| 2684805255 | Nucleotides | Building blocks of nucleic acids |  | 0 |
| 2684807142 | Base pairing | Principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine |  | 1 |
| 2684807960 | Phosphate-Deoxyribose | The two molecules that when added to A, T, G, or C make up a nucleotide |  | 2 |
| 2684811941 | Properties of Life | Order, Evolutionary Adaptation, Response to the Environment, Regulation, Energy Processing, Growth and Development, Reproduction. |  | 3 |
| 2684814097 | Example of Order | human genetic makeup, or the structure of DNA |  | 4 |
| 2684816840 | Example of Growth and Development | the cycle of a blowfly (application: forensic science) |  | 5 |
| 2684818751 | Example of Response to Environment | phototropism (stimulus: light, tropism: orientation towards light). also: Venus flytrap closing on a fly (stimulus: touch; response: activating feeding mechanism, or closing) |  | 6 |
| 2684822564 | Example of Regulation or Homeostasis | insulin and blood glucose level maintenance (negative feedback mechanism) |  | 7 |
| 2684826659 | Types of Energy | Kinetic, potential, chemical |  | 8 |
| 2684830957 | Kinetic energy | Energy of motion |  | 9 |
| 2684831827 | Potential energy | Energy stored in matter due to position |  | 10 |
| 2684832589 | Chemical energy | Energy stored in chemical bonds (ATP) |  | 11 |
| 2684833833 | Energy | the capacity to do work |  | 12 |
| 2684835083 | ATP | Adenosine tri-phosphate - the molecule that cells recognize and tap into for energy in the brain, muscles, etc. ATP releases energy for cellular work, such as respiration, reproduction, etc. |  | 13 |
| 2684838446 | Uncharged ATP | An ATP molecule with only 2 phosphates becomes ADP and is not usable for energy. It needs to be recharged with another phosphate. |  | 14 |
| 2684842667 | Two forms of Cellular Reproduction | Asexual & sexual |  | 15 |
| 2684844618 | Asexual Reproduction | Doesn't involve gametes |  | 16 |
| 2684845366 | Sexual Reproduction | Involves gametes |  | 17 |
| 2684846068 | Gametes | Sex cells. Male: sperm. Female: ova. |  | 18 |
| 2684847808 | Asexual reproduction examples | Binary fission (bacteria), mitosis (humans, cats, dogs, plants) |  | 19 |
| 2684849206 | Sexual reproduction examples | Meiosis (occurs in gonads to produce gametes) |  | 20 |
| 2684851157 | Evolutionary Adaptation | natural selection or "survival of the fittest." |  | 21 |
| 2684852235 | Example of evolutionary adaptation | Sickle cell mutation - one gene provides malaria resistance, both genes creates sickle cell anemia. |  | 22 |
| 2684855786 | Natural Selection Premise | Organisms with the desired trait will reproduce more successfully than organisms without the trait. Changes occur in DNA (mutation) to create the desired trait. |  | 23 |
| 2684858836 | Viruses | Viruses are 20x smaller than bacteria; made up of DNA or RNA; made of proteins (non-cellular); reproduce only thru host cell |  | 24 |
| 2684860472 | Bacteria | 20x larger than viruses; made up of DNA; unicellular; asexual reproduction, independent of host |  | 25 |
| 2684882186 | Emergent Properties | novel properties that appear at higher levels of organization due to the interaction of individual components (ex: cake ingredients become batter become cake, and each stage has different properties tho made up of the same things) |  | 26 |
| 2684904547 | Cell | The basic unit of life that retains the properties of life. |  | 27 |
| 2684912379 | How long can viruses survive outside the host? | A few seconds to minutes. |  | 28 |
| 2684915800 | True or False: Many bacteria don't cause infection. | True. |  | 29 |
| 2684919677 | True or False: Both viruses and bacteria can cause infection. | True. |  | 30 |
| 2684923377 | True or False: Antibiotics are effective against viruses. | False. |  | 31 |
| 2684925660 | True or False: Viral infections never go away without treatment. | False. |  | 32 |
| 2684942252 | Emergent Properties of Multicellular Organisms | Cell ---> Tissue ---> Organ ---> Organ System ---> Mollecular Organism |  | 33 |
| 2684948028 | Biosphere | Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. |  | 34 |
| 2684958887 | Ecosystem | All the living things in a particular area, along with all the nonliving components of the environment with which life interacts. |  | 35 |
| 2684964447 | Community | The array of organisms inhabiting a particular ecosystem. |  | 36 |
| 2684967024 | Population | All the members of one species in a particular ecosystem. |  | 37 |
| 2684969488 | Organelle | A functional component present in a cell.
Organelle is to cell as organ is to organ system.
Example: mitochondria |  | 38 |
| 2685001963 | Eukaryote | Cells containing membrane-enclosed organelles | 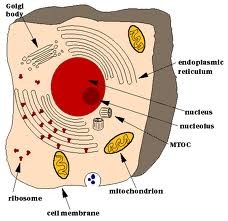 | 39 |
| 2685003560 | Prokaryote | Cells lacking a nucleus or other membrane-enclosed organelles. |  | 40 |
| 2685007485 | Taxonomic Levels of Organization | Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species |  | 41 |
| 2685014599 | Domains | The highest level of classification of living organisms. Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria |  | 42 |
| 2685015467 | Archaea | The domain that includes prokaryotes that live in Earth's most extreme environments. |  | 43 |
| 2685018647 | Kingdoms | High-level classification of organisms distinguished partly by their modes of nutrition. |  | 44 |
| 2685027122 | Eukarya | The domain that includes Kingdoms Plantae, Animalia, and Fungi. |  | 45 |
| 2685041163 | Bacteria (Domain) | The domain that includes prokaryotes which are the most diverse and widespread of all kingdoms. |  | 46 |
| 2685043430 | Independent Variable | The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied. |  | 47 |
| 2685045489 | Dependent Variable | The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable. |  | 48 |
| 2685046672 | Control | The group in an experiment which is used as a standard for comparison. |  | 49 |
| 2685047875 | Constant | A factor in an experiment that does not change. |  | 50 |
| 2685053055 | Feedback Regulation | A process in which the output, or product, of a process regulates the very process itself. |  | 51 |
| 2685055947 | Negative Feedback Mechanism | A loop in which the response reduces the initial stimulus. |  | 52 |
| 2685056959 | Positive Feedback Mechanism | A loop in which the response speeds up its own production. |  | 53 |
| 2685057990 | Null Hypothesis | States that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error. |  | 54 |
| 2685058694 | Metric Conversion Chart | Kilo Hecto Deka (Base Unit m/l/g) Deci Centi Milli Micro Nano Pico |  | 55 |
| 2685080338 | Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius | (F-32) x .556 |  | 56 |
| 2685081634 | Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit | C x 1.8 + 32 |  | 57 |
| 2685086385 | Scientific Method | Prior Knowledge
Observations
Questions
Hypothesis
Prediction
Experiment
Conclusion/Analysis |  | 58 |
| 2685115896 | Classic Experimental Design | Test Population (100 identical rats)
Experimental Group (given DDT in food)
Controlled Group (no DDT, everything else constant)
Independent Variable (under study, manipulated & changing)
Dependent Variable (variable that changes based on independent variable)
Controlled variables (water, amt. of food, everything not manipulated) |  | 59 |
| 2685123606 | Mean | Average of a group of measurements |  | 60 |
| 2685125967 | Median | The value that is in the middle of a group of measurements. |  | 61 |
| 2685127461 | Range | The difference between the smallest and the largest measurements.
R = Max - Min |  | 62 |
| 2685130530 | Deviation | Measures how the measurements vary from the mean (+ or -). In other words, what is the difference between an actual measurement and the mean, or average, of the sample? |  | 63 |
| 2685133631 | Variance | Measures how much difference, or variation, there is between the values you have obtained. The smaller the variance, the closer the values will be to the mean. |  | 64 |
| 2685136017 | Standard Deviation | Standard deviation gives you an idea of how widely spread your values are about the mean. Smaller = closer values to the average. (Picture a tall, thin, bell-shaped curve. Larger - wide bell curve.) |  | 65 |
| 2685143233 | Inductive Reasoning | A type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations.
Seeks to reduce uncertainty of claims.
"Informal" - looks for probability, not certainty. |  | 66 |
| 2685145789 | Deductive Reasoning | A type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise.
Seeks absolute certainty of conclusions.
"Formal" - seeks truth and certainty, not probability. |  | 67 |
| 2685153482 | Genes | Discrete units of hereditary information consisting of a special nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses) |  | 68 |
| 2685154899 | Gene expression | Process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function. |  | 69 |
| 2685155942 | Genome | A "library" of genetic instructions that an organism inherits. |  | 70 |
| 2685157224 | Genomics | The systematic study of whole sets of genes (or other DNA) and their interactions within a species, as well as genome comparisons between species |  | 71 |
| 2685158409 | Proteomics | The study of sets of proteins and their properties. |  | 72 |
| 2685159582 | Producers | Plants and other photosynthetic organisms. |  | 73 |
| 2685160549 | Consumers | Organisms that feed on producers and other consumers. |  | 74 |
| 2685166531 | Inquiry | The search for information and explanation, often focusing on specific questions. |  | 75 |
| 2695666426 | Cell Theory | 1. The cell is the basic unit of life.
2. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
3. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. |  | 76 |
| 2695667964 | Classification of organisms on the cellular level | 1. Unicellular: bacteria, some protists such as amoeba, paramecia, etc.
2. Multicellular: humans, trees, etc.
3. Prokaryiotic: bacteria, and blue-green algae only; no nucleus
4. Eukaryotic: animals, plants (multicellular), some protists (unicellular); have a nucleus |  | 77 |
| 2695670688 | 4 Common Cellular Features | 1. Plasma membrane
2. DNA Region
3. Cytoplasm
4. Free Ribosomes |  | 78 |
| 2695673067 | Plasma membrane | Regulates and controls what goes in and out of the cell |  | 79 |
| 2695673547 | DNA Region | DNA is organized into chromosomes; each segment of DNA that codes for a trait is a gene. In a eukaryotic cell, the DNA region is the nucleus. |  | 80 |
| 2695674338 | Cytoplasm | The contents of the cell bounded by the plasma membrane; in eukaryotes, the portion of the cell outside the nucleus. |  | 81 |
| 2695677599 | Free Ribosomes | Organelles that function in protein synthesis. |  | 82 |
| 2695678185 | Whittaker System - 5 Kingdoms | 1. Monera (Bacteria)
2. Protista
3. Fungi
4. Plantae
5. Animalia |  | 83 |
| 2695678862 | Taxonomy | The science of classification and nomenclature (naming) |  | 84 |
| 2695679222 | Ecology | The study of organisms in their physical and chemical environment |  | 85 |
| 2695680926 | Autotroph | Self-feeder |  | 86 |
| 2695681336 | Heterotroph | Other-feeder |  | 87 |
























































































































