068 | T. Hobbes | wrote Leviathan, people were by nature greedy and prone to violent welfare, government should preserve peace and stability at all cost advocated powerful ruler (absolute monarchs) | 1 | |
| 9115993144 | J. Locke | Two Treatises on Government, mankind for most part was good, all men born equal to one another and natural and unalienable rights to life, liberty, and property. primary responsibility of government was to secure and guarantee natural rights. people justified to revolt if government broke rules | 2 | |
| 9115994563 | Voltaire | French philosopher who wrote against religious intolerance./Voltaire wrote against intolerance by French royalty. He was a deist and idolized China as a country governed by elite secular scholars. | 3 | |
| 9115996841 | Diderot | French philosopher who was a leading figure of the Enlightenment in France, first encyclopedia | 4 | |
| 9116001987 | Montesquieu | argued for separation of power among the branches of the government: executive, legislative, and judicial | 5 | |
| 9116003641 | Rousseau | all men were equal and society should be organized to the general will, wrote Social Contract. people are good at will and corrupted by society | 6 | |
| 9116006025 | E. Burke | A conservative leader who was deeply troubled by the aroused spirit of reform. In 1790, he published Reforms on The Revolution in France, one of the greatest intellectual defenses of European conservatism. He defended inherited priveledges in general and those of the English monarchy and aristocracy. Glorified unrepresentitive Parliament and predicted reform would lead to much chaos/tyranny. | 7 | |
| 9116008835 | J. Wesley | English clergyman and founder of Methodism (1703-1791) | 8 | |
| 9116011317 | Deism | Belief in God but he has no play in our lives | 9 | |
| 9116012180 | T. Jefferson | Main author of the Declaration of Independence | 10 | |
| 9116015036 | Louis XVI | - King of France (1774-1792). In 1789 he summoned the Estates-General, but he did not grant the reforms that were demanded and revolution followed. Louis and his queen, Marie Antoinette, were executed in 1793. | 11 | |
| 9116018411 | M. Robespierre | Young provincial lawyer who led the most radical phases of the French Revolution. His execution ended the Reign of Terror. | 12 | |
| 9116020202 | Olympe de Gouges | French journalist who published the declaration of rights of women and the female citizens. | 13 | |
| 9116022364 | Napoleon Bonaparte | Overthrew French Directory in 1799 and became emperor of the French in 1804. Failed to defeat Great Britain and abdicated in 1814. Returned to power briefly in 1815 but was defeated and died in exile. | 14 | |
| 9116024199 | Louis XVIII | Bourbon restored on the French throne by the Quadruple Alliance. Surprisingly, he maintained Napoleon's Concordant and Civil Code. However, liberals disliked his moderation. | 15 | |
| 9127539704 | Congress of Vienna | Meeting in the aftermath of Napoleonic Wars (1815) to restore political stability in Europe and settle diplomatic disputes. | 16 | |
| 9127545252 | F. Toussaint L'Ouverture | leader of slave rebellion on the French sugar island of St. Domingue in 1791; led to creation of independent republic of Haiti in 1804 | 17 | |
| 9127564587 | J. Dessalines | September 20, 1758-October 17, 1806 A leader of the Haitian Revolution and the first ruler of an independent Haiti under the constitution | 18 | |
| 9127576789 | Simon Bolivar | Creole military officer in northern South America; won series of victories in in Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador between 1817 and 1822; military success led to creation of independent state of Gran Colombia | 19 | |
| 9127586054 | J. de San Martin | Leader of independence movement in Rio de la Plata; led to independence of the United Provinces of the Rio de la Plata by 1816; later led independence movement in Chile and Peru as well | 20 | |
| 9127589804 | Pedro I | aided in the declaration of Brazilian independence from Portugal in 1822; became constitutional emperor of Brazil | 21 | |
| 9127598008 | Peninsulares | 1450-1750 : Descendants of the original conquistadores sought to protect their privileges against immigrant newcomers; Spaniards born in the Americas (creoles) resented the pretension to superiority of those born in Spain (?)... These people came to Latin America and were of the highest social class | 22 | |
| 9127604716 | Creoles | In colonial Spanish America, term used to describe someone of European descent born in the New World. Elsewhere in the Americas, the term is used to describe all nonnative peoples. | 23 | |
| 9127619852 | Mestizo | 1450 - 1750 : The most distinctive feature of these new colonial societies in mexico and peru was their emergence. they were a mixed - race, population, initially the product of unions between Spanish men and indian women | 24 | |
| 9127623446 | Demographic Transition | A change in the rates of population growth. Before the transition, both birth and death rates are high, resulting in a slowly growing population; then the death rate drops but the birth rate remains high, causing a population explosion. | 25 | |
| 9127628418 | Conservatism | The ideology of slow or gradual change. | 26 | |
| 9127847829 | Liberalism | The ideology that encourages rapid progressive movement | 27 | |
| 9127853707 | Nationalism | The loyalty of a people to their common culture, traditions, ethnicity, geographic territory, and the idea of self-rule | 28 | |
| 9128057941 | Zionism | Jewish nationalism | 29 | |
| 9128066718 | T. Herzl | Austrian journalist and Zionist; formed World Zionist Organization in 1897; promoted Jewish migration to Palestine and formation of a Jewish state | 30 | |
| 9128109560 | O. Van Bismarck | Chancellor of Prussia from 1862 until 1871, when he became chancellor of Germany. A conservative nationalist, he led Prussia to victory against Austria (1866) and France (1870) and was responsible for the creation of the German Empire | 31 | |
| 9128133419 | Factory System | Intensification of all the processes of production at a single site during the Industrial Revolution; involved greater organization of labor and increased discipline | 32 | |
| 9128173616 | Capitalism | an economic system based on open competition in a free market, in which individuals and companies own the means of production and operate for profit | 33 | |
| 9128177157 | J. Watt | Devised a steam engine in the 1770s that could be used for production in many industries; a key step in the Industrial Revolution | 34 | |
| 9128184143 | Bourgeoisie | In early modern Europe, the class of well-off town dwellers whose wealth came from manufacturing, finance, commerce, and allied professions. | 35 | |
| 9128184144 | E. Whitney | an American inventor who developed the cotton gin. Also contributed to the concept of interchangeable parts that were exactly alike and easily assembled or exchanged | 36 | |
| 9128187727 | Luddites | Workers in Britain who responded to the replacement of their labor by machines during the Industrial Revolution by attempting to destroy machines; named after the fictional worker Ned Ludd | 37 | |
| 9128187728 | Socialism | Political ideology in 19th-century Europe; attacked private property in the name of equality; wanted state control of the means of production and an end to the capatilistic exploitation of the working class | 38 | |
| 9128191732 | K. Marx | German socialist who saw history as a class struggle between groups out of power and those controlling the means of production ; preached the inevibility of social revolution and the creation of proletarian dictatorship | 39 | |
| 9128191733 | Communism | a political theory favoring collectivism in a classless society | 40 | |
| 9128191734 | Proletariat | a social class comprising those who do manual labor or work for wages | 41 | |
| 9128194178 | Labor Unions | Organization of workers for the purpose of increased lobbying power for benefits and wages; created to defend the interests of the members | 42 | |
| 9128196504 | Mary Wollstonecraft | English writer and early feminist who denied male supremacy and advocated equal education for women | 43 | |
| 9128199435 | Suffrage Movement | the right to vote | 44 | |
| 9128202822 | Abolitionist Movement | 1750-1914 : An international movement that between approximately 1780 and 1890 succeeded in condemning slavery as morally repugnant and abolishing it in much of the world; the movement was especially prominent in Britain and the United States. | 45 | |
| 9128202823 | W. Wilberforce | British statesman and reformer; leader of abolitionist movement in English parliament that led to end of English slave trade in 1807. | 46 | |
| 9128202918 | Seneca Falls Conference | the first major meeting to discuss equal rights for women in the US, wrote Declaration of Sentiments-drafted after the Declaration of Independence, laid out womens' demands. Reactions: some women felt empowered, others were very critical | 47 | |
| 9128208442 | E. Cady Stanton | 1750-1914 : She was the leading figure of the early women's rights movement in the United States (1815-1902). She published a womens bible eliminating the parts she found offensive. As heirs to the French revolution, feminists ardently believed in progress and insisted that it must now include a radical transformation of the position of women. | 48 | |
| 9128208443 | B. Juarez | leader of of liberal rebellion against Santa Anna; liberal government defeated by French intervention under Napoleon and establishment of Mexican Empire under Maximillion; restored to power in 1867 until his death in 1872 | 49 | |
| 9128208444 | Porfirio Diaz | A dictator who dominated Mexico, permitted foriegn companies to develop natural resources and had allowed landowners to buy much of the countries land from poor peasants. | 50 | |
| 9128211523 | E. Zapata | Revolutionary and leader of peasants in the Mexican Revolution. He mobilized landless peasants in south-central Mexico in an attempt to seize and divide the lands of the wealthy landowners. Though successful for a time, he was ultimately assassinated. 819 | 51 | |
| 9179817223 | P. Villa | Mexican revolutionary leader (1877-1923) Did many good things, but killed a lot of people. Wanted to take money from the rich and give it to the poor. | 52 | |
| 9128211524 | T. Malthus | 18th century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production. | 53 | |
| 9128211525 | Sultan Selim III | Sultan who ruled Ottoman Empire from 1789 to 1807; aimed at improving administrative efficiency and building a new army and navy; toppled by Janissaries in 1807 | 54 | |
| 9128214415 | Muhammad Ali | Albanian soldier in the service of Turkey who was made viceroy of Egypt and took control away from the Ottoman Empire and established Egypt as a modern state (1769-1849) | 55 | |
| 9128214416 | Sultan Hamid II | Ruled Ottoman empire as a until the Young Turks sent him into exile. ruined constiution and stood by Tanzimat | 56 | |
| 9128220743 | Opium Wars | Fought between the British and Qing China beginning in 1839; fought to protect British trade in Opium; resulted in responding British victory, opening of Hong Kong as British port of trade | 57 | |
| 9128220744 | Taiping Rebellion | Rebellion inspired by Hong Xiuquan. Called for the destruction of the Qing dynsasty. Included: no private property, no foot binding/concubines, communal wealth, free public education, literacy.(Some wanted industrial society) | 58 | |
| 9128223841 | Empress Cixi | Ultraconservative dowager empress who dominated the last decades of the Qing dynasty; supported the Boxer Rebellion in 1898 as a means of driving out Westerners | 59 | |
| 9128223842 | Self-Strengthening Movement | A late 19th century movement in which the Chinese modernized their army and encouraged Western investment in factories and railways | 60 | |
| 9128223843 | Boxer Rebellion | Popular outburst in 1898 aimed at expelling foreigners from china; failed because of intervention of armies of western powers in china; defeat of Chinese enhanced control by Europeans and the power of provincial officials | 61 | |
| 9128225875 | Commodore Perry | a navy commander who, on July 8, 1853, became the first foreigner to break through the barriers that had kept Japan isolated from the rest of the world for 250 years. He delivered a letter from the US president, demanding that Japan open its ports to foreign trade. A year later, he returned for their reply, bringing some Western technology. | 62 | |
| 9128229322 | Ito Hirobumi | Most important journey to europe to study foreign constitutions. drew inspiration from German | 63 | |
| 9128229323 | Meiji Restoration | The political program that followed the destruction of the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1868, in which a collection of young leaders set Japan on the path of centralization, industrialization, and imperialism | 64 | |
| 9128229324 | Emperor Mutsuhito | Young emperor of Japan who took control of the nation's government from the shogun in 1867. He led a reform and modernization movement in Japan that resulted in it being a world power.The Meiji Era began under this Emperor | 65 | |
| 9128236612 | Crimean War | Russia tried to expand, but failed. Showed weakness of empire because it could not beat Europe. | 66 | |
| 9128246518 | Witte System | Russian economic policy that stimulated industrialization: railroads, coal and steel. | 67 | |
| 9128246519 | Alexander II | the son of Nicholas I who, as czar of Russia, introduced reforms that abolished serfdom | 68 | |
| 9128248913 | Nicholas II | Last tsar of Russia, he went to the frontlines in WWI to try to rally the troops, but was forced to abdicate after his wife made horrible decisions under the influence of Rasputin | 69 | |
| 9128248914 | Soviets | Council of workers; seized the government of St. Petersburg in 1917 to precipitate the Russian revolution | 70 | |
| 9128251076 | Duma | Russia's 1st parliamentary government | 71 | |
| 9128251077 | Tanzimat Reforms | Series of reforms in the Ottoman Empire between 1839 and 1876; established Western-style universities, state postal system, railways, extensive legal reforms; resulted in creation of new constitution in 1876 | 72 | |
| 9128251078 | Young Turk Movement | Group of revolutionary and nationalistic Turks who revolted against Ottoman empire in 1908 attempting to make reforms and then sided with the central powers in WWI | 73 | |
| 9179966800 | Maratha Empire | Militant Hindus who formed a breakaway state in the south and waged guerilla warfare against Aurangzeb and the Mughal Empire. | 74 | |
| 9179972855 | Zulu Kingdom | The name of a tribe of South Africa people who live in the northern part of Natal. They were the dominate tribe in the late 19th century when European Imperialism began. They resisted both the Boers and the British, but ultimately lost their homeland and freedom by 1879. | 75 | |
| 9179981210 | C. Rhodes | Born in 1853, played a major political and economic role in colonial South Africa. He was a financier, statesman, and empire builder with a philosophy of mystical imperialism. | 76 | |
| 9179989930 | R. Kipling | (1864-1936) English writer and poet; defined the "white man's burden" as the duty of European and Euro-American peoples to bring order and enlightenment to distant lands | 77 | |
| 9180053555 | Leopold II | (reigned 1865-1909) King of Belgium who employed Henry Morton Stanley to help develop commercial ventures and establish a colony called the Congo Free State in the basin of the Congo River | 78 | |
| 9180057572 | European Imperialism | the policy of extending the rule or authority of an empire or nation over foreign countries, or of acquiring and holding colonies and dependencies. | 79 | |
| 9180082127 | Queen Victoria | British Queen, under whose rule the British empire reached the height of its wealth and power, forced to accept a new, virtually powerless role after the Chartist movement | 80 | |
| 9180208130 | Queen Lili'uokalani | last queen of Hawaii; reigned 1891-1893; this queen was overthrown in 1893 by a group of planters and businesspeople who invited US to annex Hawaii (Grover Cleveland opposed it; finally done by William McKinley in 1898) | 81 | |
| 9180213178 | Monroe Doctrine | Declaration in 1823 establishing America as a completely independent country; they were supported by the British; European rules | 82 | |
| 9180220389 | A. Lincoln | (1809-1865) He was the sixteenth president of the United States and against slavery. He became president in 1860 just before the civil war, however, slavery was ended threw the emancipation proclamation and the civil war was ended, all during his presidency. | 83 | |
| 9180226700 | T. Roosevelt | He was a United States president in office 1901-1909, an enthusiastic champion of imperial expansion, the United States supported a rebellion against Columbia in 1903 and helped rebels established a breakaway state of Panama. | 84 | |
| 9180234957 | C. Darwin | English naturalist. He studied the plants and animals of South America and the Pacific islands, and in his book On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859) set forth his theory of evolution. | 85 | |
| 9180237515 | Ram Mohan Roy | called the "father of modern India"; among rhe most influential Indian elite; supported some British colonial policies | 86 | |
| 9180241028 | Suez Canal | Ship canal dug across the isthmus of Suez in Egypt, designed by Ferdinand de Lesseps. It opened to shipping in 1869 and shortened the sea voyage between Europe and Asia. Its strategic importance led to the British conquest of Egypt in 1882. | 87 | |
| 9180245492 | Panama Canal | Ship canal cut across the isthmus of Panama by United States Army engineers; it opened in 1915. It greatly shortened the sea voyage between the east and west coasts of North America. The United States turned the canal over to Panama on Jan 1, 2000 | 88 | |
| 9180252782 | Sepoy Revolt (Rebellion) | (1857) the rebellion of the Indian soldiers that fought for the British, the bullets were sealed with pig fat and they didn't want to use the bullets. | 89 | |
| 9180283396 | Great Game | European power play for control of states | 90 | |
| 9180287908 | Boer War | (1899-1902) Took place in South Africa, conflict between Dutch Boers and the British, British prevail. | 91 | |
| 9180296814 | Berlin Conference | (1884-1885) Took place in the new state of Germany, all the Western superpowers decided which parts of Africa they should get | 92 | |
| 9180306530 | Social Darwinism | Charles Darwin's theory applied to societies as a way to explain why imperialism is okay. There are superior and inferior societies. | 93 | |
| 9180332396 | S. Freud | (1856-1939) A medical doctor from Vienna who embarked on research that focused on psychological rather than physilogical explanations of mental disorders. Identified a conflict between conscious and unconscious mental processes that lay at the root of neurotic behavior. | 94 | |
| 9180344582 | Indian National Congress | A movement and political party founded in 1885 to demand greater Indian participation in government. Its membership was middle class, and its demands were modest until World War I. Led after 1920 by Mohandas K. Gandhi, appealing to the poor and organized mass protests demanding self-government and independence. | 95 | |
| 9180359973 | Emperor Guangxo | Wanted to make China a constitutional monarchy, admitted China was headed in the wrong direction, faced resistance from the conservatives. | 96 | |
| 9180382829 | M. Hidalgo | Mexican priest who established an independence movement among Indians and mestizos in 1810; after early victories he was captured and executed. | 97 | |
| 9180386587 | Battle of Vertieres | the last major battle of the Second War of Haitian Independence, and the final part of the Haitian Revolution under Jean Jacques Dessalines. | 98 | |
| 9180416063 | The Directory | (1795-1799) created by the new constitution it was the first bicameral legislature in French history. It consisted of a parliament of 500 representatives, but the majority of French people wanted to be rid of them. They habitually disregarded the terms of the constitution, and, when the elections went against them, appealed to the sword. They resolved to prolong the war because state finances had been so ruined that the government could not meet its expenses without the plunder and the tribute of foreign countries. If peace were made, the armies would return home and the directors would have to face the angry, unemployed soldiers and power hungry generals. The directors was were not supported and their general maladministration heightened their unpopularity. | 99 | |
| 9180422437 | Reign of Terror | Period in the French Revolution. It was established by the government on Sept. 5, 1793, to take harsh measures against those suspected of being enemies of the Revolution (including nobles, priests, and hoarders). Controlled by the radical Committee of Public Safety and Maximilien Robespierre, the Terror eliminated enemies on the left (Jacques Hébert and his followers) and the right (Georges Danton and the Indulgents). | 100 | |
| 9180436216 | Jacobins | Radical republicans during the French Revolution. They were led by Maximilien Robespierre from 1793 to 1794. believed france needed complete restructuring; secular | 101 | |
| 9180439370 | Decl. of the Rights of Man & Citizen | One of the fundamental documents of the French Revolution, defining a set of individual rights and collective rights of all of the estates as one. Influenced by the doctrine of natural rights, these rights are universal: they are supposed to be valid in all times and places, pertaining to human nature itself. | 102 | |
| 9180449902 | Tennis Court Oath | On June 20, 1788 the delegates of the third estate, excluded from their hall because of "repairs," moved to a a large tennis court were they swore this famous deceleration. | 103 | |
| 9180458559 | Bastille | The political prison and armory stormed on July 14, 1789, by Partisian city workers alarmed by the king's concentration of troops at Versailles | 104 | |
| 9180462863 | Decl. of Independence | the document recording the proclamation of the second Continental Congress (4 July 1776) asserting the independence of the colonies from Great Britain | 105 | |
| 9180477554 | U.S. Constitution | The document written in 1787 and ratified in 1788 that sets forth the institutional structure of the U.S. government and the tasks these institutions perform. It replaced the Articles of Confederation. | 106 | |
| 9180484846 | G. Garibaldi | the "sword", used guerilla tactics, won Sicily, and Naples, republic, turns over land to Victor Emmanuel for sake of Italy | 107 | |
| 9180496451 | Laissez Faire | Government is hands off of industry | 108 | |
| 9180500525 | Sino-Japanese War | (1894-1895) Japan vs China over land and Japan wins. | 109 | |
| 9180526418 | Russo-Japanese War | (1904-1905) Russia vs Japan and Japan wins, establishes Japan as a global power. | 110 | |
| 9180534417 | A. Smith | (1723-1790) Scottish who wrote the Wealth of Nations in 1776, outlines capitalism, argued that education creates compassion, the free market is based on supply and demand, the key to capitalism is competition, no monopolies. | 111 | |
| 9180577969 | J. Priestly | (1733-1804) English chemist & clergyman, did experiments about the properties of air and discovered the existence of oxygen. His studies on carbon dioxide led to his invention of carbonated drinks (like soda) | 112 | |
| 9180637805 | Philosophes | - for example: John Locke, Voltaire, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau - rarely challenged monarchical rule, but sought instead o make kings responsible to the people the governed - philosophical thinkers - called for freedom and equality and began to question long-standing notions of sovereignty - the intellectuals of the 18th century Enlightenment | 113 |
Chapter 17 AP World History Flashcards
| 7966260690 | Niccolo Machiavelli | (1469-1527) author of The Prince (16th century); emphasized realistic discussions of how to seize and maintain power; one of most influential authors of Italian Renaissance. | 0 | |
| 7966260691 | humanism | focus on humankind as center of intellectual and artistic endeavor; method of study that emphasized the superiority of classical forms over medieval styles, in particular the study of ancient languages. | 1 | |
| 7966260692 | Northern Renaissance | cultural and intellectual movement of northern Europe; began later than Italian Renaissance around 1450; centered in France, Low Countries, England, and German; featured greater emphasis on religion than Italian Renaissance. | 2 | |
| 7966260693 | Francis I | King of France in the 16th century; regarded as Renaissance monarch; patron of arts; imposed new controls on Catholic church; ally of Ottoman sultan against Holy Roman emperor. | 3 | |
| 7966260694 | Johannes Gutenberg | introduced moveable type to western Europe in 15th century; credited with greatly expanded availability of printed books and pamphlets. | 4 | |
| 7966260695 | European-style family | originated in 15th century among peasants and artisans of western Europe, featuring late marriage age, emphasis on the nuclear family, and a large minority who never married. | 5 | |
| 7966260696 | Martin Luther | (1483-1546) German monk; initiated Protestant Reformation in 1517 by nailing 95 theses to door to Wittenberg church; emphasized primacy of faith over works stressed in Catholic church; accepted state control of church. | 6 | |
| 7966260697 | Protestantism | general wave of religious dissent against Catholic church; generally held to have begun with Martin Luther's attack on Catholic beliefs in 1517; included many varieties of religious belief. | 7 | |
| 7966260698 | Anglican church | form of Protestantism set up in England after 1534; established by Henry VIII with himself as head, at least in part to obtain a divorce from his first wife; became increasingly Protestant following Henry's death. | 8 | |
| 7966260699 | Jean Calvin | French Protestant (16th century) who stressed doctrine of predestination; established canter of his group at Swiss canton of Geneva; encouraged ideas of wider access to government, wider public education; Calvinism spread from Switzerland to northern Europe and North America. | 9 | |
| 7966260700 | Catholic reformation | restatement of traditional Catholic beliefs in response to Protestant Reformation (16th century); established councils that revived Catholic doctrine and refuted Protestant beliefs. | 10 | |
| 7966260701 | Jesuits | a new religious order founded during the Catholic Reformation; active in politics, education, and missionary work; sponsored missions to South America, North America, and Asia. | 11 | |
| 7966260702 | Edict of Nantes | grant of tolerance to Protestants in France in 1598; granted only after lengthy civil war between Catholic and Protestant factions. | 12 | |
| 7966260703 | Thirty Years War | war within the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain; ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia. | 13 | |
| 7966260704 | Treaty of Westphalia | ended Thirty Years War in 1648; granted right to individual rulers within the Holy Roman Empire to choose their own religion-- either Protestant or Catholic. | 14 | |
| 7966260705 | English Civil War | conflict from 1640 to 1660; featured religious disputes mixed with constitutional issues concerning the powers of the monarchy; ended with restoration of the monarchy in 1660 following execution of previous king. | 15 | |
| 7966260706 | proletariat | class of working people without access to producing property; typically manufacturing workers, paid laborers in agricultural economy, or urban poor; in Europe, product of economic changes of 16th and 17th centuries. | 16 | |
| 7966260707 | witchcraft persecution | reflected resentment against the poor, uncertainties about religious truth; resulted in death of over 100,000 Europeans between 1590 and 1650; particularly common in Protestant areas. | 17 | |
| 7966260708 | Scientific Revolution | culminated in 17th century; period of empirical advances associated with the development of wider theoretical generalizations; resulted in change in traditional beliefs of Middle Ages. | 18 | |
| 7966260709 | Copernicus | Polish monk and astronomer (16th century); disproved Hellenistic belief that the Earth was the center of the universe. | 19 | |
| 7966260710 | Johannes Kepler | (December 27, 1517 - November 15, 1630) was an astronomer and mathematician who was a prominent figure in the scientific revolution. | 20 | |
| 7966260711 | Galileo | published Copernicus's findings (17th century); added own discoveries concerning laws of gravity and planetary motion; condemned by the Catholic church for his work. | 21 | |
| 7966260712 | William Harvey | English physician (17th century) who demonstrated circular movement of blood in animals, function of heart as pump. | 22 | |
| 7966260713 | Francis Bacon | (22 January 1561 - 9 April 1626) was an English philosopher, statesman, author, and scientist. He was an influential member of the scientific revolution, and is best known for work on the scientific method. | 23 | |
| 7966260714 | René Descartes | established importance of skeptical review of all received wisdom (17th century); argued that human reason could then develop laws that would explain the fundamental workings of nature. | 24 | |
| 7966260715 | Isaac Newton | (1643-1727) English scientist; author of Principia Mathematica; drew together astronomical and physical observations and wider theories into a neat framework of natural laws; established principles of motion; defined forces of gravity. | 25 | |
| 7966260716 | deism | concept of God current during the Scientific Revolution; role of divinity was to set natural laws in motion, not to regulate once process was begun. | 26 | |
| 7966260717 | John Locke | (1632-1704) English philosopher who argued that people could learn everything through senses and reason and that power of government came from the people, not from divine right of kings; offered possibility of revolution to overthrow tyrants. | 27 | |
| 7966260718 | absolute monarchy | concept of government developed during rise of nation-states in western Europe during the 17th century; featured monarchs who passed laws without parliaments, appointed professionalized armies and bureaucracies, established state churched, imposed state economic policies. | 28 | |
| 7966260719 | Louis XIV | (1638-1715) French monarch of the late 17th century who personified absolute monarchy; best example of absolute monarchy | 29 | |
| 7966260720 | Glorious Revolution | English overthrow of James II in 1688; resulted in affirmation of parliament as having basic sovereignty over the king. | 30 | |
| 7966260721 | parliamentary monarchy | originated in England and Holland, 17th century, with kings partially checked by significant legislative powers in parliaments. | 31 | |
| 7966260722 | Frederick the Great | Prussian king of the 18th century; attempted to introduce Enlightenment reforms into Germany; built on military and bureaucratic foundations of his predecessors; introduced freedom of religion; increased state control of economy. | 32 | |
| 7966260723 | Enlightenment | intellectual movement centered in France during the 18th century; featured scientific advance, application of scientific methods to study of human society; belief that rational laws could describe social behavior. | 33 | |
| 7966260724 | Adam Smith | established liberal economics (Wealth of Nations 1776); argued that government should avoid regulation of economy in favor of the operation of market forces. | 34 | |
| 7966260725 | Denis Diderot | (October 5, 1713 - July 31, 1784) a French Enlightenment figure best known for his work on the first encyclopedia. | 35 | |
| 7966260726 | Mary Wollstonecraft | (1750-1797) Enlightenment feminist thinker in England; argued that political rights should extend to women. | 36 | |
| 7966260727 | mass consumerism | refers to the spread of deep interest in acquiring material goods and services spreading below elite levels, along with a growing economy capacity to afford some of these goods. While hints of mass consumerism can be found in several premodern societies, it developed most clearly, beginning in western Europe, from the 18th century onward. | 37 | |
| 7966260728 | secular | outside of the church | 38 | |
| 7966260729 | Italy | Beginning of Renaissance | 39 | |
| 7966260733 | Michelangelo | applied classical styles in painting and culture. | 40 | |
| 7966260734 | Leonardo da Vinci | realistic portrayal of human body. | 41 | |
| 7966260735 | Shakespeare & Cervantes | wrote a new set of classics for literary traditions in major western languages. | 42 | |
| 7966260736 | European style families | married in late 20's & have a nuclear family of parents and children. Marriage is now based on access to property. | 43 | |
| 7966260737 | Martin Luther | began Protestant reformation in 1517; believed that the Bible is the only thing that should be followed; wrote the 95 Theses. | 44 | |
| 7966260738 | 95 Theses | -protested against the selling of indulgences - monasticism is wrong - priests could marry - people should have the Bible in their own language | 45 | |
| 7966260739 | Lutheranism | supported by the common people because it sanctioned money making. | 46 | |
| 7966260741 | Calvinism | sought the participation of all believers in church administration which had political implications of encouraging the ideal of wider access to the government; strong in Switzerland, parts of Germany & France, the Netherlands, England, and Scotland. | 47 | |
| 7966260742 | Catholic Reformation | helped to defend the Catholic church in southern Europe, Austria, Poland, much of Hungary, and key parts of Germany. | 48 |
AP WORLD HISTORY UNIT 5 STUDY GUIDE PART 2 Flashcards
| 6260891733 | Maroons | Runaway slaves who gathered in mountainous, forested, or swampy areas and formed their own self-governing communities. raided plantations for supplies, had military skills from Africa. | 0 | |
| 6260893178 | Dutch Settlers | - its the colonies in North America became known as New Netherlands - they built new Amsterdam on Manhattan Island it become a big settlement for the Dutch in North America | 1 | |
| 6260897357 | Portuguese raiders and traders | - traded textiles, weapons, & advisors for knogolese gold, silver, ivory, slvaes -merchants helped Christianity reach sun- sahara Africa -started started the early slave trade on the atlantic - | 2 | |
| 6260930637 | yongle | - fianancial supporter for zheng he voyages -Zhu Di - . 3rd emperor of the Ming. Ruled in the early 1400s and relocated the capital to its present-day capital of Beijing; rebuilt the whole city, built the Forbidden City. Immense symbol of power. He is known for appointing Zheng He to captain the treasure fleet and sending him on seven major expeditions around the world | 3 | |
| 6260931635 | Kangxi (1661- 1722) | - a Confucian scholar; effective, enlightened ruler - conquered Taiwan; extended to Mongolia, central Asia, and Tibet - began policy of strict control on foreign contact | 4 | |
| 6260940124 | Qianlong (1736- 1795) | - a sophisticated and learned ruler, poet, and artist - Vietnam, Burma, & Nepal made vassal states of china - under his rule china was peaceful, prosperous, and powerful | 5 | |
| 6260941193 | zheng He | - was muslim - was a eunuch -was Chinese greatest admiral - he led 7 voyages throughout the indian ocean - the indian ocean trade routes were already known to him -he visited Africa, india, & middle east | 6 | |
| 6260942740 | Matteo Ricci ( 1552- 1610) | - an Italian Jesuit in the ming court - a learned man who mastered written & oral Chinese -impressed Chinese with European science & mathematics | 7 | |
| 6260943856 | IEYASU | - shogun - established a military government known as bakufu | 8 | |
| 6260943857 | MING DYNASTY | -the government drove the Mongols out of china (1368-1644) -centralized government control; faced new invasions from the Mongols -rebuilt and repaired the great wall to prevent northern invasions -restored Chinese cultural traditions & civil service examinations *DELINE: coastal cities & trade disrupted by pirates (1520s-1560s) government corruption & inefficiency caused by powerful eunuchs famines & peasant rebellions (1630s and 1640s) *Manchu invaders with peasant support led to final Ming collapse - 1644 | 9 | |
| 6260961392 | GREAT WALL | -was built to protect enemies, nomads from the steepe - was built under the ming dynasty - | 10 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

