AP World History Important Dates Flashcards
| 7315234365 | 1954 | Vietnamese defeat French at Dien Bien Phu | 0 | |
| 7315234366 | 1956 | De-Stalinzation/Nationalization of Suez Canal | 1 | |
| 7315234367 | 1959 | Cuban Revolution | 2 | |
| 7315234368 | 1962 | Cuban Missile Crisis | 3 | |
| 7315234369 | 1967 | 6-Day War/Chinese Cultural Revolution | 4 | |
| 7315234370 | 1973 | Yom Kippur War | 5 | |
| 7315234371 | 1979 | Iranian Revolution | 6 | |
| 7315234372 | 1987 | 1st Palestinian Intifada | 7 | |
| 7315234373 | 1989 | Tiananmen Square/Fall of Berlin Wall | 8 | |
| 7315234374 | 1991 | Fall of USSR/1st Gulf War | 9 | |
| 7315234375 | 1994 | Rwanda genocide/1st free elections in South Africa | 10 | |
| 7315234376 | 2001 | 9/11 attacks | 11 | |
| 7315234377 | 1914-1918 | World War I | 12 | |
| 7315234378 | 1917 | Russian Revolution | 13 | |
| 7315234379 | 1919 | Treaty of Versailles (End of WWI) | 14 | |
| 7315234380 | 1929 | Stock Market Crash | 15 | |
| 7315234381 | 1931 | Japanese invasion of Manchuria | 16 | |
| 7315234382 | 1935 | Italian invasion of Ethiopia | 17 | |
| 7315234383 | 1939 | German blitzkrieg in Poland | 18 | |
| 7315234384 | 1941 | Japanese bomb Pearl Harbor | 19 | |
| 7315234385 | 1945 | World War 2 Ends | 20 | |
| 7315234386 | 1947 | Independence and partition of India | 21 | |
| 7315234387 | 1948 | Birth of Israel | 22 | |
| 7315234388 | 1949 | Chinese Communist Revolution | 23 | |
| 7315234389 | 1950-1953 | Korean War | 24 | |
| 7315234390 | 1804 | Haitian Independence | 25 | |
| 7315234391 | 1815 | Congress of Vienna | 26 | |
| 7315234392 | 1820's | Independence in Latin America | 27 | |
| 7315234393 | 1839 | 1st Opium War in China | 28 | |
| 7315234394 | 1848 | European Revolutions/Communist Manifesto written | 29 | |
| 7315234395 | 1853 | Commodore Perry opens Japan | 30 | |
| 7315234396 | 1857 | Sepoy Mutiny | 31 | |
| 7315234397 | 1861 | End of Russian serfdom/Italian unification | 32 | |
| 7315234398 | 1863 | Emancipation Proclamation in US | 33 | |
| 7315234399 | 1871 | German Unification | 34 | |
| 7315234400 | 1885 | Berlin Confrence (division of Africa) | 35 | |
| 7315234401 | 1898 | Spanish-American War | 36 | |
| 7315234402 | 1899 | Boer War (British control South Africa) | 37 | |
| 7315234403 | 1905 | Russo-Japanese War | 38 | |
| 7315234404 | 1910-1920 | Mexican Revolution | 39 | |
| 7315234405 | 1911 | Chinese Revolution/End of Dynastic China | 40 | |
| 7315234406 | 1453 | Ottomans capture Constantinople | 41 | |
| 7315234407 | 1488 | Dias rounded Cape of Good Hope | 42 | |
| 7315234408 | 1492 | Columbus' First voyage/reconquista of Spain | 43 | |
| 7315234409 | 1502 | First slaves to Americas | 44 | |
| 7315234410 | 1517 | Martin Luther/95 Theses | 45 | |
| 7315234411 | 1521 | Cortez Conquered Aztecs | 46 | |
| 7315234412 | 1533 | Pizarro Conquered Incas | 47 | |
| 7315234413 | 1588 | British defeat Spanish Armada | 48 | |
| 7315234414 | 1600 | Unification of Japan under Tokugawa rule | 49 | |
| 7315234415 | 1607 | Foundation of Jamestown | 50 | |
| 7315234416 | 1618-1648 | 30 Years War | 51 | |
| 7315234417 | 1683 | Unsuccessful Ottoman siege of Vienna | 52 | |
| 7315234418 | 1689 | Glorious Revolution/English Bill of Rights | 53 | |
| 7315234419 | 1756-1763 | 7 Years War (French and Indian War) | 54 | |
| 7315234420 | 1776 | American Revolution/Smith writes Wealth of Nations | 55 | |
| 7315234421 | 1789 | French Revolution begins | 56 | |
| 7315234422 | 622 | Rise of Islam | 57 | |
| 7315234423 | 732 | Battle of Tours (end of Muslim move into France) | 58 | |
| 7315234424 | 800 | Coronation of Charlemagne | 59 | |
| 7315234425 | 1054 | 1st Schism in Christian Church | 60 | |
| 7315234426 | 1066 | Norman conquest of England | 61 | |
| 7315234427 | 1071 | Battle of Manzikert (Seljuk Turks over Byzantium) | 62 | |
| 7315234428 | 1095 | First Crusade | 63 | |
| 7315234429 | 1206 | Mongols united under Genghis Khan | 64 | |
| 7315234430 | 1271-1295 | Marco Polo's travels | 65 | |
| 7315234431 | 1324 | Mansa Musa's Pilgrimage | 66 | |
| 7315234432 | 1325-1349 | Travels of Ibn Battuta | 67 | |
| 7315234433 | 1347-1348 | Bubonic Plague in Europe | 68 | |
| 7315234434 | 1433 | End Of Zheng He's Voyages | 69 | |
| 7315234435 | 14th C. | Rise of Ottomans | 70 | |
| 7315234436 | 8000 BCE | Beginnings of Agriculture | 71 | |
| 7315234437 | 3000 BCE | Beginnings of Bronze Age and early civilizations | 72 | |
| 7315234438 | 1300 BCE | Iron Age | 73 | |
| 7315234439 | 6th C BCE | Beginnings of Confucianism, Buddhism, Taoism (Daoism) | 74 | |
| 7315234440 | 5th C BCE | Greek Golden Age (philosophers, ect.) | 75 | |
| 7315234441 | 323 BCE | Alexander the Great | 76 | |
| 7315234442 | 221 BCE | Qin unified China | 77 | |
| 7315234443 | 32 | Beginnings of Christianity | 78 | |
| 7315234444 | 180 | End of Pax Romana | 79 | |
| 7315234445 | 220 | End of Han Dynasty | 80 | |
| 7315234446 | 333 | Roman capital moved to Constantinople | 81 | |
| 7315234447 | 4th C | Beginning of Trans-Saharan trade routes | 82 | |
| 7315234448 | 476 | Fall of Rome | 83 | |
| 7315234449 | 527 | Justinian Rule of Byzantine Empire | 84 |
Flashcards
Flashcards
Ap World history Chapter 4 Vocab Flashcards
| 7515183335 | Legalism | Excessive adherence to law or formula: Dependence on moral law rather than on personal religious faith. | 0 | |
| 7515184758 | Ban Zhao | First known female Chinese historian. She completed her brother Ban Gu's work on the history of the Western Han, the Book of Han. She also wrote Lessons for Women, an influential work on women's conduct. | 1 | |
| 7515195330 | Vedas | The most ancient Hindu scriptures, written in early Sanskrit and containing hymns, philosophy, and guidance on ritual for the priests of Vedic religion. Believed to have been directly revealed to seers among the early Aryans in India, and preserved by oral tradition, the four chief collections are the Rig Veda, Sama Veda, Yajur Veda, and Atharva Veda. | 2 | |
| 7515202425 | Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha) | Gautama Buddha, also known as Siddhārtha Gautama, Shakyamuni Buddha, or simply the Buddha, after the title of Buddha, was an ascetic and sage, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. | 3 | |
| 7515207203 | Theravada/Mahayana | Theravada Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism share the same core beliefs and devotion to the life and teaching of Buddha, but they do have some differences. Theravada Buddhism is associated with South East Asia and is perhaps closer to the original Indian form of Buddhism. | 4 | |
| 7515244844 | Bhagavad Gita | The Bhagavad Gita is an ancient Indian text that became an important work of Hindu tradition in terms of both literature and philosophy. The earliest translations of this work from Sanskrit into English were made around 1795 CE by Sir Charles Wilkins. The name Bhagavad Gita means "the song of the Lord". | 5 | |
| 7515244845 | Judaism | the monotheistic religion of the Jews. | 6 | |
| 7515254622 | Socrates, Plato, Aristotle | Greek philosopher. As represented in the writings of his disciple Plato, he engaged in dialogue with others in an attempt to define ethical concepts by exposing and dispelling error (the Socratic method). Plato was a student of Socrates and later became the teacher of Aristotle. He founded a school in Athens called the Academy. Most of his writings are dialogues. He is best known for his theory that ideal Forms or Ideas, such as Truth or the Good, exist in a realm beyond the material world. Aristotle is a towering figure in ancient Greek philosophy, making contributions to logic, metaphysics, mathematics, physics, biology, botany, ethics, politics, agriculture, medicine, dance and theatre. He was a student of Plato who in turn studied under Socrates. | 7 | |
| 7515260160 | Saint Paul | Saint Paul, the Apostle. Saint Paul, the Apostle, original name Saul of Tarsus (born 4 bc?, Tarsus in Cilicia [now in Turkey]—died c. ad 62-64, Rome [Italy]), one of the leaders of the first generation of Christians, often considered to be the second most important person in the history of Christianity. | 8 | |
| 7515263451 | Perpetua | Perpetua and Felicity (believed to have died in 203 AD) were Christian martyrs of the 3rd century. Vibia Perpetua was a married noblewoman, said to have been 22 years old at the time of her death, and mother of an infant she was nursing. | 9 | |
| 7515269875 | Confucianism | Confucianism, also known as Ruism, is described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or simply a way of life. | 10 | |
| 7515277258 | Daoism | a religious or philosophical tradition of Chinese origin which emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao | 11 | |
| 7515278738 | Upanishads | The Upanishads are a collection of ancient Sanskrit texts that contain some of the central philosophical concepts and ideas of Hinduism, some of which are shared with Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. | 12 | |
| 7515278739 | Nalanda | Nalanda was an acclaimed Mahavihara, a large Buddhist monastery in the ancient kingdom of Magadha in India. | 13 | |
| 7515280941 | Zoroastrianism | Zoroastrianism is one of the world's oldest monotheistic religions. It was founded by the Prophet Zoroaster in ancient Iran approximately 3500 years ago. expand all. | 14 | |
| 7515284727 | Greek Rationalism | He was a student of the Classical Greece philosopher Socrates, the credited founder of Western philosophy. Aristotle was another of Greece's known thinkers. Aristotle's contribution to rationalism comes from a use of *syllogistic logic. | 15 | |
| 7515287901 | Jesus of Nazareth | a teacher and prophet born in Bethlehem and active in Nazareth; his life and sermons form the basis for Christianity (circa 4 BC - AD 29) Synonyms: Christ, Deliverer, Good Shepherd, Jesus, Jesus Christ, Redeemer, Savior, Saviour, the Nazarene Examples: El Nino. | 16 | |
| 7515290787 | Church of the East | The Church of the East, also known as the Nestorian Church, was an Eastern Christian Church in the Persian Empire and other parts of Asia during the late antiquity period and throughout the middle ages. | 17 |
AP Human Geography - Unit 1 Flashcards
| 9682312513 | Human Geography | a branch of geography that focuses on the study of patterns and processes that shape human interaction with the built environment, with particular reference to the causes and consequences of the spatial distribution of human activity on the Earth's surface | 0 | |
| 9682312514 | Globalization | The act of becoming global. The spread of information, ideas, etc from one place in the world to another. | 1 | |
| 9682312515 | Spatial Perspective | observing variations in geographic phenomena across space | 2 | |
| 9682312516 | Location | The position of anything on Earth's surface. | 3 | |
| 9682312517 | Absolute Location | Coordinates, Address, Etc. | 4 | |
| 9682312518 | Relative Location | Location of a place in relation to another place or landmark. (LANDMARK) | 5 | |
| 9682312519 | Site | The exact location's physical spot. (think construction) | 6 | |
| 9682312520 | Situation | The areas around the location which contribute to the sense of the place. | 7 | |
| 9682312521 | Human-Environment Interactions | How people interact/change the place/location. | 8 | |
| 9682312522 | Place | A specific point on Earth distinguished by particular characteristics. Uniqueness of the point. | 9 | |
| 9682312523 | Sense of Place | What makes a place unique | 10 | |
| 9682312524 | Perception of Place | belief or "understanding" about a place developed through books, movies, stories or pictures | 11 | |
| 9682312525 | Movement | the change from one location to another | 12 | |
| 9682312526 | Landscape | the overall appearance of an area. Most are comprised of a combination of natural and human-induced influences. | 13 | |
| 9682312527 | Cultural Landscape | How a culture affects the landscape of an area/shapes the world around it. | 14 | |
| 9682312528 | Distortion | Inaccuracies in a map due to the translation of a 3D image to a 2D surface. | 15 | |
| 9682312529 | Equal-area projection maps | Shapes and directions are distorted but land area is kept in tact. (Peters) | 16 | |
| 9682312530 | Conformal Maps | Maps that distort area but keep shapes intact (Mercator) | 17 | |
| 9682312531 | Scale | The scope Generally, the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole, specifically the relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earth's surface. (Scope of view.) | 18 | |
| 9682312532 | Cylindrical Projection Maps | Surface of a globe projected as if on a cylinder. Most distortion at the poles, least at the equator. (Shows Accurate Direction) | 19 | |
| 9682312533 | Conic Projection Map | Map projected onto the surface of a cone whose point is usually above one of the poles. (Keeps distance, loses direction) | 20 | |
| 9682312534 | Oval Projection Maps | Used for world maps (16th and 17th century). Neither conformal or equal area. Usually a little distortion everywhere. (Combination of Cylindrical and Conic) | 21 | |
| 9682312535 | Reference Maps | Used for transportation and locating places. | 22 | |
| 9682312536 | Thematic Maps | Used to display data about a location. | 23 | |
| 9682312537 | Cartograms | Shows data in relation to size | 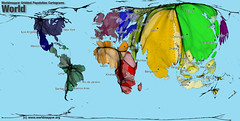 | 24 |
| 9682312538 | Choropleth Maps | Shows data in relation to color/intensity/shade |  | 25 |
| 9682312539 | Dot Maps | Each dot represents an amount of data. More dots = more of the variable |  | 26 |
| 9682312540 | Isoline Map | Map that uses continuous lines connecting areas of same value. (Topographic Maps do this) |  | 27 |
| 9682312541 | Parallels/Latitude | Lines measuring location on earth that wrap around, don't touch. | 28 | |
| 9682312542 | Meridians/Longitude | Lines measuring location and time zones (1 hr each 15 degrees) on earth that wrap around and touch at the poles. | 29 | |
| 9682312543 | Equator | The longest line of latitude at 0 degrees and has a constant amount of sun exposure. | 30 | |
| 9682312544 | North and South Poles | The locations on the earth which receive the least amount of sun during the winter. | 31 | |
| 9682312545 | Prime Meridian | Runs through Greenwich, England. 0 longitude. Could have been placed anywhere in the world, but was placed there. | 32 | |
| 9682312546 | International Date Line | An arc that for the most part follows 180° longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross it heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day. | 33 | |
| 9682312547 | Mental Maps | Image or picture of the way space is organized as determined by an individual's perception, impression, and knowledge of that space | 34 | |
| 9682312548 | Global Positioning System | Tells you where you are on the earth. | 35 | |
| 9682312549 | Remote Sensing | Collecting data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet. | 36 | |
| 9682312550 | Geographic Information Systems | Organizes, stores, analyzes, and displays geographic data. Each layer of information is a thematic layer. | 37 | |
| 9682312551 | Regions | An area or division, especially part of a country or the world having definable characteristics but not always fixed boundaries. | 38 | |
| 9682312552 | Formal Region | Formally recognized areas determined by a governing body. Sometimes called Uniform Region. | 39 | |
| 9682312553 | Functional/nodel region | A region around a central node tied by transportation and communication or by economic or functional associations | 40 | |
| 9682312554 | Perceptual/vernacular region | A place believed to exist as a part of cultural identity. (The South, The North, The Deep South) | 41 | |
| 9682312555 | Culture | Comprised of shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by a society. | 42 | |
| 9682312556 | Cultural Trait | The specific customs that are part of the everyday life of a particular culture, such as language, religion, ethnicity, social institutions, and aspects of popular culture. | 43 | |
| 9682312557 | Diffusion | The spread of things or ideas from one place (a hearth) to another. | 44 | |
| 9682312558 | Cultural Diffusion | The spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another. | 45 | |
| 9682312559 | distance decay | The idea that the further something is away/more inconvenient it is, the less frequent/intense interaction with it will be. |  | 46 |
| 9682312560 | Cultural Barriers | Prevailing cultural attitude rendering certain innovations, ideas or practices unacceptable or unadoptable in that particular culture | 47 | |
| 9682312561 | Expansion Diffusion | When the idea/thing being spread continues to exist in it's original location as well as spreading to new locations. | 48 | |
| 9682312562 | Contagious/Viral Diffusion | The spread of a disease, an innovation, or cultural traits through direct contact with another person or another place. |  | 49 |
| 9682312563 | Hierarchical Diffusion | the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places |  | 50 |
| 9682312564 | Stimulus Diffusion | A form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place | 51 | |
| 9682312565 | Relocation Diffusion | Diffusion from one place to another where the idea does not stay in the origin and moves with the people. | 52 | |
| 9682312566 | Distribution | the frequency or occurrence of something | 53 | |
| 9682312567 | Density | The amount of something in a given space. | 54 | |
| 9682312568 | Concentration | The spread of something over a given area. | 55 | |
| 9682312569 | Pattern | a consistent or characteristic arrangement | 56 | |
| 9682312570 | Enviornmental Determinism | The belief that physical environment determines potential for societal development. | 57 | |
| 9682312571 | Possibilism | The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives. | 58 | |
| 9682312572 | Cultural Ecology | Geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships. | 59 |
AP World History: Chapter 12 Vocabulary Flashcards
| 8237431695 | Aztec Empire | These people welled in Mexico, practiced polytheism and human sacrifice, were semi-nomadic, were ruled by a king, and had rich resources such as cocoa and gold. | 0 | |
| 8237437060 | Benin | This was an African agricultural society ruled by Ewuare, a warrior king, and had a centralized government who encouraged trade, art, and metal work. | 1 | |
| 8237437061 | Christopher Columbus | Genoses mariner commissioned by Spain to search for a new trading route to Asia; in 1492, he found America instead. | 2 | |
| 8237441230 | European Renaissance | The "Rebirth of Europe" was a reflection on ancient Greek and Roman culture and a focus on humanism. | 3 | |
| 8237449494 | Fulbe | West Africa's largest pastoral society, whose members gradually adopted Islam and took on a religious leadership role that lead to the creation of a number of new states. | 4 | |
| 8237452908 | Huitzilopochtli | Aztec tribal patron god; central figure of cult of human sacrifice and warfare; identified with old sun god | 5 | |
| 8237453866 | Hundred Years War | Major conflict between France and England over rival claims to territory in France; the two states' need to finance the war helped encourage their administrative development. | 6 | |
| 8237453867 | Igbo | This was a stateless society in Africa that enforced universities, educations, and different, yet equally important occupations held by all people to maintain balance. | 7 | |
| 8237455551 | Inca Empire | These people were located along the Andes mountains and modern-day Peru, were one of the largest states and spoke Quechua. | 8 | |
| 8237455552 | Iroquis League of Five Nations | This was a collected group of elders from each of the five Iroquois clans who, under the Great Law of Peace, banded together to stop tribal disputes. | 9 | |
| 8237459328 | Malacca | This was a major trade center located in the state of Malacca near the Asiatic - Pacific coastline, where Chinese goods were most likely available. | 10 | |
| 8237460246 | Mexica | Semi-nomadic people of northern Mexico who by 1325 had established themselves on a small island in Lake Texcoco, where they built their capital, Tenochitlán. | 11 | |
| 8237460247 | Ming Dynasty | This dynasty focused on rebuilding China to the glory it had before the rule of the Mongols; they accomplished this through reforestation, encouraging art and metal work, and maritime adventure/trade. | 12 | |
| 8237461604 | Mughal Empire | Established by Babur in India in 1526; the name is taken from the supposed Mongol descent of Babur, but there is little indication of any Mongol influence in the dynasty; became weak after the rule of Aurangzeb in first decades of 18th century. | 13 | |
| 8237462943 | Nezahualcoyotl | A poet and king of the city-state of Texcoco, which was part of the Aztec Empire. | 14 | |
| 8237462944 | Ottoman Empire | This was a Turkish, Islamic Empire that expanded across Northern Africa, Greece and Anatolia, and partly Saudi Arabia. They encouraged and wanted to Restore Islam to its full glory and were ruled by Sultans/Caliphs. | 15 | |
| 8237465073 | Paleolithic Persistence | This was the continued existence of hunter-gatherer civilizations despite the flourishing, advanced societies around them. | 16 | |
| 8237465074 | Pochteca | Special merchant class in Aztec society; specialized in long-distance trade in luxury items. | 17 | |
| 8237467627 | Safavid Empire | Originally a Turkic nomadic group; family originated in Sufi mystic group; espoused Shi'ism; conquered territory and established kingdom in region equivalent to modern Iran; lasted until 1722. | 18 | |
| 8237469154 | Songhay Empire | West African Savannas, second half of 15th century, most recent and largest in a series of states operating in the trans-Saharan trade routes, Islam. Created a mix of cultures, represented a substantial Islamic state on the African frontier of a still expanding Muslim world, major crossroads of trade. | 19 | |
| 8237470240 | Tenochtitlán | Founded c. 1325 on marshy island in Lake Texcoco; became center of Aztec power; joined with Tlacopan and Texcoco in 1434 to form a triple alliance that controlled most of central plateau of Mesoamerica. | 20 | |
| 8237470241 | Timbuktu | This was a city located in Mali, Africa that served as a major trading port, offering salt, gold, etc. and harbored many Islamic scholars. | 21 | |
| 8237471305 | Timur | He was a Chinese Emperor who ruled before the Ming Dynasty and attempted to restore China to the time of the Mongols. | 22 | |
| 8237472725 | Triple Alliance | Military and political alliance formed before World War I to counter moves by potential rivals England, France, and Russia; consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. | 23 | |
| 8237472726 | Vasco da Gama | Portuguese explorer whose voyage was the first European venture to reach India by circling the tip of South Africa. | 24 | |
| 8237475707 | Yongle | Reign period of Zhu Di (1360-1424), the third emperor of the Ming Empire (r. 1403-1424).Sponsored the building of the Forbidden City, a huge encyclopedia project, the expeditions of Zheng He, and the reopening of China's borders to trade and travel (355) | 25 | |
| 8237477567 | Zheng He | He was a Chinese explorer who sailed the South China Sea and Indian Ocean with 300 massive ships and 27,000 men; he provided China an opportunity to monopolize trade. | 26 |
Pre-AP World History - Test Review - Period 1 Flashcards
Period 1 Review - NGA
| 5284509313 | Agricultural Revolution | The change from food gathering to food production that occurred between ca. 8000 and 2000 B.C.E. Also known as the Neolithic Revolution. | 0 | |
| 5284509314 | Sedentary | Settled in one area; inhabiting the same locality throughout life; not migratory or nomadic. | 1 | |
| 5284509315 | Amulet | a trinket or piece of jewelry thought to be a protection against evil | 2 | |
| 5284509316 | Anthropomorphic | suggesting HUMAN characteristics for animals or inanimate things | 3 | |
| 5284509317 | Babylon | The largest and most important city in Mesopotamia. It achieved particular eminence as the capital of the Amorite king Hammurabi in the eighteenth century B.C.E. and the Neo-Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar in the sixth century B.C.E. (p. 29) | 4 | |
| 5284509318 | Bronze | an alloy of copper and tin and sometimes other elements | 5 | |
| 5284509319 | Carthage | City located in present-day Tunisia, founded by Phoenicians ca. 800 B.C.E. It became a major commercial center and naval power in the western Mediterranean until defeated by Rome in the third century B.C.E. | 6 | |
| 5284509320 | Catal Hüyük | One of first true cities in history, created in the Neolithic Era in 6500 to 5500 BC, from which were created agriculture, trading, temples, housing, and religions | 7 | |
| 5284509321 | Celts | Peoples sharing a common language and culture that originated in Central Europe in the first half of the first millennium B.C.E.. After 500 B.C.E. they spread as far as Anatolia in the east, Spain and the British Isles in the west, onquered by Romans | 8 | |
| 5284509322 | Chavin | First major urban civilization in South America. Capital is de Huantar, was located in the Andes Mountains of Peru. Has 2 distinct ecological zones, the Peruvian Costal Plain and the Andean Foothills. | 9 | |
| 5284509323 | City-state | A city with political and economic control over the surrounding countryside | 10 | |
| 5284509324 | Civilization | a society in an advanced state of social development (e.g., with complex legal and political and religious organizations) | 11 | |
| 5284509325 | Code of Hammurabi | the set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi dating to the 18th century BC, the earliest legal code known in its entirety | 12 | |
| 5284509326 | Confucius | Chinese philosopher, administrator, and moralist. His social and moral teachings, collected in the Analects , tried to replace former religious observances | 13 | |
| 5284509327 | Culture | the attitudes and behavior that are characteristic of a particular social group or organization | 14 | |
| 5284509328 | Cuneiform | an ancient wedge-shaped script used in Mesopotamia and Persia | 15 | |
| 5284509329 | Daoism | philosophical system developed by of Lao-tzu and Chuang-tzu advocating a simple honest life and noninterference with the course of natural events | 16 | |
| 5284509330 | Druids | The class of religious experts who conducted rituals and preserved sacred lore among some ancient Celtic peoples. They provided education, mediated disputes between kinship groups, and were suppressed by the Romans as potential resistance. | 17 | |
| 5284509331 | First Temple | A monumental sanctuary built in Jerusalem by King Solomon in the tenth century B.C.E. to be the religious center for the Israelite god Yahweh. The Temple priesthood conducted sacrifices, received a tithe or percentage of agricultural revenues. | 18 | |
| 5284509332 | Foragers | people who support themselves by hunting wild animals and gathering wild edible plants and insects | 19 | |
| 5284509333 | Hammurabi | Amorite ruler of Babylon (r. 1792-1750 B.C.E.). He conquered many city-states in southern and northern Mesopotamia and is best known for a code of laws, inscribed on a black stone pillar, illustrating the principles to be used in legal cases. | 20 | |
| 5284509334 | Harappa | Site of one of the great cities of the Indus Valley civilization of the third millennium B.C.E. It was located on the northwest frontier of the zone of cultivation , and may have been a center for the acquisition of raw materials. (p. 48) | 21 | |
| 5284509335 | Hatshepsut | Queen of Egypt (1473-1458 B.C.E.). Dispatched a naval expedition down the Red Sea to Punt (possibly Somalia), the faraway source of myrrh. There is evidence of opposition to a woman as ruler, and after her death her name was frequently expunged | 22 | |
| 5284509336 | Hebrew Bible | A collection of sacred books containing diverse materials concerning the origins, experiences, beliefs, and practices of the Israelites. Most of the text was compiled by members of the priestly class in the fifth century B.C.E. Known as the Torah. | 23 | |
| 5284509337 | Hieroglyphics | an ancient Egyptian writing system in which pictures were used to represent ideas and sounds | 24 | |
| 5284509338 | History | the discipline that records and interprets past events involving human beings | 25 | |
| 5284509339 | Hittites | A people from central Anatolia who established an empire in Anatolia and Syria in the Late Bronze Age. With wealth from the trade in metals and military power based on chariot forces, the hittites vied with New Kingdom Egypt over Syria | 26 | |
| 5284509340 | Iron Age | the period following the Bronze Age; characterized by rapid spread of iron tools and weapons | 27 | |
| 5284509341 | Israel | an ancient kingdom of the Hebrew tribes at the southeastern end of the Mediterranean Sea | 28 | |
| 5284509342 | Jericho | Oldest Neolithic community in the West Bank between Israel and Jordan | 29 | |
| 5284509343 | Kush | An African state that developed along the upper reaches of the Nile c. 100 B.C.E.; conquered Egypt and ruled it for several centuries. | 30 | |
| 5284509344 | Library of Ashurbanipal | A large collection of writings drawn from the ancient literary, religious, and scientific traditions of Mesopotamia. It was assembled by the sixth century B.C.E. Assyrian ruler Ashurbanipal. The many tablets unearthed by archaeologists constitute one of the most important sources of present-day knowledge of the long literary tradition of Mesopotamia. | 31 | |
| 5284509345 | Linear B | the modern name for the script, composed of signs and pictures, in which Mycenaean Greeks kept records on tablets of clay | 32 | |
| 5284509346 | Llama | wild or domesticated South American cud-chewing animal related to camels but smaller and lacking a hump | 33 | |
| 5284509347 | Loess | a fine-grained unstratified accumulation of clay and silt deposited by the wind | 34 | |
| 5284509348 | Ma'at | Egyptian term for the concept of divinely created and maintained order in the universe. Reflecting the ancient Egyptians' belief in an essentially beneficent world, the divine ruler was the earthly guarantor of this order. | 35 | |
| 5284509349 | Mandate of Heaven | a political theory of ancient China in which those in power were given the right to rule from a divine source | 36 | |
| 5284509350 | Mass deportation | The forcible removal and relocation of large numbers of people or entire populations | 37 | |
| 5284509351 | Matrilineal | based on or tracing descent through the female line | 38 | |
| 5284509352 | Megaliths | Structures and complexes of very large stones constructed for ceremonial and religious purposes in Neolithic times. | 39 | |
| 5284509353 | Memphis | The capital of Old Kingdom Egypt, near the head of the Nile Delta. Early rulers were interred in the nearby pyramids | 40 | |
| 5284509354 | Minoan | Prosperous civilization on the Aegean island of Crete in the second millennium B.C.E. The Minoans engaged in far-flung commerce around the Mediterranean and exerted powerful cultural influences on the early Greeks. | 41 | |
| 5284509355 | Mohenjo-Daro | Largest city of the Indus Valley civilization. It was centrally located in the extensive floodplain of the Indus River. Little is known about the political institutions of Indus Valley communities, but the large-scale implies central planning. | 42 | |
| 5284509356 | Monotheism | belief in a single God | 43 | |
| 5284509357 | Meroe | Capital of a flourishing kingdom in southern Nubia from the fourth century B.C.E. to the fourth century C.E.. In this period Nubian culture shows more independence from Egypt and the influence of Sub-Saharan Africa. | 44 | |
| 5284509358 | egalitarian | of, relating to, or believing in the principle that all people are equal and deserve equal rights and opportunities. | 45 | |
| 5284509359 | Mycenae | Site of a fortified palace complex in southern Greece that controlled a Late Bronze Age kingdom.. Achaeans were a member of this principal (mainland) Greek tribe since 1900 B.C.E. | 46 | |
| 5284509360 | Neo-Assyrian Empire | A major Mesopotamian empire between 934-608 BCE. They used force and terror and exploited the wealth and labor of their subjects. They were an iron-age resurgence of a previous bronze age empire. | 47 | |
| 5284509361 | Neo-Babylonian Kingdom | Under the Chaldaeans (nomadic kinship groups that settled in southern Mesopotamia in the early first millennium B.C.E.), Babylon again became a major political and cultural center in the seventh and sixth centuries B.C.E. After participating in the destruction of Assyrian power, the monarchs Nabopolassar and Nebuchadnezzar took over the southern portion of the Assyrian domains. | 48 | |
| 5284509362 | Neolithic | latest part of the Stone Age beginning about 10,000 BC in the middle east (but later elsewhere) | 49 | |
| 5284509363 | Social Stratification | the condition of being arranged in social strata or classes within a group | 50 | |
| 5284509364 | Olmec | a member of an early Mesoamerican civilization contered around Veracruz that flourished between 1300 and 400 BC | 51 | |
| 5284509365 | Paleolithic | second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC | 52 | |
| 5284509366 | Papyrus | paper made from the papyrus plant by cutting it in strips and pressing it flat | 53 | |
| 5284509367 | Patrilineal | based on or tracing descent through the male line | 54 | |
| 5284509368 | Pharaoh | the title of the ancient Egyptian kings | 55 | |
| 5284509369 | Phoenicians | located on eastern Mediterranean coast; invented the alphabet which used sounds rather than symbols like cuneiform | 56 | |
| 5284509370 | Ramesses II | A long-lived ruler of New Kingdom Egypt (r. 1290-1224 B.C.E.). He reached an accommodation with the Hittites of Anatolia after a military standoff. He built on a grand scale throughout Egypt. | 57 | |
| 5284509371 | Scribe | a sharp-pointed awl for marking wood or metal to be cut | 58 | |
| 5284509372 | Semitic | of or relating to or characteristic of Semites | 59 | |
| 5284509373 | Shaft graves | A term used for the burial sites of elite members of Mycenaean Greek society in the mid-second millennium B.C.E. At the bottom of deep shafts lined with stone slabs, the bodies were laid out along with gold and bronze jewelry, implements, weapons, and masks. | 60 | |
| 5284509374 | Shang | The dominant people in the earliest Chinese dynasty for which we have written records (ca. 1750-1027 B.C.E.). Ancestor worship, divination by means of oracle bones, and the use of bronze vessels for ritual purposes were major elements of this culture. | 61 | |
| 5284509375 | Stone Age | The historical period characterized by the production of tools from stone (lithic) and other nonmetallic substances. It was followed in some places by the Bronze Age | 62 | |
| 5284509376 | Sumerians | People who dominated Southern Mesopotamia through the end of the 3rd Millennium BCE. Responsible for the creation of irrigation technology, cunieform, and religious conceptions. | 63 | |
| 5284509377 | Thebes | Capital city of Egypt and home of the ruling dynasties during the Middle and New Kingdoms. Amon, patron deity of Thebes, became one of the chief gods of Egypt. Monarchs were buried across the river in the Valley of the Kings | 64 | |
| 5284509378 | Yin/yang | In Daoist belief, complementary factors that help to maintain the equilibrium of the world. One is associated with masculine, light, and active qualities while the other with feminine, dark, and passive qualities. | 65 | |
| 5284509379 | Zhou | The people and dynasty that took over the dominant position in north China from the Shang and created the concept of the Mandate of Heaven to justify their rule. Remembered as prosperous era in Chinese History. | 66 | |
| 5284509380 | Ziggurat | a rectangular tiered temple or terraced mound erected by the ancient Assyrians and Babylonians | 67 | |
| 5284573188 | patriarchal | of, relating to, or characteristic of a system of society or government controlled by men. | 68 | |
| 5284587132 | Archaeology | the study of human history and prehistory through the excavation of sites and the analysis of ARTIFACTS and other physical remains. | 69 | |
| 5284590414 | Anthropology | the study of HUMANKIND, in particular. the comparative study of human societies and cultures and their development. | 70 | |
| 5284600546 | benevolent | well meaning and kindly. (of an organization) serving a charitable rather than a profit-making purpose. | 71 | |
| 5284613151 | Agricultural surplus | an amount of agriculture (crops) left over when requirements have been met; an excess of production or supply over demand | 72 | |
| 5284619173 | theocratic state | a system of government in which priests rule in the name of God or a god. i.e. Egyptians, and the commonwealth of Israel from the time of Moses until the election of Saul as King. | 73 | |
| 5284643708 | hierarchy | a system or organization in which people or groups are RANKED one above the other according to status or authority. | 74 | |
| 5284655628 | Aegean Sea | an arm of the Mediterranean Sea Greece and Turkey; a main trade route for the ancient civilizations of Crete and Greece and Rome and Persia | 75 | |
| 5284659493 | cultural hearth | Locations on earth's surface where specific cultures first arose. Symbolic of one's home. | 76 | |
| 5284674940 | secular authority | worldly, earthy matters; not having to do with spiritual or religious matters | 77 | |
| 5284773596 | pastoralism | the branch of agriculture concerned with the raising of livestock. It is animal husbandry: the care, tending and use of animals such as camels, goats, cattle, yaks, llamas, and sheep | 78 |
AMSCO AP World History Chapter 15 Vocab Flashcards
| 9372046592 | Henry IV | Sanctioned religious toleration of the Huguenots, French Calvanists, converted to Catholicism for the sake of solidifying his power. His rule saw increasing emphasis on national sovereignty. | 0 | |
| 9372046593 | Henry VIII | A king of England in the early sixteenth century. With the support of his Parliament, established himself as head of the Christian Church in England, in place of the pope, after the pope refused to allow his marriage to Catherine of Aragon to be dissolved. (1491-1547) | 1 | |
| 9372046594 | Anne Boleyn | Queen of England from 1533 to 1536 as the second wife of King Henry VIII, and Marquess of Pembroke in her own right. | 2 | |
| 9372046595 | Charles V, Holy Roman Empire | Was ruler of both the Spanish Empire from 1516 and the Holy Roman Empire from 1519, as well as of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1506. | 3 | |
| 9372046596 | Philip II | King of Spain and Portugal and husband of Mary I; he supported the Counter Reformation and sent the Spanish Armada to invade England (1527-1598) ... king of ancient Macedonia and father of Alexander the Great (382-336 BC) | 4 | |
| 9372046597 | Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand | A king and queen of Spain in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries. They united their country and sponsored the exploration of the New World by Christopher Columbus. | 5 | |
| 9372046598 | James I | King of England (1603-1625) and of Scotland (1567-1625). The son of Mary Queen of Scots, he succeeded the heirless Elizabeth I as the first Stuart king of England. | 6 | |
| 9372046599 | Charles I | King of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1625-1649). His power struggles with Parliament resulted in the English Civil War (1642-1648) in which he was defeated. | 7 | |
| 9372046600 | Oliver Cromwell | Was an English military and political leader and later Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland, and Ireland. | 8 | |
| 9372046601 | Charles II | King of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1660-1685) who reigned during the Restoration, a period of expanding trade and colonization as well as strong opposition to Catholicism. | 9 | |
| 9372046602 | James II | King of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1685-1688). The last Stuart king to rule both England and Scotland, he was deposed by his Protestant daughter Mary (later, Mary II) and her husband, William of Orange. | 10 | |
| 9372046603 | William and Mary | Ruled jointly after the Glorious Revolution of 1688 had expelled Mary's father, King James II. | 11 | |
| 9372046605 | Cardinal Richelieu | Was the chief of government under King Louis XIII. He achieved two difficult goals in his career: establishing absolute monarchy in France and breaking the political power of the Huguenots, or French Protestants. | 12 | |
| 9372046606 | Louis XIV | Ruled 1643-1715, King of France, his reign, the longest in French history, was characterized by a magnificent court, the expansion of French influence in Europe, and the establishment of overseas colonies. | 13 | |
| 9372046607 | Prince Henry the Navigator | Was a Portuguese royal prince, soldier, and patron of explorers. Henry sent many sailing expeditions down Africa's west coast, but did not go on them himself. | 14 | |
| 9372046608 | Thirty Years War | A war waged in the early seventeenth century that involved France, Spain, Sweden, Denmark, Austria, and numerous states of Germany. The causes of the war were rooted in national rivalries and in conflict between Roman Catholics and Protestants. | 15 | |
| 9372046609 | War of the Spanish Succession | A war (1701-14) fought by Austria, England, the Netherlands, and Prussia against France and Spain, arising from disputes about the succession in Spain after the death of Charles II of Spain. | 16 | |
| 9372046610 | Maritime Empires | A state with primarily maritime realms—an empire at sea (such as the Phoenician network of merchant cities) or a sea-borne empire. | 17 | |
| 9372046611 | Sepoys | An Indian soldier serving under British or other European orders. | 18 | |
| 9372046612 | Huguenots | A French Protestant of the 16th-17th centuries. Largely Calvinist, the Huguenots suffered severe persecution at the hands of the Catholic majority, and many thousands emigrated from France. | 19 | |
| 9372046613 | Clunaic Reforms | Were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of the Western Church focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. | 20 | |
| 9372046614 | Simony | The buying or selling of ecclesiastical privileges, for example pardons or benefices. | 21 | |
| 9372046615 | Reformed Church of Scotland | Is a Christian denomination. It is the original church of the Reformed Presbyterian tradition (commonly known as the RP's). The RPCS formed in 1690 when its members declined to be part of the establishment. | 22 | |
| 9372046616 | Anglican Church | The Church of England and the churches in other nations that are in complete agreement with it as to doctrine and discipline and are in communion with the Archbishop of Canterbury. | 23 | |
| 9372046617 | Johannes Kepler | Was a German mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer. | 24 | |
| 9372046618 | Francis Bacon | Was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, jurist, orator, and author. He served both as Attorney General and as Lord Chancellor of England. | 25 | |
| 9372046619 | Galileo | Italian astronomer and mathematician who was the first to use a telescope to study the stars; demonstrated that different weights descend at the same rate; perfected the refracting telescope that enabled him to make many discoveries (1564-1642) | 26 | |
| 9372046620 | Sir Isaac Newton | English mathematician and physicist; remembered for developing the calculus and for his law of gravitation and his three laws of motion (1642-1727). | 27 | |
| 9372046621 | Michaelangelo | Was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance who exerted an unparalleled influence on the development of Western art. | 28 | |
| 9372046622 | Leonardo da Vinci | 1452-1519. Italian painter, engineer, and scientist. | 29 | |
| 9372046623 | John Locke | A seventeenth-century English philosopher. Argued against the belief that human beings are born with certain ideas already in their minds. He claimed that, on the contrary, the mind is a tabula rasa (blank slate) until experience begins to "write" on it. | 30 | |
| 9372046624 | Adam Smith | Is one of the world's most famous economists. Modern capitalism owes its roots to him and his Wealth of Nations, which many consider the single most important economic work in history. | 31 | |
| 9372046625 | Edict of Nates | Signed probably on 30 April 1598 by King Henry IV of France, granted the Calvinist Protestants of France (also known as Huguenots) substantial rights in the nation, which was still considered essentially Catholic at the time. | 32 | |
| 9372046626 | Peace of Westaphilia | Was a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War over succession within the Holy Roman Empire as well as the Eighty Years' War between Holland and Spain for Dutch independence. | 33 | |
| 9372046627 | Vasco da Gama | Portuguese explorer. In 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from Europe to sail to India, opening an important commercial sea route. | 34 | |
| 9372046628 | spanish armada | the great fleet sent from Spain against England by Philip II in 1588 | 35 | |
| 9372046629 | schmalkaldic league | protestant alliance formed by Lutherans against the Holy Roman Empire | 36 | |
| 9372046630 | peace of augsburg | 1555 agreement declaring that the religion of each German state would be decided by its ruler | 37 | |
| 9372046632 | puritan revolution | England goes from a monarchy to puritan republic under Cromwell | 38 | |
| 9372046633 | petition of right | a written document asking for a limit to the king's power | 39 | |
| 9372046634 | glorious revolution | the revolution against James II | 40 | |
| 9372046635 | English bill of rights | 1689 laws protecting the rights of English subjects and Parliament | 41 | |
| 9372046636 | divine right of the monarchy | the claim that the right to rule was given to a king by God | 42 | |
| 9372046637 | intendants | French government agents who collected taxes and administered justice. | 43 | |
| 9372046638 | versailles | Palace constructed by Louis XIV outside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility. | 44 | |
| 9372046640 | reformation | a movement for religious reform | 45 | |
| 9372046641 | huldrych zwingli | swiss priest who led the protestant movement in switzerland | 46 | |
| 9372046642 | Martin luther | German monk who started the Protestant Reformation | 47 | |
| 9372046643 | 95 theses | Arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church. They were posted on Octobe 31, 1517. | 48 | |
| 9372046644 | indulgences | pardon sold by catholic church to reduce one's punishment | 49 | |
| 9372046645 | John calvin | Believed in predestination | 50 | |
| 9372046646 | the elect | Calvinistic belief that this is the group of souls who God selected to be predetermined for Heaven. | 51 | |
| 9372046647 | predestined | destiny; fate; decided beforehand | 52 | |
| 9372046648 | puritans | a group of Anglicans in England who wanted to purify their church of Catholic ways | 53 | |
| 9372046649 | jesuits | members of the society of jesus | 54 | |
| 9372046650 | council of Trent | A meeting held to discuss and reform practices of the Catholic Church. | 55 | |
| 9372046651 | index of prohibited books | list of books forbidden for Catholics to read. issued by holy office | 56 | |
| 9372046652 | social contract | An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed | 57 | |
| 9372046653 | empiricism | the belief that accurate knowledge can be acquired through observation | 58 | |
| 9372046654 | scholasticism | a medieval philosophical and theological system that tried to reconcile faith and reason | 59 | |
| 9372046655 | joint-stock companies | businesses in which a group of people invest together | 60 | |
| 9372046656 | mercantilism | belief in the benefits of profitable trading; commercialism. | 61 | |
| 9372046657 | capital | An economic system based on private ownership of capital | 62 | |
| 9372046658 | cottage industries | small-scale industries based in the home | 63 | |
| 9372046659 | physiocrates | philosophe who wrote about economics; attacked economy in Europe | 64 | |
| 9372046660 | the wealth of nations | written by Adam Smith, promoted laissez-faire, free-market economy, and supply-and-demand economics | 65 | |
| 9372046661 | commercial revolution | expansion of trade and business | 66 | |
| 9372046662 | east India company | Benefitted from tea act | 67 | |
| 9372046663 | manila | a strong paper or thin cardboard with a smooth light brown finish made from e.g. Manila hemp the strong fiber of a Philippine plant, used for rope, matting, paper, etc. | 68 | |
| 9372046664 | factors | Numbers that are multiplied together to get a product | 69 | |
| 9372046665 | cartography | the science of making maps | 70 | |
| 9372046666 | Bartholomew Diaz | (1487-1488) Portuguese, first European to reach the southern tip of Africa in 1488. | 71 | |
| 9372046667 | Ferdinand magellan | Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain | 72 |
Enlightenment - AP World History Flashcards
| 9865943528 | Deism | The belief that God has created the universe and set it in motion to operate like clockwork. God is literally in the wings watching the show go on as humans forge their own destiny. | 0 | |
| 9865943529 | Rene Descarte | Deductive thinker whose famous saying I"I'll think, there I am" challenged the notion of truth as being derived from tradition and Scriptures | 1 | |
| 9865943530 | Enlightenment | The intellectual revolution of the eighteenth century in which the philosophes stressed reason, natural law, and progress in their criticism of prevailing social injustices | 2 | |
| 9865943531 | Laissez-faire | The economic concept of the Scottish philosophe Adam Smith (1723-1790). In opposition to mercantilism, Smith argued governments to keep hands off the operation of the economy. He believed the role of government was analogous to the night watchman, guarding and protecting but not intervening in the operation of the economy, which must be left to run in accord with the natural law of supply and demand | 3 | |
| 9865943532 | Philosophes | Social critics of the eighteenth century who subject social institutions and practices to test of reason | 4 | |
| 9865943533 | Tabula rasa | John Locke's concept of the mind as a blank sheet ultimately bombarded by sense impression that, aided by human reasoning, formulate ideas | 5 | |
| 9865943535 | Thomas Hobbes | Most famous work is LEVIATHAN (1651). Heavily influenced by what he saw in the English Civil War. Believes all humans are naturally selfish and wicked; government needed to keep order. Argues that a social contract exists between the government and the governed in which the citizen gives up some rights in exchange for being protected. Believes in absolute control by ruler | 6 | |
| 9865943536 | John Locke | Most famous work is TWO TREATISES ON GOVERNMENT (1690). Heavily influenced by what he saw during the Glorious Revolution. Believes that all people are born free and equal with ability to learn from experience, and possess three natural rights (the freedoms of life, liberty, and property). Also believes in a social contract, but believes that citizens have right to end the contract and overthrow the government if ruler(s) fail to protect rights | 7 | |
| 9865943537 | Voltaire (Francois Marie Arouet) | Most famous work is CANDIDE. Heavily influencd by relatively oppressive French society of the 1700's in comparison to the relatively egalitarian society of Britain. Political and social satirist who wrote multiple works about the need for tolerance, reason, freedom, of religious beliefs, and freedom of speech. Pushes for separation of church and state, or the separation of religion from the government | 8 | |
| 9865943538 | Baron de Montesquieu | Most famous work is ON THE SPIRIT OF LAWS (1748). Main influence is the concept of the separation of powers, in which political power in a government is divided equally among multiple parts. In addition, Montesquieu believed that "power should be checked to power", referring to the system of "checks and balances" created by having each branch having a specific action that negates the power of another if necessary | 9 | |
| 9865943539 | Jean Jacques Rousseau | Most famous work is THE SOCIAL CONTRACT (1762). Believes that civilization corrupts people's natural goodness. Argued that the only good government was one that was freely formed by the people and guided by the "general will" of society. Like Locke, he believes that the social contract between government and citizens is only valid as long as the government defends the rights of the people. His belief is that the government only rules by "the consent of the governed". More radical than Locke due to the belief that all titles of nobility should be abolished to create a classless society | 10 | |
| 9865943540 | Cesare Beccaria | Most famous work is CRIMES AND PUNISHMENT (1764)- Believes that laws exist to preserve social order, not to avenge crimes, and therefore punishment should reflect this as well. Argues for the use of a trial by jury that must be delivered in a swift and timely manner, without the use o possibility of torture or cruel and unusual punishments. In addition, he believes that the punishment must match, not exceed, the crime committed | 11 | |
| 9865943541 | Mary Wollstonecraft | Most famous work is A VINDICATION OF THE RIGHTS OF WOMAN (1792). Argues that women, just like women, need education to become virtuous and useful. The use of education should make all professions available, not just traditional ones, and women should be allowed to become involved in politics | 12 | |
| 9865943542 | Olympe De Gouge | Most famous work is DECLARATION OF THE RIGHTS OF WOMEN AND THE FEMALE CITIZEN. Was the daughter of a baker and rose to run her own salon. She was an abolitionist. She was executed during the Reign of Terror | 13 | |
| 9865943543 | Adam Smith | Most famous work is AN INQUIRY INTO THE NATURE AND CAUSES OF THE WEALTH OF NATIONS (1776). Wrote most original theories on capitalism and is credited by many with creating modern economics | 14 | |
| 9865943545 | Immanuel Kant | Most famous work is CRITIQUE OF PRACTICAL REASON. Argued in 1784 that freedom of the press will result in Enlightenment for the masses. He separated science and morality into distinct branches of knowledge. He believed that science could describe natural phenomena of the material world but could not provide a guide for morality | 15 | |
| 9865943546 | David Hume | Most famous work is a TREATISE OF HUMAN NATURE. Emphasized limitations of human reasoning and stated that the human mind is nothing but a bundle of impressions. Later he became dogmatic skeptic who undermined the Enlightenment | 16 | |
| 9865943549 | Denis Diderot | Best known as the editor of the first European ENCYCLOPEDIA, which was supported by Voltaire and Catherine II of Russia. He was a writer and member of prominent salons in Paris. | 17 | |
| 9865943551 | Thomas Paine | Most famous works THE AGE OF REASON AND COMMON SENSE. Advocated deism and progress, the idea of an improved society through natural laws. He moved to the British Colonies in America and advocated for American Independence | 18 | |
| 9865943555 | Frederick II (Frederick the Great) | Referred to himself as the "first servant of the state" who through military changes made Prussia into a major power in Europe. An urbane and educated man who patronized the great Voltaire, a domestic reformer who improved education, codified laws, fostered industry, invited immigration, and extended religious tolerance | 19 | |
| 9865943556 | Catherine II (Catherine the Great) | A German who succeeded to the throne after the murder of her husband. Was a patron of many of the French philosophes and considered herself an Enlightened Despot. When personal rule was threatened, became reactionary and ended many Enlightened reforms. | 20 |
Pages
Need Help?
We hope your visit has been a productive one. If you're having any problems, or would like to give some feedback, we'd love to hear from you.
For general help, questions, and suggestions, try our dedicated support forums.
If you need to contact the Course-Notes.Org web experience team, please use our contact form.
Need Notes?
While we strive to provide the most comprehensive notes for as many high school textbooks as possible, there are certainly going to be some that we miss. Drop us a note and let us know which textbooks you need. Be sure to include which edition of the textbook you are using! If we see enough demand, we'll do whatever we can to get those notes up on the site for you!

